Abstract
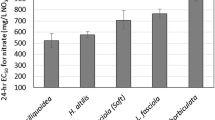
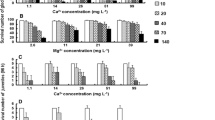
In this study we test the sensitivity of three sizes of golden mussel (Limnoperna fortunei), an introduced species in Argentina, to a 96-h exposure to \(\hbox {Cd}^{2+}\), \(\hbox {Cr}^{6+}\), and \(\hbox {Ni}^{2+}\). We also analysed the relative sensitivity of L. fortunei compared to other freshwater bivalve equivalent sensitivity data. The ANOVA results showed that both factors, heavy metal and size, had significant effects (p = 0.0013 and p = 0.0091, respectively) on the mortality of the golden mussel. Tukey’s test showed significant differences for \(\hbox {Cr}^{6+}\) treatment and the smallest size class (7 mm \(\pm 1\)). The relative sensitivity analysis showed that \(\hbox {LC}_{{50}}\) values for the smallest size class of L. fortunei exposed to \(\hbox {Ni}^{2+}\) and \(\hbox {Cd}^{2+}\) were in the low range, with values of 11.40 mg/L and 12.65 mg/L, respectively. In the case of \(\hbox {Cr}^{6+}\) (1.66 mg/L), its \(\hbox {LC}_{{50}}\) was in the medium-low range of the freshwater bivalve sensitivity distribution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Gawad S (2006) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of Cadmium in the freshwater bivalve Corbicula Fluminalis Müller, 1774. EgyptJ Aquat Biol Fish 10(4):33–43
Abraham TJ, Salih KYM, Chacko J (1986) Effects of heavy metals on the filtration rate of bivalve Villorita cyprinoides (Hanley) var. cochinensis. Indian J Mar Sci 15(3):195–196
Belaich M, Oliver C, Pilloff M, Porta A (2006) Evaluation of a biomarker of cd (II) exposure on Limnoperna fortunei. Environ Pollut 144(1):280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.015
Bhamre PR, Thorat SP, Desai AE, Deoray BM (2010) Evaluation of acute toxicity of mercury, cadmium and zinc to a freshwater mussel Lamellidens consobrinus. Our Nature 8(1):180–184
Black MC (2003) Water quality standards for North Carolina’s endangered mussels. University of Georgia, Department of Environmental Health Science
Bonel N, Lorda J (2015) Growth and body weight variability of the invasive mussel Limnoperna fortunei (mytilidae) across habitat and season. Malacologia 58(1–2):129–146. https://doi.org/10.4002/040.058.0202
Cataldo D, Boltovskoy D, Pose M (2003) Toxicity of chlorine and three nonoxidizing molluscicides to the pest mussel Limnoperna fortunei. J Am Water Works Assoc 95(1):66–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1551-8833.2003.tb10270.x
Chin HC, Chou FF (1978) Acute chromium toxicity of the freshwater mussel, Hyriopsis cumingii Lea. Nan-Ch-ing Ta Hsueh Hsueh PaoTsu Jan K’o Hsueh Pan 4:96–101
Chung KS (1980) Acute toxicity of selected heavy metals to mangrove oyster Crassostrea rhizophorae. Bull Jap Soc Sci Fish 46(6):777–780
do Amaral QDF, Da Rosa E, Wronski JG, Zuravski L, Querol MVM, dos Anjos B, de deAndrade CFF, Machado MM, de Oliveira LFS (2019) Golden mussel (Limnoperna fortunei) as a bioindicator in aquatic environments contaminated with mercury: cytotoxic and genotoxic aspects. Sci Total Environ 675:343–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.108
Darrigran G, Damborenea C (2006) Capítulo 3 características de la especie. In: Darrigran G, Damborenea C (eds) Bio-invasón del mejillón dorado en el continente americano. Editorial de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata (EDULP), Argentina, pp 69–79
Darrigran G, Lagreca M (2005) Moluscos litorales del estuario del río de la plata, argentina. ProBiota 8:41
Ezcurra de Drago I, Montalto L, Oliveros O (2006) Desarrollo y ecología larval de Limnoperna fortunei. In: Darrigran G, Damborenea C (eds) Bioinvasilón del mejillón dorado en el continente americano. Editorial de la Universidad Nacional de La Plata (EDULP), Argentina, pp 85–93
Elder JF, Collins JJ (1991) Freshwater molluscs as indicators of bioavailability and toxicity of metals in surface-water systems. In: Ware G (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York, pp 37–79
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis, 3d edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gibson KJ (2015) Acute toxicity testing on freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionidae) and freshwater snails (Gastropoda: Caenogastropoda). Doctoral dissertation, Troy University
Gupta SK, Singh J et al (2011) Evaluation of mollusc as sensitive indicator of heavy metal pollution in aquatic system: a review. IIOAB J 2(1):49–57
Ituarte CF (1988) Características de la incubación branquial en Eupera platensis doello-jurado, 1921 y Byssanodonta paranensis d’orbigny, 1846 (pelecypoda: Sphaeriidae. Iheringia 68:41–47
