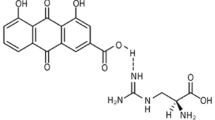
Abstract
Vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED) interrupts the integrity and function of endothelial lining through enhanced markers of oxidative stress and decrease endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression. The main aim of the present study has been designed to investigate the possible vasculoprotective role of linagliptin against sodium arsenite-induced VED. Sodium arsenite (1.5 mg/kg, i.p., 2 weeks) abrogated the acetylcholine-induced, endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation by depicting the decrease in serum nitrite/nitrate concentration, reduced glutathione level, and simultaneously enhance the thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) level, superoxide level, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. These elevated markers interrupt the integrity of endothelial lining of thoracic aorta which was assessed histologically. The study elicits dose dependent effect of linagliptin (1.5 mg/kg, i.p. and 3 mg/kg, i.p.) or atorvastatin (30 mg/kg, p.o.) treatment, improved the endothelium-dependent independent relaxation, improve the integrity of endothelium lining which was assessed histologically by enhancing the serum nitrite/nitrate level, reduced glutathione level and simultaneously decreasing the TBARS level, superoxide anion level and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) level. L-NAME (25 mg/kg, i.p.), eNOS inhibitor, abrogated the ameliorative potential of linagliptin. However, the ameliorative potential of linagliptin has been enhanced by l-arginine (200 mg/kg, i.p.) which elicits that ameliorative potential of linagliptin was through eNOS signaling cascade and it may be concluded that linagliptin 3 mg/kg, i.p. has more significantly activated the eNOS and decreased the oxidative markers than linagliptin 1.5 mg/kg, i.p. and prevented sodium arsenite-induced VED.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argos M, Kalra T, Rathouz PJ, Chen Y, Pierce B, Parvez F, Islam T, Ahmed A, Rakibuzzaman M, Hasan R, Sarwar G, Slavkovich V, Geen AV, Graziano J, Ahsan H (2010) Arsenic exposure from drinking water and all cause and chronic disease mortalities in Bangladesh (HEALS): a prospective cohort study. Lancet 376:252–258
Aroor AR, Sowers JR, Jia G, De Marco VG (2014) Pleiotropic effects of the dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors on the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 307(4):H477–H492
Balakumar P, Kaur J (2009) Arsenic exposure and cardiovascular disorders: an overview. Cardiovasc Toxicol 9:169–176
Bohm M (2007) Angiotensin receptor blockers versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: where do we stand now? Am J Cardiol 100:38–44
Bonetti PO, Lerman LO, Lerman A (2003) Endothelial dysfunction: a marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:168–175
Bunderson M, Coffin JD, Beall HD (2002) Arsenic induces peroxynitrite generation and cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression in aortic endothelial cells: possible role of atherosclerosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 184:11–18
Chuaiphichai S, McNeill E, Douglas G, Crabtree MJ, Bendall JK, Hale AB, Alp NJ, Channon KM (2014) Cell-autonomous role of endothelial GTP cyclohydrolase 1 and tetrahydrobiopterin in blood pressure regulation. Hypertens 64:530–540
Desjardins F, Balligand JL (2006) Nitric oxide-dependent endothelial function and cardiovascular disease. Acta Clin Belg 61:326–334
Flora SJS, Flora GJ, Saxena G (2009) Arsenicals: toxicity, their use as chemical warfare agents and possible remedial measures. In: Gupta RC (ed) Handbook of the toxicology of chemical warfare agents. Academic, San Diego, pp 109–133
Giansante C, Fiotti N (2006) Insights into human hypertension: the role of endothelial dysfunction. J Human Hypertens 20:725–726
Goyal S, Kumar S, Bijjem KV, Singh M (2010) Role of glucagon-like peptide in vascular endothelial dysfunction. Indian J Exp Biol 48:61–69
Han L, Yu Y, Sun X, Wang B (2012) Exendin-4 directly improves endothelial dysfunction in isolated aorta from obese rat through cAMP or AMPK-eNOS pathway. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:453–460
Hwang J, Kleimbenz DJ, Lassegue B, Griendling KK, Dikalov S, Hart CM (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands regulate endothelial membrane superoxide production. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C899–C905
Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS, Chaudhuri G (1988) Pharmacological evidence that endothelium-derived relaxing factor is nitric oxide: use of pyrogallol and superoxide dismutase to study endothelium-dependent and nitric oxide-elicited vascular smooth muscle relaxation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:181–189
Kesavan M, Sarath TS, Kannan K, Suresh S, Gupta P, Vijay Akaran K, Sankar P, Kurade PN, Mishra SK, Sarkar SN (2014) Atorvastatin restores arsenic induced vascular dysfunction in rats: modulation of nitric oxide signaling and inflammatory mediators. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:107–116
Kohn AD, Summer SA, Bimbaum MJ, Roth RA (1996) Expression of constituvely active Akt Ser/Thr kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes stimulates glucose uptake and glucose transporter 4 translocation. J Biol Chem 271:31372
Koibuchi N, Hasegawa Y, Katayama T, Toyama K, Uekawa K, Sueta D, Kusaka H, Ma M, Nakagawa T, Lin B, Kim-Mitsuyama S (2014) DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin ameliorates cardiovascular injury in salt-sensitive hypertensive rats independently of blood glucose and blood pressure. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13:157
