Abstract
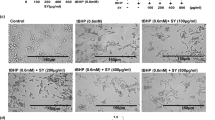
Oxidative stress, a pathological condition, contributes to the pathophysiology of a number of diseases including carcinogenesis. Numerous studies pointed out the disturbed antioxidants status and accumulation of oxidative stress markers in the carcinogenesis. The present study analyzed the anticancer efficacy of chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles by utilizing the oxidative stress biomarkers as an endpoint in mice with skin cancer developed by 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA). Oxidative stress markers’ (lipid peroxidation by-products and antioxidants) levels or activities were measured using colorimetric assays. While mice exposed with DMBA alone showed a 100% tumor incidence, 0 and 50% tumor formation was seen in mice treated with DMBA + topical application of the nanoparticles and DMBA + orally administered nanoparticles, respectively. Also, the study noticed a 33% and 67% tumor incidence in mice treated with DMBA + topical application of free chlorogenic acid and DMBA + orally administered free chlorogenic acid, respectively. The present study noticed that the topical application of chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles to DMBA-painted mice completely suppressed the tumor growth and restored the levels or activities of oxidative stress markers as compared to mice that received DMBA + oral administration of chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles. The study observed that chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles are more potent than free chlorogenic acid in preventing skin cancer in mice caused by DMBA. Thus, the present investigation explores the tumor-inhibiting efficacy of chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles in experimental skin cancer, and the tumor preventive efficiency could be attributed to their antilipid peroxidative and antioxidant effects.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Alias LM, Manoharan S, Vellaichamy L, Balakrishnan S, Ramachandran CR (2009) Protective effect of ferulic acid on 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61(3):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2008.09.001
Anusuya C, Manoharan S (2011) Antitumor initiating potential of rosmarinic acid in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 30(3):199–211. https://doi.org/10.1615/jenvironpatholtoxicoloncol.v30.i3.30
Apalla Z, Lallas A, Sotiriou E, Lazaridou E, Ioannides D (2017) Epidemiological trends in skin cancer. Dermatology Practical & Conceptual 7(2):1–6. https://doi.org/10.5826/dpc.0702a01
Beutler E, Kelly BM (1963) The effect of sodium nitrite on red cell GSH. Experientia 19:96–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02148042
Calvo P, Remuñan-López C, Vila-Jato JL, Alonso MJ (1997) Chitosan and chitosan/ethylene oxide-propylene oxide block copolymer nanoparticles as novel carriers for proteins and vaccines. Pharm Res 14(10):1431–1436. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1012128907225
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1985) Glutathione reductase. Methods Enzymol 113:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13062-4
Cheng Z, Li M, Dey R, Chen Y (2021) Nanomaterials for cancer therapy: current progress and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol 14(1):85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-021-01096-0
Di Santo MC, D’ Antoni CL, Domínguez Rubio AP, Alaimo A, Pérez OE (2021) Chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles designed to encapsulate polyphenolic compounds for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications - a review. Biomed Pharmacother 142:111970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111970
Forman HJ, Zhang H (2021) Targeting Oxidative Stress in Disease: Promise and Limitations of Antioxidant Therapy Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 20(9):689–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases The first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem (New York, N.Y.) 249(22):7130–7139
Huang H, Ullah F, Zhou DX, Yi M, Zhao Y (2019) Mechanisms of ROS regulation of plant development and stress responses. Front Plant Sci 10:800. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00800
Juan CA, Pérez de la Lastra JM, Plou FJ, Pérez-Lebeña E (2021) The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: outlining their role in biological macromolecules (DNA, lipids and proteins) and induced pathologies. Int J Mol Sci 22:4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094642
Kakkar P, Das B, Viswanathan PN (1984) A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21(2):130–132
Karthikeyan S, Srinivasan R, Wani SA, Manoharan S (2013) Chemopreventive potential of chrysin in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis 3:46–53. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0738.106993
Labani S, Asthana S, Rathore K, Sardana K (2021) Incidence of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancers in Indian and the global regions. J Cancer Res Ther 17(4):906–911. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT-785-19
Leiter U, Keim U, Garbe C (2020) Epidemiology of skin cancer. Update 2019. Adv Exp Med Biol 1268:123–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46227-76
Le Yao-Jin, He Li-Yuan, Li Sha, Xiong Chun-Jiang, Chun-Hua Lu, Yang Xiao-Yan (2022) FEMS Microbiol Lett 369(1):fnac061. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnac061
Liou GY, Storz P (2010) Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radical Res 44(5):479–496. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715761003667554
Liu CG, Desai KG, Chen XG, Park HJ (2005) Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles containing trypsin based on hydrophobically modified chitosan. J Agric Food Chem 53(5):1728–1733. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf040304v
Manimaran A, Manoharan S (2018) Tumor preventive efficacy of emodin in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced oral carcinogenesis: a histopathological and biochemical approach. Pathology Oncology Research POR 24(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0205-7
Mariadoss AVA, Vinayagam R, Senthilkumar V, Paulpandi M, Murugan K, Xu B, K M G, Kotakadi VS, David E, (2019) Phloretin loaded chitosan nanoparticles augments the pH-dependent mitochondrial-mediated intrinsic apoptosis in human oral cancer cells. Int J Biol Macromol 1(130):997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.031
Memon A, Bannister P, Rogers I, Sundin J, Al-Ayadhy B, James PW, McNally R (2021) Changing epidemiology and age-specific incidence of cutaneous malignant melanoma in England: an analysis of the national cancer registration data by age, gender and anatomical site, 1981–2018. The Lancet Regional Health Europe 2:100024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100024
