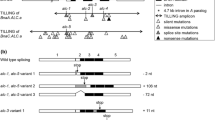
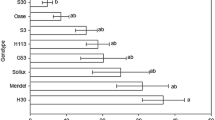
Abstract
Key message
This study elucidates the influence of indehiscent mutations on rapeseed silique shatter resistance. A phenotype with enlarged replum-valve joint area and altered cell dimensions in the dehiscence zone is described.
Abstract
Silique shattering is a major factor reducing the yield stability of oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Attempts to improve shatter resistance often include the use of mutations in target genes identified from Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). A variety of phenotyping methods assessing the level of shatter resistance were previously described. However, a comparative and comprehensive evaluation of the methods has not yet been undertaken. We verified the increase of shatter resistance in indehiscent double knock-down mutants obtained by TILLING with a systematic approach comparing three independent phenotyping methods. A positive correlation of silique length and shatter resistance was observed and accounted for in the analyses. Microscopic studies ruled out the influence of different lignification patterns. Instead, we propose a model to explain increased shattering resistance of indehiscent rapeseed mutants by altered cell shapes and sizes within the contact surfaces of replum and valves.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud N, Girin T, Sorefan K, Fuentes S, Wood TA, Lawrenson T, Sablowski R, Ostergaard L (2011) Gibberellins control fruit patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene Dev 24(19):2127–2132. https://doi.org/10.1101/Gad.593410
Arzt E, Gorb S, Spolenak R (2003) From micro to nano contacts in biological attachment devices. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(19):10603–10606. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1534701100
Bruce DM, Hobson RN, Morgan CL, Child RD (2001) Threshability of shatter-resistant seed pods in oilseed rape. J Agric Eng Res 80(4):343–350. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaer.2001.0748
Bruce DM, Farrent JW, Morgan CL, Child RD (2002) Determining the oilseed rape pod strength needed to reduce seed loss due to pod shatter. Biosyst Eng 81(2):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1006/bioe.2001.0002
Cochran WG (1957) Analysis of covariance—its nature and uses. Biometrics 13(3):261–281. https://doi.org/10.2307/2527916
Dening K, Heepe L, Afferrante L, Carbone G, Gorb SN (2014) Adhesion control by inflation: implications from biology to artificial attachment device. Appl Phys A 116(2):567–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8504-2
Etzold H (2002) Simultanfärbung von Pflanzenschnitten mit Fuchsin, Chrysoidin und Astrablau. Mikrokosmos 91(5):316
Ferrándiz C (2000) Negative regulation of the SHATTERPROOF genes by FRUITFULL during Arabidopsis fruit development. Science 289(5478):436–438. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5478.436
Gao H, Ji B, Jäger IL, Arzt E, Fratzl P (2003) Materials become insensitive to flaws at nanoscale: lessons from nature. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(10):5597–5600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0631609100
Girin T, Stephenson P, Goldsack CMP, Kempin SA, Perez A, Pires N, Sparrow PA, Wood TA, Yanofsky MF, Østergaard L (2010) Brassicaceae INDEHISCENT genes specify valve margin cell fate and repress replum formation. Plant J 63(2):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04244.x
Girin T, Paicu T, Stephenson P, Fuentes S, Korner E, O’Brien M, Sorefan K, Wood TA, Balanza V, Ferrándiz C, Smyth DR, Ostergaard L (2011) INDEHISCENT and SPATULA interact to specify carpel and valve margin tissue and thus promote seed dispersal in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23(10):3641–3653. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.090944
Groszmann M, Paicu T, Alvarez JP, Swain SM, Smyth DR (2011) SPATULA and ALCATRAZ, are partially redundant, functionally diverging bHLH genes required for Arabidopsis gynoecium and fruit development. Plant J 68(5):816–829. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04732.x
Gulden RH, Shirtliffe SJ, Thomas AG (2003) Harvest losses of canola (Brassica napus) cause large seedbank inputs. Weed Sci 51(1):83–86
Harloff HJ, Lemcke S, Mittasch J, Frolov A, Wu JG, Dreyer F, Leckband G, Jung C (2012) A mutation screening platform for rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and the detection of sinapine biosynthesis mutants. Theor Appl Genet 124(5):957–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1760-z