Korokin MV, Pokrovsky MV, Novikov OO, Gureev VV, Denisyak TA, Korokina LV, Polyanskaya OS, Ragulina VA, Pokrovskaya TG, Danilenko LM, Belous AS (2011) Effects of L-arginine, vitamin B6, and folic acid on parameters of endothelial dysfunction and microcirculation in the placenta in modelling of L-NAME induced NO deficiency. Bull Exp Biol Med 152:77–79
Kroller-Schon S, Knorr M, Hausding M, Oelze M, Schuff A, Schell R, Sudowe S, Scholz A, Daub S, Karbach S, Kossmann S, Gori W, Schulz P, Grabbe E, Klein S, Munzel T, Daiber A (2012) Glucose-independent improvement of vascular dysfunction in experimental sepsis by dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibition. Cardiovasc Res 96(1):140–149
Liang C, Ren Y, Tan H, He Z, Jiang Q, Wu J, Zhen Y, Fan M, Wu Z (2009) Rosiglitazone via up-regulation of Akt/eNOS pathways attenuates dysfunction if endothelial progenitor cells, induced by advanced glycation end products. Br J Pharmacol 158:1865–1873
Ma F, Liu L, Xiong X (2003) Protective effects of pravastatin on vascular endothelium injured by low density lipoprotein. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:1027–1032
Matsubara J, Sugiyama S, Akiyama E, Iwashita S, Kurokawa H, Ohba K, Maeda H, Fujisue K, Yamamoto E, Kaikita K, Hokimoto S, Jinnouchi H, Ogawa H (2013) Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor, sitagliptin, improves endothelial dysfunction in association with its anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease and uncontrolled diabetes. Circ J 77(5):1337–1344
Mittra S, Singh M (1998) Possible mechanism of captopril induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in isolated rabbit aorta. Mol Cell Biochem 183:63–67
Moya M, Campana V, Gavotto A, Spitale L, Simes J, Palma J (1999) Histopathological lesions in aorta from rats with hiperfrinogenemia published by 2nd virtual congress of cardiology
Nakashima S, Matsui T, Takeuchi H, Yamagishi S (2014) Linagliptin blocks renal damage in type 1 diabetic rats by suppressing advanced glycation end products receptor axis. Horm Metab Res 46:717–721
Neumiller JJ, Stephen M (2012) Review of linagliptin or the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 34:993–1005
Pieper GM (1997) Acute amelioration of diabetic endothelial dysfunction with a derivative of the nitric oxide synthase cofactor, tetrahydrobioprotein. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 29:8–15
Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De Tata V, Casini AF (2003) The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol 66(8):1499–1503
Pratico D (2005) Antioxidants and endothelium protection. Atherosclerosis 181:215–224
Salheen SM, Panchapakesan U, Pollock CA, Woodman OL (2015) The DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin and the GLP-1 receptor agonist exendin-4 improve endothelium-dependent relaxation of rat mesenteric arteries in the presence of high glucose. Pharmacol Res 94:26–33
Salim HM, Fukuda D, Higashikuni Y, Tanaka K, Hirata Y, Yagi S, Soeki T, Shimabukuro M, Sata M (2015) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, linagliptin, ameliorates endothelial dysfunction and atherogenesis in normoglycemic apolipoprotein-E deficient mice, Vasc Pharmacol article in press
Sastry KV, Moudgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS, Rao GS (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper-cadmium alloy. Anal Biochem 306:79–82
Scheen AJ (2013) Cardiovascular effects of gliptins. Nat Res Cardiol 10:73–84
Sfikakis PP, Papamichael C, Stamatelopoulos KS, Tousoulis D, Fragiadaki KG, Katasichti P, Stefanadis C, Mavrikakis M (2007) Improvement of vascular endothelial function using the oral endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 56:1985–1993
Stea I, Bianchi F, Cori L, Sicari R (2014) Cardiovascular effect of arsenic: clinical and epidemiological finding. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:244–251
Takai S, Sakonjo H, Jin D (2014) Significance of vascular dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibition on vascular protection in zuckar diabetic fatty rats. Pharmacol Sci 125:386–393
Takayama M, Yao K, Wada M (2009) The dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker benidipine prevents lysophosphatidylcholine induced endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta. J Bio Med Sci 16:57
Terasaki M, Nagashima M, Nohtomi K, Kohashi K, Tomoyasu M, Sinmura K, Nogi Y, Katayama Y, Sato K, Itoh F, Watanabe T, Hirano T (2013) Preventive effect of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor on atherosclerosis is mainly attributable to incretin's actions in nondiabetic and diabetic apolipoprotein E-null mice. PLoS One 8(8):e70933
Wang HD, Pagano PJ, Du Y (1998) Superoxide anion from the adventitia of the rat thoracic aorta inactivates nitric oxide. Circ Res 82:810–818
Widenmaier SB, Sampaio AV, Underhill TM, McIntosh CHS (2009) Noncanonical activation of Akt/protein kinase B in β-cells by the incretin hormone glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. J Biol Chem 284:10764
Yamagishi S, Ishibashi Y, Ojima A, Sugiura T, Matsui T (2014) Linagliptin, a xanthine-based dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, decreases serum uric acid levels in type 2 diabetic patients partly by suppressing xanthine oxidase activity. Int J Cardiol 176:550–552
Yang Z, Ming XF (2006) Recent advances in understanding endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Clin Med Res 4:53–56
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the management and teaching faculty of ISF College of Pharmacy, Moga, India, for providing requisite facilities. Special thanks to Dr. R. K. Goel, Professor, DPSDR, Punjabi University, Patiala, India, for his technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jyoti, U., Kansal, S.K., Kumar, P. et al. Possible vasculoprotective role of linagliptin against sodium arsenite-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 167–175 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1184-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1184-4