Abstract
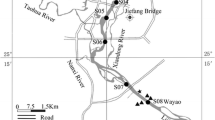
Thirty surface sediments, corresponding overlying water and porewater samples were collected for analysis of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) from Taihu Lake, China in May 2010. Altogether six OCPs, i.e. hexachlorobenzene (HCB), β-hexachlorohexane (β-HCH), p,p′-DDE, p,p′-DDD, p,p′-DDT, and o,p′-DDT were detected, and the total OCPs varied from 7.84 to 32.23 ng g−1 in sediments, from 136.97 to 2,185.14 ng L−1 in porewater and from 24.27 to 154.07 ng L−1 in overlying water, respectively. The highest levels of contamination in sediment was observed in southeast of the lake, while in water and porewater samples highest levels were found in Zhushan Bay, the seriously polluted area in the north part of Taihu Lake. The partition coefficient of measured OCPs between sediment-overlying water was five and six fold higher than that between sediment-porewater, indicating the different distribution patterns of OCPs among sediment, overlying water and porewater matrices. The ratios of DDT/(DDD + DDE) ranged from 0.57 to 2.28 in sediments, 0.93–13.02 in porewater and 0.84–15.98 in overlying water, respectively, suggesting the potential new source of DDTs into the lake. The ratios of o,p′-DDT/p,p′-DDT in the three matrices were centered around 0.2–0.3, indicating the o,p′-DDT in the lake was originated from historical usage of technical DDTs.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao HY, Liang T, Tao S, Zhang CS (2007) Simulating the temporal changes of OCP pollution in Hangzhou, China. Chemosphere 67:1335–1345
Cheng HX, Fu S, Liu YH, Li DS, Zhou JH, Xia XJ (2008) Organochlorine pesticides in the soil in Linfen, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:599–603
Fan CX, Wang CX (2007) Eutrophication and environmental geochemistry of the shallow lakes along the Yangtze River. Science Press, Beijing, pp 160–166 (in Chinese)
Jaga K, Dharmani C (2003) Global surveillance of DDT and DDE levels in human tissues. Int J Occup Med Environ Health 16:7–20
Luthy RG, Aiken GR, Brusseau ML, Cunningham SD, Gschwend PM, Pignatello JJ, Reinhard M, Traina SJ, Weber WJ Jr, Westall JC (1997) Sequestration of hydrophobic organic contaminants by geosorbents. Environ Sci Technol 31:3341–3347
Nam K, Alexander M (1998) Role of nanoporosity and hydrophobicity in sequestration and bioavailability: tests with model solids. Environ Sci Technol 32:71–77
Qiu XH, Zhu T, Li J, Pan HS, Li QL, Miao GF, Gong JC (2004) Organochlorine pesticides in the air around the Taihu Lake, China. Environ Sci Technol 38:1368–1374
Qiu X, Zhu T, Yao B, Hu JX, Hu SW (2005) Contribution of dicofol to the current DDT pollution in China. Environ Sci Technol 39:4385–4390
Sun JH, Feng JL, Liu Q, Li QL (2010) Distribution and sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments from upper reach of Huaihe River, East China. J Hazard Mater 184:141–146
Xu J, Yu Y, Wang P, Guo WF, Dai SG, Sun HW (2007) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface sediments from Yellow River, China. Chemosphere 67:1408–1414
Xu J, Wu LS, Chang AC (2009a) Degradation and adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 77:1299–1305
Xu J, Chen WP, Wu LS, Chang AC (2009b) Adsorption and degradation of ketoprofen in soils. J Environ Qual 38:1177–1182
Yang RQ, Lv AH, Shi JB, Jiang GB (2005) The levels and distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in sediments from the Haihe River, China. Chemosphere 61:347–354
Yu Y, Xu J, Wang P, Sun HW, Dai SG (2009) Sediment-porewater partition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from Lanzhou Reach of Yellow River, China. J Hazard Mater 165:494–500
Zhang LF, Dong L, Shi SX, Zhou L, Zhang T, Huang YR (2009) Organochlorine pesticides contamination in surface soils from two pesticide factories in Southeast china. Chemosphere 77:628–633
Zhang Y, Lu Y, Xu J, Yu T, Zhao WY (2011) Spatial distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from Lake Taihu, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:80–85
Zhao ZH, Zhang L, Wu JL, Fan CX (2009) Distribution and bioaccumulation of organochlorine pesticides in surface sediments and benthic organisms from Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 77:1191–1198
Zhao ZH, Zhang L, Wu JL, Fan CX, Shang JG (2010) Assessment of the potential mutagenicity of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in contaminated sediments from Taihu Lake, China. Mutation Res 696:62–68
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by China’s national basic research program: “Water environmental quality evolution and water quality criteria in lakes” (2008CB418201) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51079155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xu, J., Guo, C. et al. Distribution and Sources of Organochlorine Pesticides in Taihu Lake, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 1235–1239 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0854-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0854-x