Abstract
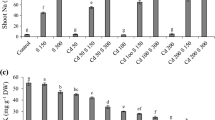
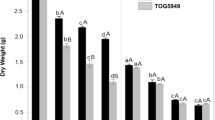
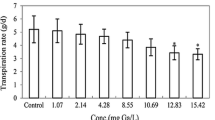
The acute toxicity of potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) and ammonium thiocyanate (NH4SCN) to rice seedlings was tested. Hydroponically-grown plants showed different responses to the two species of thiocyanate. NH4SCN caused more severe stress to rice seedlings than KSCN. A significant reduction in transpiration and relative growth was observed with all NH4SCN treatments (p < 0.01), while the effect of KSCN on rice seedlings was more evident at greater than 100 mg SCN/L (p < 0.01). Both chemicals had a negligible effect on total chlorophyll content in shoots of rice seedlings (p > 0.05). Although phyto-transport of thiocyanate was apparent, rice seedlings showed significantly higher removal potential for NH4SCN than KSCN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa T, Kawano Y, Kataoka S, Katayama Y, Kamiya N, Yohda M, Odaka M (2007) Structure of thiocyanate hydrolase: a new nitrile hydratase family protein with a novel five-coordinate cobalt(III) center. J Mol Biol 366:1497–1509
Bezsudnova EY, Sorokin DY, Tikhonova TV, Popov VO (2007) Thiocyanate hydrolase, the primary enzyme initiating thiocyanate degradation in the novel obligately chemolithoautotrophic halophilic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium Thiohalophilus thiocyanoxidans. Biochem Biophys Acta 23:1563–1570
Bhunia F, Saha NC, Kaviraj A (2000) Toxicity of thiocyanate to fish, plankton, worm and aquatic system. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:197–204
Boening DW, Chew CM (1999) A critical review: general toxicity and environmental fate of three aqueous cyanide ions and associated ligands. Wat Air Soil Pollut 109:67–79
Chakraborty S, Veeramani H (2006) Effect of HRT and recycle ratio on removal of cyanide, phenol, thiocyanate and ammonia in an anaerobic-anoxic-aerobic continuous system. Process Biochem 41:96–105
Ebbs SD, Piccinin RC, Goodger JQD, Kolev SD, Woodrow IE, Baker AJM (2008) Transport of ferrocyanide by two eucalypt species and sorghum. Int J Phytorem 10:343–357
Heming TA, Thurston RV, Meyn EL, Zajdel RK (1985) Acute toxicity of thiocyanate on trout. Trans Am Fish Soc 114:895–905
Hung CH, Pavlostathis SG (1998) Fate and transformation of thiocyanate and cyanate under methanogenic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:112–116
Katayama Y, Hashimoto K, Nakayama H, Mino H, Nojiri M, Ono TA, Nyunoya H, Yohda M, Takio K, Odaka M (2006) Thiocyanate hydrolyase is a cobalt-containing metalloenzyme with a cysteine-sulfinic acid ligand. J Am Chem Soc 128:728–729
Katz U, Lau KR, Ramos MMP, Elloy JC (1982) Thiocyanate transport across fish intestine (Pleuronectes platessa). J Membrane Biol 66:9–14
Kwon HK, Woo SH, Park JM (2002) Thiocyanate degradation by Acremonium strictum and inhibition by secondary toxicants. Biotechnol Let 24:1347–1351
Lee C, Kim J, Do H, Hwang S (2008) Monitoring thiocyanate-degrading microbial community in relation to changes in process performance in mixed culture systems near washout. Wat Res 42:1154–1162
Sorokin DY, Tourova TP, Lysenko AM, Kuenen JG (2001) Microbial thiocyanate utilization under highly alkaline conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:528–538
Speyer MR, Raymond P (1988) The acute toxicity of thiocyanate and cyanate to rainbow trout as modified by water temperature and pH. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:565–571
Watson SJ, Maly EJ (1987) Thiocyanate toxicity to Daphina magna: modified by pH and temperature. Aquat Toxicol 10:1–8
Wood PA, Kelly PD, McDonald RI, Jordan LS, Morgan DT, Khan S, Murrell JG, Borodina E (1998) A novel pink-pigmented facultative methylotroph, Methylobacterium thiocyanatum sp. nov., capable of growth of thiocyanate or cyanate as sole nitrogen sources. Arch Microbiol 169:148–158
Yu XZ, Gu JD (2007) Accumulation and distribution of trivalent chromium and effects on hybrid willow (Salix matsudana Koidz × alba L.) metabolism. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:503–511
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by The Education Department of Hunan Province, PR China (grant no: 11A047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, XZ., Zhang, FZ. & Li, F. Phytotoxicity of Thiocyanate to Rice Seedlings. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 703–706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0545-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0545-7