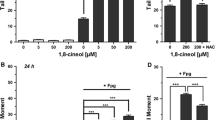
Abstract
Methyleugenol is a substituted alkenylbenzene found in several herbs and spices. It is classified by the European Union’s Scientific Committee on Food as a genotoxic carcinogen. We addressed the biological mechanism of the genotoxic properties of methyleugenol and its oxidative metabolites. Methyleugenol and the oxidative metabolites significantly enhanced the DNA damage in human colon carcinoma cells (HT29). Methyleugenol did not affect the protein status of γH2AX, a biomarker of DNA double-strand breaks, whereas its metabolites methyleugenol-2′,3′-epoxide and 3′-oxomethylisoeugenol significantly increased the cellular phosphorylated H2AX level. Both of these metabolites also showed a significant induction of micronuclei in HT29 cells. Furthermore, we investigated whether topoisomerase interaction contribute to the observed effect on DNA integrity. Methyleugenol-2′,3′-epoxide and 3′-oxomethylisoeugenol inhibited the activity of recombinant topoisomerase I. In HT29 cells, neither methyleugenol nor the metabolites affected the level of topoisomerase protein bound to DNA, excluding a topoisomerase poisoning mode of action. In addition, 3′-oxomethylisoeugenol potently diminished the level of camptothecin-stabilized topoisomerase I/DNA intermediates and camptothecin-induced DNA strand breaks. In conclusion, it could be suggested that 3′-oxomethylisoeugenol may also interact with classical or food-borne topoisomerase I poisons, diminishing their poisoning effectiveness.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Subeihi AA, Spenkelink B, Rachmawati N, Boersma MG, Punt A, Vervoort J, van Bladeren PJ, Rietjens IM (2011) Physiologically based biokinetic model of bioactivation and detoxification of the alkenylbenzene methyleugenol in rat”. Toxicol In Vitro 25:267–285
Banath JP, Olive PL (2003) Expression of phosphorylated histone H2AX as a surrogate marker of cell killing by drugs that create DNA double-strand breaks. Cancer Res 63:4347–4350
Bandele OJ, Osheroff N (2007) Bioflavonoids as poisons of human topoisomerase II alpha and II beta. Biochemistry 46:6097–6108
Bandele OJ, Osheroff N (2008a) (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate, a major constituent of green tea, poisons human type II topoisomerases. Chem Res Toxicol 21:936–943
Bandele OJ, Osheroff N (2008b) The efficacy of topoisomerases II-targeted anticancer agents reflects the persistence of drug-induced cleavage complexes in cells. Biochemistry 47:11900–11908
Bandele OJ, Clawson SJ, Osheroff N (2008) Dieatary polyphenols as topoisomerase II poisons: B ring and C ring substituents determine the mechanism of enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage enhancement. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1253–1260
Boege F (1996) Analysis of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases and topoisomerase-directed drug effects. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 34:873–888
Bonner WM, Redon CE, Dickey JS, Nakamura AJ (2008) GammaH2AX and Cancer. Nat Rev 8:957–967
Bourgine J, Billaut-Laden I, Happillon M, Lo-Guidice JM, Maunoury V, Imbenotte M, Broly F (2012) Gene expression profiling of systems involved in the metabolism and the disposition of xenobiotics: comparison between human intestinal biopsy samples and colon cell lines. Drug Metab Dispos 40:694–705
Cartus AT, Hermann K, Weishaupt LW, Merz KH, Engst W, Glatt H, Schrenk D (2012) Metabolism of methyleugenol in liver microsomes and primary hepatocytes: pattern of metabolites, cytotoxicity, and DNA-adduct formation. Toxicol Sci 129:21–34
Champoux JJ (2001) DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem 70:369–413
Collins A (2004) The comet assay for DNA damage and repair: principles, applications and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261