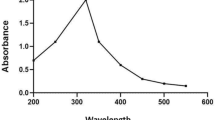
Nallamuthu I, Devi A, Khanum F (2015) Chlorogenic acid loaded chitosan nanoparticles with sustained release property, retained antioxidant activity and enhanced bioavailability. Asian J Pharm Sci 10(3):203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.09.005
Naveed M, Hejazi V, Abbas M, Kamboh AA, Khan GJ, Shumzaid M, Ahmad F, Babazadeh D, FangFang X, Modarresi-Ghazani F, WenHua L, XiaoHui Z (2018) Chlorogenic acid (CGA): a pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie 97:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.064
Neelakandan M, Vasudevan K, Senthamaraikannan K, Manoharan S (2017) Pharmacological effects of chlorogenic acid: an overview. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences 8:28–32
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. i. evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
Pizzino G, Irrera N, Cucinotta M, Pallio G, Mannino F, Arcoraci V, Squadrito F, Altavilla D, Bitto A (2017) Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:8416763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8416763
Rajasekaran D, Manoharan S, Prabhakar MM, Manimaran A (2015) Enicostemma littorale prevents tumor formation in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. Hum Exp Toxicol 34(9):911–921. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327114562033
Renju GL, Manoharan S, Senthil BS, N, (2007) Chemopreventive and antilipid peroxidative potential of Clerodendron inerme (L.) Gaertn in 7, 12- dimethylbenz(a)anthracene skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Pak J Biol Sci 10:1465–1470. https://doi.org/10.3923/PJBS.2007.1465.1470
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Sci 179(4073):588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.179.4073.588
Saravanakumar K, Mariadoss AV, Sathiyaseelan A, Wang MH (2020) Synthesis and characterization of nano-chitosan capped gold nanoparticles with multifunctional bioactive properties. Int J Biol Macromol 15(165):747–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.177
Selvasundaram R, Manoharan S, Buddhan R, Neelakandan M, Murali Naidu R (2018) Chemopreventive potential of esculetin in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 448(1–2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3321-0
Senthil N, Manoharan S, Ramachandran BS, C R and Muralinaidu R, (2007) Chemopreventive and antilipidperoxidative efficacy of Piper longum (Linn) on 7, 12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. J Appl Sci 7:1036–1042. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2007.1036.1042
Sharifi-Rad J, Quispe C, Butnariu M, Rotariu LS, Sytar O, Sestito S, Rapposelli S, Akram M, Iqbal M, Krishna A, Kumar NVA, Braga SS, Cardoso SM, Jafernik K, Ekiert H, Cruz-Martins N, Szopa A, Villagran M, Mardones L, Martorell M, Docea AO, Calina D (2021) Chitosan nanoparticles as a promising tool in nanomedicine with particular emphasis on oncological treatment. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):318. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02025-4
Sharmila R, Manoharan S (2012) Anti-tumor activity of rosmarinic acid in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) induced skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Indian J Exp Biol 50(3):187–194
Silvan S, Manoharan S, Baskaran N, Anusuya C, Karthikeyan S, Prabhakar MM (2011) Chemopreventive potential of apigenin in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene induced experimental oral carcinogenesis. Eur J Pharmacol 670(2–3):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.09.179
Silvan S, Manoharan S, Baskaran N, Anusuya C, Karthikeyan S, Prabhakar MM (2011) Chemopreventive potential of apigenin in 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene induced experimental oral carcinogenesis. Eur J Pharmacol 670(2–3):571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.09.179
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47(2):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(72)90132-7
Tajik N, Tajik M, Mack I, Enck P (2017) The potential effects of chlorogenic acid, the main phenolic components in coffee, on health: a comprehensive review of the literature. Eur J Nutr 56(7):2215–2244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1379-1
Vellaichamy L, Balakrishnan S, Panjamurthy K, Manoharan S, Alias LM (2009) Chemopreventive potential of piperine in 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced skin carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2009.01.008
Vona R, Pallotta L, Cappelletti M, Severi C, Matarrese P (2021) The impact of oxidative stress in human pathology: focus on gastrointestinal disorders. Antioxidants (basel Switzerland) 10(2):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10020201
Wei Y, Gao Y, Xie Q et al (2011) Isolation of chlorogenic acid from Flaveria bidentis (L.) Kuntze by CCC and synthesis of chlorogenic acid-intercalated layered double hydroxide. Chromatographia 73(1):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-010-1877-2
Wen H, Jung H, Li X (2015) Drug delivery approaches in addressing clinical pharmacology-related issues: opportunities and challenges. AAPS J 17(6):1327–1340. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9814-9
Yagi K (1987) Lipid peroxides and human diseases. Chem Phys Lipid 45(2–4):337–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-3084(87)90071-5
Zein R, Sharrouf W, Selting K (2020) Physical properties of nanoparticles that result in improved cancer targeting. J Oncol 2020:5194780. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5194780
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance from the Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, is gratefully acknowledged. The authors gratefully acknowledge the UGC-SAP and DST FIST support in the form of providing necessary infrastructural facilities to carry out the work successfully.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Neelakandan: carried out the present research work.
S. Manoharan: designed and supervised the research work. Preparation of the manuscript and edited as well.
R. Muralinaidu: contribution in the histopathological work
J. Monsi@Thara: assisted in the research work and statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Neelakandan, M., Manoharan, S., Muralinaidu, R. et al. Tumor preventive and antioxidant efficacy of chlorogenic acid–loaded chitosan nanoparticles in experimental skin carcinogenesis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 533–546 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02330-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02330-3