Abstract
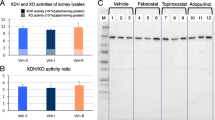
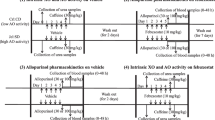
To clarify the toxicological aspects of FYX-051, a xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor, which is currently being developed as a therapeutic agent against gout and hyperuricemia, we performed the study focused on species differences in FYX-051-induced nephropathy. In the repeated toxicology testing by oral administration, nephropathy was seen at 1 mg/kg and more in rats and at 100 mg/kg in dogs, in contrast to no toxicity even at the practical maximum dose (300 mg/kg) in monkeys. The HPLC and LC-MS/MS analyses of intrarenal deposits in dogs have proven that the entity was xanthine. The study on dose dependency of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, urinary xanthine excretion, and kidney xanthine content by oral administration at 0.3, 1, and 3 mg/kg to rats revealed the involvement of xanthine in the occurrence of nephropathy, thus suggesting that plasma concentrations of FYX-051 can contribute to species differences. Regarding the possible factors of species differences, the daily urinary excretion of total purine metabolites was 30.5- and 6.3-fold greater in rats and dogs, respectively, than in monkeys. Urinary xanthine solubility was 2.3- and 6.3-fold higher in dogs and monkeys, respectively, than in rats. Plasma concentrations of FYX-051 were fivefold higher in rats than in dogs and monkeys, without differences between the latter two species. Therefore, the present study indicated that species differences in nephropathy were produced by the combined effects of purine metabolism, urinary xanthine solubility, and plasma concentrations of FYX-051.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashizawa N, Shimo T, Matsumoto K, Oba K, Nakazawa T, Nagata O (2006) Strain differences in the responsiveness between Sprague-Dawley and Fischer rats to nephropathy induced by FYX-051, a xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217:260–265
Elion GB, Callahan S, Nathan H, Bieber S, Rundles RW, Hitchings GH (1963) Potentiation by inhibition of drug degradation. Biochem Pharmacol 12:85–93
European Medicines Agency (2008) CHMP assessment report for adenuric (febuxostat). Doc Ref: EMEA/258531
Hitchings GH (1966) Effects of allopurinol in relation to purine biosynthesis. Ann Rheum Dis 25:601–607
Horiuchi H, Ota M, Kobayashi M, Kaneko H, Kasahara Y, Nishimura S, Kondo S, Komoriya K (1999) A comparative study on the hypouricemic activity and potency in renal xanthine calculus formation of two xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase inhibitors: TEI-6720 and allopurinol in rats. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 104:307–319
Okamoto K, Matsumoto K, Hille R, Eger BT, Pai EF, Nishino T (2004) The crystal structure of xanthine oxidoreductase during catalysis: implications for reaction mechanism and enzyme inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7931–7936
Shimo T, Ashizawa N, Matsumoto K, Nakazawa T, Nagata O (2005) Simultaneous treatment with citrate prevents nephropathy induced by FYX-051, a xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor, in rats. Toxicol Sci 87:267–276
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mrs. Kazuhiko Oba and Koji Matsumoto, Research Laboratories 2, Fuji Yakuhin Co., Ltd., for their technical support. Conflict of interest: none declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimo, T., Ashizawa, N., Moto, M. et al. Study on species differences in nephropathy induced by FYX-051, a xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor. Arch Toxicol 85, 505–512 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0598-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0598-5