Corbett KD, Berger JM (2004) Structure, molecular mechanisms, and evolutionary relationships in DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 33:95–118
Dickey JS, Redon CE, Nakamura AJ, Baird BJ (2009) H2AX: functional roles and potential applications. Chromosoma 118:683–692
Ding W, Levy DD, Bishop ME, Lyn-Cook Lascelles E, Kulkarni R, Chang CW, Aidoo A, Manjanatha MG (2011) Methyleugenol genotoxicity in the Fischer 344 rat using the comet assay and pathway-focused gene expression profiling. Toxicol Sci 123:103–112
Doehmer J (2009) The use and value of in vitro technologies in metabolism studies. Altern Lab Anim 37:29–32
Esselen M, Fritz J, Hutter M, Marko D (2009) Delphinidin modulates the DNA-damaging properties of topoisomerase II poisons. Chem Res Toxicol 22:554–564
Esselen M, Fritz J, Hutter M, Teller N, Baechler S, Boettler U, Marczylo TH, Gescher AJ, Marko D (2011) Anthocyanin-rich extracts suppress DNA damaging effects of topoisomerase poisons in human colon cancer cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:143–153
Gardner I, Wakazono H, Bergin P, de Waziers I, Beaune P, Kenna JG, Caldwell J (1997) Cytochrome P450 mediated bioactivation of methyleugenol to 1′-hydroxymethyleugenol in Fischer 344 rat and human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 18:1775–1783
Gedik CM, Wood SG, Collins AR (1998) Measuring oxidative damage to DNA; HPLC and the comet assay compared. Free Radic Res 29:609–615
Glatt H, Gemperlein I, Setiabudi F, Platt KL, Oesch F (1990) Expression of xenobioticmetabolizing enzymes in propagatable cell cultures and induction of micronuclei by 13 compounds. Mutagenesis 5:24–249
Groh IAM, Cartus AT, Vallicotti S, Kajzar J, Merz KH, Schrenk D, Esselen M (2012) Genotoxic potential of methyleugenol and selected methyleugenol metabolites in cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells. Food Funct 3:428–436
Groh IAM, Chen C, Lüske C, Cartus AT, Esselen M (2013) Plant polyphenols and oxidative metabolites of the herbal alkenylbenzene methyleugenol suppress histone deacetylase activity in human colon carcinoma cells. J Nutr Metab. doi:10.1155/2013/821082
Guenthner TM, Luo G (2001) Investigation of the role of the 2′,3′-epoxidation pathway in the bioactivation and genotoxicity of dietary allylbenzene analogs. Toxicology 160:47–58
Gupta M, Fujimori A, Pommier Y (1995) Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases I. Biochem Biophys Acta 1262:1–14
Habermeyer M, Fritz J, Barthelmes HU, Christensen MO, Larsen MK, Boege F, Marko D (2005) Anthocyanidins modulate the activity of human DNA topoisomerases I and II and affect cellular DNA integrity. Chem Res Toxicol 18:1395–1404
Ichijima Y, Yoshioka K, Yoshioka Y, Shinohe K, Fujimori H, Unno J, Takagi M, Goto H, Inagaki M, Mizutani S, Teraoka H (2010) DNA lesions induced by replication stress trigger mitotic aberration and tetraploidy development. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008821
Jeurissen SM, Bogaards JJ, Boersma MG, ter Horst JP, Awad HM, Fiamegos YC, van Beek TA, Alink GM, Sudhölter EJ, Cnubben NH, Rietjens IM (2006) Human cytochrome P450 enzymes of importance for the bioactivation of methyleugenol to the proximate carcinogen 1′-hydroxymethyleugenol. Chem Res Toxicol 19:111–116
Jo JY, Gonzalez de Mejia E, Lila MA (2006) Catalytic inhibition of human DNA topoisomerase II by interactions of grape cell culture polyphenols. J Agric Food Chem 54:2083–2087
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) (2008) Compendium of food additive specifications. In: 69th Meeting. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. http://www.fao.org/ag/AGN/agns/files/jecfa69_final.pdf
