Abstract
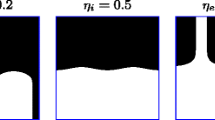
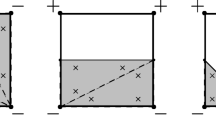
To ensure manufacturability and mesh independence in density-based topology optimization schemes, it is imperative to use restriction methods. This paper introduces a new class of morphology-based restriction schemes that work as density filters; that is, the physical stiffness of an element is based on a function of the design variables of the neighboring elements. The new filters have the advantage that they eliminate grey scale transitions between solid and void regions. Using different test examples, it is shown that the schemes, in general, provide black and white designs with minimum length-scale constraints on either or both minimum hole sizes and minimum structural feature sizes. The new schemes are compared with methods and modified methods found in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Ambrosio L, Buttazzo G (1993) An optimal design problem with perimeter penalization. Calc Var 1:55–69
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP (1995) Optimization of structural topology, shape and material. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization—theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, XIV+370 pp.
Borel PI, Frandsen LH, Harpøth A, Kristensen M, Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2005) Topology optimised broadband photonic crystal Y-splitter. Electron Lett 41(2):69–71
Borrvall T (2001) Topology optimization of elastic continua using restriction. Arch Comput Methods Eng 8(4):351–385
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2001) Topology optimization using regularized intermediate density control. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190:4911–4928
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(9):2143–2158
Bourdin B, Chambolle A (2003) Design-dependent loads in topology optimization. ESAIM COCV Abr 9:19–48
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2001) Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(26-27):3443–3459
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2003) An element removal and reintroduction strategy for the topology optimization of structures and compliant mechanisms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57(10):1413–1430
Cardoso EL, Fonseca JSO (2003) Complexity control in the topology optimization of continuum structures. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng (3):293–301
Guest J, Prevost J, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Guo X, Gu YX (2004) A new density-stiffness interpolation scheme for topology optimization of continuum structures. Eng Comput Int J Comput Aided Eng 21(1):9–22
Haber RB, Jog CS, Bendsøe MP (1994) Variable-topology shape optimization with a constraint on perimeter. In: Gilmore B, et al. (eds) Advances in design automation, vol DE 69-2. ASME, New York, pp 261–272
Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2004) Systematic design of photonic crystal structures using topology optimization: low-loss waveguide bends. Appl Phys Lett 84(12):2022–2024
Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2005) Topology optimization of photonic crystal structures: a high-bandwidth low-loss T-junction waveguide. J Opt Soc Am B: Opt Phys 22(6):1191–1198
Kim YY, Yoon GH (2000) Multi-resolution multi-scale topology optimization—a new paradigm. Int J Solids Struct 37:5529–5559
Kreisselmeier G, Steinhauser R (1983) Application of vector performance optimization to a robust control loop design for a fighter aircraft. Int J Control 37(2):251–84
Niordson FI (1983) Optimal design of plates with a constraint on the slope of the thickness function. Int J Solids Struct 19:141–151
Petersson J, Sigmund O (1998) Slope constrained topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41(8):1417– 1434
Poulsen TA (2002) Topology optimization in wavelet space. Int J Numer Methods Eng 53:567–582
Poulsen TA (2003) A new scheme for imposing a minimum length scale in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 57(6):741–760
Pratt WK (1991) Digital image processing. Wiley, New York
Sethian JA, Wiegmann A (2000) Structural boundary design via level set and immersed interface methods. J Comput Phys 163(2):489–528
Sigmund O (1994) Design of material structures using topology optimization. PhD thesis, Department of Solid Mechanics, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Lyngby, the Danish Center for Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, DCAMM Special Report No. S69
Sigmund O (1997) On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization. Mechan Struct Mach 25(4):493– 524
Sigmund O (2000) Topology optimization: a tool for the tailoring of structures and materials. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci 358(1765):211–228
Sigmund O (2001a) A 99 line topology optimization code written in MATLAB. Struct Multidisc Optim 21:120–127. DOI 10.1007/s001580050176, MATLAB code available online at www.topopt.dtu.dk
Sigmund O (2001b) Design of multiphysics actuators using topology optimization - Part II: two-material structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(49-50):6605–6627. DOI 10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00252-3
Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2003) Systematic design of phononic band gap materials and structures by topology optimization. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 361:1001–1019
Sigmund O, Petersson J (1998) Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: a survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct Optim 16(1):68–75
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Wang M, Zhou S (2004) Phase field: a variational method for structural topology optimization. Comput Model Eng Sci 6(6):547–566
Wang M, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1-2):227–246
Wang MY, Wang S (2005) Bilateral filtering for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 63(13):1911–1938
Zhou M, Shyy YK, Thomas HL (2001) Checkerboard and minimum member size control in topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 21:152–158
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sigmund, O. Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 33, 401–424 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0087-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0087-x