Abstract
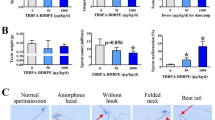
No data are available regarding aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) polymorphisms related to the reproductive toxicity possibly caused by ethyl tertiary butyl ether (ETBE). In this study, two inhalation experiments were performed in Aldh2 knockout (KO), heterogeneous (HT) and wild type (WT) C57BL/6 male mice exposed to ETBE, and the data about general toxicity, testicular histopathology, sperm head numbers, sperm motility and sperm DNA damage were collected. The results showed that the 13-week exposure to 0, 500, 1,750 and 5,000 ppm ETBE significantly decreased sperm motility and increased levels of sperm DNA strand breaks and 8-hydroxy-deoxyguanosine in both WT and KO mice, the effects were found in 1,750 and 5,000 ppm groups of WT mice, and all of the three exposed groups of KO mice compared to the corresponding control; furthermore, ETBE also caused decrease in the relative weights of testes and epididymides, the slight atrophy of seminiferous tubules of testis and reduction in sperm numbers of KO mice exposed to ≥500 ppm. In the experiment of exposure to lower concentrations of ETBE (0, 50, 200 and 500 ppm) for 9 weeks, the remarkable effects of ETBE on sperm head numbers, sperm motility and sperm DNA damage were further observed in KO and HT mice exposed to 200 ppm ETBE, but not in WT mice. Our findings suggested that only exposure to high concentrations of ETBE might result in reproductive toxicity in mice with normal active ALDH2, while low active and inactive ALDH2 enzyme significantly enhanced the ETBE-induced reproductive toxicity in mice, even exposed to low concentrations of ETBE, mainly due to the accumulation of acetaldehyde as a primary metabolite of ETBE.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ETBE:
-
Ethyl tertiary butyl ether
- AA:
-
Acetaldehyde
- ALDH2:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2
- WT:
-
Wild type
- HT:
-
Heterogeneous
- KO:
-
Knockout
- TBA:
-
Tertiary butyl alcohol
- MPD:
-
2-Methyl-1,2-propanediol
- MTBE:
-
Methyl tertiary butyl ether
- IARC:
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer
- hOGG1:
-
8-Hydroxyguanine DNA-glycosylase
- 8-OH-dG:
-
8-Hydroxy-deoxyguanosine
References
Aitken J, Fisher H (1994) Reactive oxygen species generation and human spermatozoa: the balance of benefit and risk. BioEssays 16:259–267
Aitken RJ, Krausz C (2001) Oxidative stress, DNA damage and the Y chromosome. Reproduction 122:497–506
Aitken RJ, Baker MA, Sawyer D (2003) Oxidative stress in the male germ line and its role in the aetiology of male infertility and genetic disease. Reprod Biomed Online 7:65–70
Aitken RJ, Koopman P, Lewis SE (2004) Seeds of concern. Nature 432:48–52
Bevan C, Tyl RW, Neeper-Bradley TL, Fisher LC, Panson RD, Douglas JF, Andrews LS (1997) Developmental toxicity evaluation of methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE) by inhalation in mice and rabbits. J Appl Toxicol 17(Suppl 1):S21–S29
Brennan P, Lewis S, Hashibe M, Bell DA, Boffetta P, Bouchardy C, Caporaso N, Chen C, Coutelle C, Diehl SR, Hayes RB, Olshan AF, Schwartz SM, Sturgis EM, Wei Q, Zavras AI, Benhamou S (2004) Pooled analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase genotypes and head and neck cancer: a HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol 159:1–16
Conaway CC, Schroeder RE, Snyder NK (1985) Teratology evaluation of methyl tertiary butyl ether in rats and mice. J Toxicol Environ Health 16:797–809
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J (2003) Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J 17:1195–1214
de Peyster A (2010) Ethyl t-butyl ether: review of reproductive and developmental toxicity. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 89:239–263