Hu ZY, Hua W, Huang SM, Yang HL, Zhan GM, Wang XF, Liu GH, Wang HZ (2012) Discovery of pod shatter-resistant associated SNPs by deep sequencing of a representative library followed by bulk segregant analysis in rapeseed. PLoS One 7(4):e34253. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034253
Hu Z, Yang H, Zhang L, Wang X, Liu G, Wang H, Hua W (2015) A large replum-valve joint area is associated with increased resistance to pod shattering in rapeseed. J Plant Res 128(5):813–819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-015-0732-9
Hua S, Shamsi IH, Guo Y, Pak H, Chen M, Shi C, Meng H, Jiang L (2009) Sequence, expression divergence, and complementation of homologous ALCATRAZ loci in Brassica napus. Planta 230(3):493–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0961-z
Hui C-Y, Glassmaker N, Tang T, Jagota A (2004) Design of biomimetic fibrillar interfaces: 2. Mechanics of enhanced adhesion. J R Soc Interface 1(1):35–48. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2004.0005
Jung C (2010) Breeding with genetically modified plants. In: Kempken F, Jung C (eds) modification of plants: agriculture, horticulture and forestry. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry, 64th edn. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 103–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02391-0_6
Kadkol GP, Macmillan RH, Burrow RP, Halloran GM (1984) Evaluation of Brassica genotypes for resistance to shatter. I. Development of a laboratory test. Euphytica 33(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00022751
Kay P, Groszmann M, Ross JJ, Parish RW, Swain SM (2013) Modifications of a conserved regulatory network involving INDEHISCENT controls multiple aspects of reproductive tissue development in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 197(1):73–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04373.x
Laga B (2013) Brassica plant comprising a mutant ALCATRAZ allele. US Patent Application US20130291235A1, 31.10.2013
Laga B, Lambert B, Boer Bd (2015) Brassica plant comprising a mutant INDEHISCENT allele. Europe Patent EP2220239B1, 20.05.2015
Laird NM, Ware JH (1982) Random-effects models for longitudinal data. Biometrics 38(4):963–974. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529876
Lenser T, Theißen G (2013) Conservation of fruit dehiscence pathways between Lepidium campestre and Arabidopsis thaliana sheds light on the regulation of INDEHISCENT. Plant J 76(4):545–556. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12321
Liljegren SJ, Ditta GS, Eshed HY, Savidge B, Bowman JL, Yanofsky MF (2000) SHATTERPROOF MADS-box genes control seed dispersal in Arabidopsis. Nature 404(6779):766–770. https://doi.org/10.1038/35008089
Liljegren SJ, Roeder AHK, Kempin SA, Gremski K, Ostergaard L, Guimil S, Reyes DK, Yanofsky MF (2004) Control of fruit patterning in Arabidopsis by INDEHISCENT. Cell 116(6):843–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00217-X
Liu J, Wang J, Wang H, Wang W, Mei D, Zhou R, Cheng H, Yang J, Raman H, Hu Q (2016) Multigenic control of pod shattering resistance in Chinese rapeseed germplasm revealed by genome-wide association and linkage analyses. Front Plant Sci 7:1058. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01058
Mason AS, Higgins EE, Snowdon RJ, Batley J, Stein A, Werner C, Parkin IAP (2017) A user guide to the Brassica 60 K Illumina Infinium™ SNP genotyping array. Theor Appl Genet 130(4):621–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2849-1
Meakin PJ, Roberts JA (1990) Dehiscence of fruit in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L).1. Anatomy of pod dehiscence. J Exp Bot 41(229):995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1093/Jxb/41.8.995
Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M (2008) NAC transcription factors NST1 and NST3 regulate pod shattering in a partially redundant manner by promoting secondary wall formation after the establishment of tissue identity. Plant J 56(5):768–778. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03633.x
Mulisch M, Welsch U (eds) (2015) Romeis—Mikroskopische Technik, 19th edn. Springer, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-55190-1
Ogawa M, Kay P, Wilson S, Swain SM (2009) ARABIDOPSIS DEHISCENCE ZONE POLYGALACTURONASE1 (ADPG1), ADPG2, and QUARTET2 are polygalacturonases required for cell separation during reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21(1):216–233. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.063768
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Price JS, Hobson RN, Neale MA, Bruce DM (1996) Seed losses in commercial harvesting of oilseed rape. J Agric Eng Res 65(3):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaer.1996.0091