Iummato MM, Sabatini SE, Cacciatore LC, Cochón AC, Cataldo D, de Molina MdCR, Juárez ÁB (2018) Biochemical responses of the golden mussel Limnoperna fortunei under dietary glyphosate exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.046
Keller AE (2000) Memorandum to Rob Pepin. Subject: water quality and toxicity data for unpublished unionid mussels tests. USEPA, Chicago, IL, 14 p
Keller AE, Zam SG (1991) The acute toxicity of selected metals to the fresh water mussel, Anodonta imbecillis. Environ Toxicol Chem 10:539–546
Mackie GL (1989) Tolerances of five benthic invertebrates to hydrogen ions and metals (Cd, Pb, Al). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18(1–2):215–223
Oliveira MD, Campos MC, Paolucci EM, Mansur MC, Hamilton SK (2015) Colonization and spread of Limnoperna fortunei in south america. In: Boltovskoy D (ed) Limnoperna Fortunei. Springer, Cham, pp 333–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-13494-9_19
Olson KR, Harrel RC (1973) Effect of salinity on acute toxicity of mercury, copper, and chromium for Rangia cuneata (Pelecypoda, Mactridae). Contrib Mar Sci 17:9–13
Pastorino G, Darrigran G, Stella Maris M, Lunaschi L (1993) Limnoperna fortunei (dunker, 1857) (mytilidae), nuevo bivalvo invasor en aguas del río de la plata. Neotropica 39:34
Pereyra PJ, Bulus Rossini G, Darrigran G (2011) Toxicity of three commercial tannins to the nuisance invasive species Limnoperna fortunei(dunker, 1857): implications for control. Fresenius Environ Bull 20(6):1432–1437
Pereyra PJ, Bulus Rossini G, Darrigran G (2012) Toxicity of neem’s oil, a potential biocide against the invasive mussel Limnoperna fortunei (dunker 1857). Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 84(4):1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0001-37652012005000059
Raj AIM, Hameed PS (1990) Freshwater mussel, Lamellidens marginalis (Lamarck) (mollusca: bivalvia: unionidae) as an indicator of river pollution. Chem Ecol 4(2):57–64
Ricciardi A (1998) Global range expansion of the asian mussel Limnoperna fortunei (mytilidae): another fouling threat to freshwater systems. Biofouling 13(2):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927019809378374
Santos-Medrano GE, Martinez RR (2019) Acute sensitivity comparison among daphnia magna straus, 1820 daphnia pulex leydig, 1860 and simocephalus vetulus müller, 1776, exposed to nine toxicants. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 19(7):615–623. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v19_7_08
Silva J, Fuentealba C, Bay-Schmith E, Larrain A (2007) Estandarizacion del bioensayo de toxicidad aguad con Diplodon chilensis usando un toxico de referencia. Gayana (Concepción) 71(2):135–141
Soares M, Pereira D, Santos C, Mansur M, Pires M, Breintenbach J, Grespan C (2009) Toxicidade do sulfato de cobre ao mexilhão dourado, Limnoperna fortunei (dunker, 1857), em água bruta. J Braz Soc Ecotoxicol 4(1–3):37–48. https://doi.org/10.5132/jbse.2009.01.006
USEPA (1996) Water quality criteria documents for the protection of aquatic life in ambient water: 1995 updates
Vareda JP, Valente AJ, Durães L (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: a review. J Environ Manag 246:101–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.126
Villar C, Stripeikis J, D’huicque L, Tudino M, Troccoli O, Bonetto C (1999) Cd, cu and zn concentrations in sediments and the invasive bivalves Limnoperna fortunei and Corbicula fluminea at the rio de la plata basin, argentina. Hydrobiologia 416:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003811223880
Wang N, Ivey CD, Ingersoll CG, Brumbaugh WG, Alvarez D, Hammer EJ, Bauer CR, Augspurger T, Raimondo S, Christopher Barnhart M (2017) Acute sensitivity of a broad range of freshwater mussels to chemicals with different modes of toxic action. Environ Toxicol Chem 36(3):786–796
Zhou Q, Zhang J, Fu J, Shi J, Jiang G (2008) Biomonitoring: an appealing tool for assessment of metal pollution in the aquatic ecosystem. Anal Chim Acta 606(2):135–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.11.018
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Faculty of Exact Science of the National University of La Plata (FCEx-UNLP) for providing the space to conduct the experiments involved in this article, and to the reviewers whose valuable observations helped us improve and clarify our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The authors declare that all studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bálsamo Crespo, E., Pereyra, P.J., Silvestro, A. et al. Acute Toxicity of \(\hbox {Cd}^{2+}\), \(\hbox {Cr}^{6+}\), and \(\hbox {Ni}^{2+}\) to the Golden Mussel Limnoperna fortunei (Dunker 1857). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104, 748–754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02854-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02854-5