de Peyster A, Stanard B, Westover C (2009) Effect of ETBE on reproductive steroids in male rats and rat Leydig cell cultures. Toxicol Lett 190:74–80
Donnelly ET, McClure N, Lewis SE (1999) The effect of ascorbate and alpha-tocopherol supplementation in vitro on DNA integrity and hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in human spermatozoa. Mutagenesis 14:505–512
Faulkner TP, Wiechart JD, Hartman DM, Hussain AS (1989) The effects of prenatal tertiary butanol administration in CBA/J and C57BL/6 J mice. Life Sci 45:1989–1995
Gaoua W (2003) Ethyl tertiary butyl ether (ETBE), CAS No. 637-92-3: Reproduction/developmental toxicity dose-range finding/probe study by the oral (gavage) route in two strains of rat. CIT Study No. 24168 RSR. Unpublished study for Totalfinaelf on behalf of the ETBE Producers’ Consortium
Genesca A, Caballin MR, Miro R, Benet J, Germa JR, Egozcue J (1992) Repair of human sperm chromosome aberrations in the hamster egg. Hum Genet 89:181–186
Hagiwara A, Doi Y, Imai N, Nakashima H, Ono T, Kawabe M, Furukawa F, Tamano S, Nagano K, Fukushima S (2011) Medium-term multi-organ carcinogenesis bioassay of ethyl tertiary-butyl ether in rats. Toxicology 289:160–166
Kitagawa K, Kawamoto T, Kunugita N, Tsukiyama T, Okamoto K, Yoshida A, Nakayama K (2000) Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) 2 associates with oxidation of methoxyacetaldehyde; in vitro analysis with liver subcellular fraction derived from human and Aldh2 gene targeting mouse. FEBS Lett 476:306–311
Latendresse JR, Warbrittion AR, Jonassen H, Creasy DM (2002) Fixation of testes and eyes using a modified Davidson’s fluid: comparison with Bouin’s fluid and conventional Davidson’s fluid. Toxicol Pathol 30:524–533
Le Gal A, Dreano Y, Gervasi PG, Berthou F (2001) Human cytochrome P450 2A6 is the major enzyme involved in the metabolism of three alkoxyethers used as oxyfuels. Toxicol Lett 124:47–58
Lewis SE (2007) Is sperm evaluation useful in predicting human fertility? Reproduction 134:31–40
Lewis SE, Agbaje IM (2008) Using the alkaline comet assay in prognostic tests for male infertility and assisted reproductive technology outcomes. Mutagenesis 23:163–170
Lewis SE, Agbaje I, Alvarez J (2008) Sperm DNA tests as useful adjuncts to semen analysis. Syst Biol Reprod Med 54:111–125
Li Q, Kobayashi M, Inagaki H, Hirata Y, Hirata K, Shimizu T, Wang RS, Suda M, Kawamoto T, Nakajima T, Kawada T (2011) Effects of subchronic inhalation exposure to ethyl tertiary butyl ether on splenocytes in mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:837–847
McGregor D (2010) Tertiary-butanol: a toxicological review. Crit Rev Toxicol 40:697–727
Meamar M, Zribi N, Cambi M, Tamburrino L, Marchiani S, Filimberti E, Fino MG, Biggeri A, Menezo Y, Forti G, Baldi E, Muratori M (2012) Sperm DNA fragmentation induced by cryopreservation: new insights and effect of a natural extract from Opuntia ficus-indica. Fertil Steril 98:326–333
Medinsky MA, Wolf DC, Cattley RC, Wong B, Janszen DB, Farris GM, Wright GA, Bond JA (1999) Effects of a thirteen-week inhalation exposure to ethyl tertiary butyl ether on fischer-344 rats and CD-1 mice. Toxicol Sci 51:108–118
Niemela O, Parkkila S, Bradford B, Iimuro Y, Pasanen M, Thurman RG (2002) Effect of Kupffer cell inactivation on ethanol-induced protein adducts in the liver. Free Radic Biol Med 33:350–355
Novitskiy G, Traore K, Wang L, Trush MA, Mezey E (2006) Effects of ethanol and acetaldehyde on reactive oxygen species production in rat hepatic stellate cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:1429–1435
O’Brien PJ, Siraki AG, Shangari N (2005) Aldehyde sources, metabolism, molecular toxicity mechanisms, and possible effects on human health. Crit Rev Toxicol 35:609–662