Kalfalah FM, Mielke C, Christensen MO, Baechler S, Marko D, Boege F (2011) Genotoxicity of dietary, environmental and therapeutic topoisomerase II poisons is uniformly correlated to prolongation of enzyme DNA residence. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:127–142
Keck JL, Berger JM (1999) Enzymes that push DNA around. Nat Struct Biol 6:900–902
MacPhail SH, Banath JP, Yu TY, Chu EH (2003a) Expression of phosphorylated histone H2AX in cultured cell lines following exposure to X-rays. Int J Radiat Bio 79:351–358
MacPhail SH, Banath JP, Yu TY, Chu EH, Olive PL (2003b) Cell cycle-dependent expression of phosphorylated histone H2AX: reduced expression in unirradiated but not X-irradiated G1-phase cells. Radiat Res 159:759–767
Mah LJ, El-Osta A, Karagiannia TC (2010) gammaH2AX: a sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia 24:679–686
Maralhas A, Monteiro A, Martins C, Kranendonk M, Laires A, Rueff J, Rodriques AS (2006) Genotoxicity and endoreduplication inducing activity of the food flavouring eugenol. Mutagenesis 21:199–204
Osheroff N, Zechiedrich EL, Gale KC (1991) Catalytic function of DNA topoisomerase II. Bioessays 13:269–273
Pfuhler S, Wolf HU (1996) Detection of DNA-crosslinking agents with the alkaline comet assay. Environ Mol Mutagen 27:196–201
Rafter J, Govers M, Martel P, Pannemans D, Pool-Zobel B, Rechkemmer G, Rowland I, Tuijtelaars S, van Loo J (2004) PASSCLAIM—diet-related cancer. Eur J Nutr 43:1147–1184
Robison SH, Barr DB (2006) Use of biomonitoring data to evaluate methyl eugenol exposure. Environ Health Perspect 114:1797–1801
Sak K (2012) Chemotherapy and dietary phytochemical agents. Chemother Res Pract. doi:10.1155/2012/282570
SCF, Scientific Committee on Food (2001) Opinion of the scientific committee on food on methyleugenol (4-allyl-1,2- dimethoxybenzene). http://ec.europa.eu/food/fs/sc/scf/out102_en.pdf
Schmidt F, Knobbe CB, Frank B, Wolburg H, Weller M (2008) The topoisomerase II inhibitor, genistein, induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human malignant glioma cell lines. Oncol Rep 19:1061–1066
Smith RL, Adam TB, Doull J, Feron VJ, Goodman JI, Marnett LJ, Portoghese PS, Waddell WJ, Wagner BM, Rogers AE, Caldwell J, Sipes IG (2002) Safety assessment of allylalkoxybenzene derivatives used as flavouring substances—methyl eugenol and estragole. Food Chem Toxicol 40:851–870
Smith B, Cadby P, Leblanc JC, Woordow-Setzer R (2010) Application of the margin of exposure (MoE) approach to substances in food that are genotoxic and carcinogenic example: methyleugenol. Food Chem Toxicol 48:89–97
Strumberg D, Nitiss JL, Dong J, Kohn KW, Pommier Y (1999) Molecular analysis of yeast and human type II topoisomerases. Enzyme–DNA and drug interactions. J Biol Chem 274:28246–28255
Subramanian D, Furbee CS, Muller MT (2001) ICE bioassay. Isolating in vivo complexes of enzyme to DNA. Methods Mol Biol 95:137–147
Tice RR, Agurel E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Tomasz M (1994) DNA adducts of the mitomycins. IARC Sci Publ 125:349–357
Watters GP, Smart DJ, Harvey JS, Austin CA (2009) H2AX phosphorylation as a genotoxicity endpoint. Mutat Res 679:50–58
Yu LJ, Matias J, Scudiero DA, Hite KM, Monks A, Sausville EA, Waxman DJ (2001) P450 enzyme expression patterns in the NCI human tumor cell line panel. Drug Metab Dispos 29:304–312
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Boehringer Ingelheim Fonds which financed the research habitation at the University of Vienna by a travel grant. The study was also supported by the grant ES419/2-1 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Groh, I.A.M., Rudakovski, O., Gründken, M. et al. Methyleugenol and oxidative metabolites induce DNA damage and interact with human topoisomerases. Arch Toxicol 90, 2809–2823 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1625-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1625-3