R Core Team (2015) R: A language and environment for statistical computing, 3.2.0 edn. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rajani S, Sundaresan V (2001) The Arabidopsis myc/bHLH gene ALCATRAZ enables cell separation in fruit dehiscence. Curr Biol 11(24):1914–1922. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00593-0
Raman H, Raman R, Kilian A, Detering F, Carling J, Coombes N, Diffey S, Kadkol G, Edwards D, McCully M, Ruperao P, Parkin IAP, Batley J, Luckett DJ, Wratten N (2014) Genome-wide delineation of natural variation for pod shatter resistance in Brassica napus. PLoS One 9(7):e101673. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101673
Sander L, Child R, Ulvskov P, Albrechtsen M, Borkhardt B (2001) Analysis of a dehiscence zone endo-polygalacturonase in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) and Arabidopsis thaliana: evidence for roles in cell separation in dehiscence and abscission zones, and in stylar tissues during pollen tube growth. Plant Mol Biol 46(4):469–479. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010619002833
Schondelmaier J, Steinrücken G, Jung C (1996) Integration of AFLP markers into a linkage map of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Plant Breed 115(4):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.1996.tb00909.x
Sorefan K, Girin T, Liljegren SJ, Ljung K, Robles P, Galván-Ampudia CS, Offringa R, Friml J, Yanofsky MF, Østergaard L (2009) A regulated auxin minimum is required for seed dispersal in Arabidopsis. Nature 459(7246):583–586. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07875
Summers JE, Bruce DM, Vancanneyt G, Redig P, Werner CP, Morgan C, Child RD (2003) Pod shatter resistance in the resynthesized Brassica napus line DK142. J Agric Sci 140(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1017/s002185960200285x
Tan XL, Xia ZW, Zhang LL, Zhang ZY, Guo ZJ, Qi CK (2009) Cloning and sequence analysis of oilseed rape (Brassica napus) SHP2 gene. Bot Stud 50(4):403–412
Till BJ, Zerr T, Comai L, Henikoff S (2006) A protocol for TILLING and Ecotilling in plants and animals. Nat Protoc 1(5):2465–2477. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.329
Udall JA, Quijada PA, Lambert B, Osborn TC (2006) Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): 2. Identification of alleles from unadapted germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 113(4):597–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0324-0
van Gelderen K, van Rongen M, Aa Liu, Otten A, Offringa R (2016) An INDEHISCENT-controlled auxin response specifies the separation layer in early Arabidopsis fruit. Mol Plant 9(6):857–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.03.005
Varenberg M, Pugno NM, Gorb SN (2010) Spatulate structures in biological fibrillar adhesion. Soft Matter 6(14):3269–3272. https://doi.org/10.1039/C003207G
Verbeke G, Lesaffre E (1997) The effect of misspecifying the random-effects distribution in linear mixed models for longitudinal data. Comput Stat Data Anal 23(4):541–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9473(96)00047-3
Wang R, Ripley VL, Rakow G (2007) Pod shatter resistance evaluation in cultivars and breeding lines of Brassica napus, B. juncea and Sinapis alba. Plant Breed 126(6):588–595. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2007.01382.x
Zerr T, Henikoff S (2005) Automated band mapping in electrophoretic gel images using background information. Nucleic Acids Res 33(9):2806–2812. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki580
Zhang Y, Shen YY, Wu XM, Wang JB (2016) The basis of pod dehiscence: anatomical traits of the dehiscence zone and expression of eight pod shatter-related genes in four species of Brassicaceae. Biol Plant 60(2):343–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-016-0599-1
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Stiftung Schleswig-Holsteinische Landschaft under Grant no. 2013/69. We thank Monika Bruisch, Hilke Jensen, Lara Wostupatsch, and Niloufar Nezaratizadeh for technical assistance; Mario Hasler for support on statistical analyses; Maria Mulisch and Cay Kruse for assistance with light microscopy of cryosections; the Institute of Clinical Molecular Biology in Kiel for Sanger sequencing; the breeding company Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke for collaboration regarding the EMS mutant population.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Lixi Jiang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braatz, J., Harloff, HJ., Emrani, N. et al. The effect of INDEHISCENT point mutations on silique shatter resistance in oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Theor Appl Genet 131, 959–971 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3051-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3051-4