Ollero M, Gil-Guzman E, Lopez MC, Sharma RK, Agarwal A, Larson K, Evenson D, Thomas AJ Jr, Alvarez JG (2001) Characterization of subsets of human spermatozoa at different stages of maturation: implications in the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility. Hum Reprod 16:1912–1921
Saito A, Sasaki T, Kasai T, Katagiri T, Nishizawa T, Noguchi T, Aiso S, Nagano K, Fukushima S (2013) Hepatotumorigenicity of ethyl tertiary-butyl ether with 2-year inhalation exposure in F344 rats. Arch Toxicol 87:905–914
Secretan B, Straif K, Baan R, Grosse Y, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V (2009) A review of human carcinogens—part E: tobacco, areca nut, alcohol, coal smoke, and salted fish. Lancet Oncol 10:1033–1034
Seitz HK, Stickel F (2007) Molecular mechanisms of alcohol-mediated carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7:599–612
Sgambato A, Iavicoli I, De Paola B, Bianchino G, Boninsegna A, Bergamaschi A, Pietroiusti A, Cittadini A (2009) Differential toxic effects of methyl tertiary butyl ether and tert-butanol on rat fibroblasts in vitro. Toxicol Ind Health 25:141–151
Simon L, Brunborg G, Stevenson M, Lutton D, McManus J, Lewis SE (2010) Clinical significance of sperm DNA damage in assisted reproduction outcome. Hum Reprod 25:1594–1608
Simon L, Lutton D, McManus J, Lewis SE (2011) Sperm DNA damage measured by the alkaline Comet assay as an independent predictor of male infertility and in vitro fertilization success. Fertil Steril 95:652–657
Smith CC, O’Donovan MR, Martin EA (2006) hOGG1 recognizes oxidative damage using the comet assay with greater specificity than FPG or ENDOIII. Mutagenesis 21:185–190
Stanard B, Westover C, Hirakawa B, Gonzalez J, and de Peyster A (2003) Effect of ethyl t-butyl ether (ETBE) on testosterone in male rats. Toxicologist 72:S1, Abstract 644. Toxicologist
Thomson LK, Fleming SD, Aitken RJ, De Iuliis GN, Zieschang JA, Clark AM (2009) Cryopreservation-induced human sperm DNA damage is predominantly mediated by oxidative stress rather than apoptosis. Hum Reprod 24:2061–2070
Wang M, McIntee EJ, Cheng G, Shi Y, Villalta PW, Hecht SS (2000) Identification of DNA adducts of acetaldehyde. Chem Res Toxicol 13:1149–1157
Weng Z, Suda M, Ohtani K, Mei N, Kawamoto T, Nakajima T, Wang RS (2011) Aldh2 knockout mice were more sensitive to DNA damage in leukocytes due to ethyl tertiary butyl ether exposure. Ind Health 49:396–399
Weng Z, Suda M, Ohtani K, Mei N, Kawamoto T, Nakajima T, Wang RS (2012) Differential genotoxic effects of subchronic exposure to ethyl tertiary butyl ether in the livers of Aldh2 knockout and wild-type mice. Arch Toxicol 86:675–682
Weng Z, Suda M, Ohtani K, Mei N, Kawamoto T, Nakajima T, Wang RS (2013) Subchronic exposure to ethyl tertiary butyl ether resulting in genetic damage in Aldh2 knockout mice. Toxicology 311:107–114
Yamaki K, Yoshino S (2009) Inhibition of IgE-induced mast cell activation by ethyl tertiary-butyl ether, a bioethanol-derived fuel oxygenate. J Pharm Pharmacol 61:1243–1248
Yuan Y, Wang HF, Sun HF, Du HF, Xu LH, Liu YF, Ding XF, Fu DP, Liu KX (2007) Adduction of DNA with MTBE and TBA in mice studied by accelerator mass spectrometry. Environ Toxicol 22:630–635
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Ms. S. Watanabe for her assistance in the manipulation of the animals, and Dr. R. Hojo for her helps in the experiments. This work was supported by grant-in-aid for project research from the Japan National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, Japan (P21-03).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, Z., Ohtani, K., Suda, M. et al. Assessment of the reproductive toxicity of inhalation exposure to ethyl tertiary butyl ether in male mice with normal, low active and inactive ALDH2. Arch Toxicol 88, 1007–1021 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1192-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1192-z