Abstract
Rationale
Dysfunction of executive neuropsychological performance, mediated by the prefrontal cortex, has been the central focus of recent attention deficit/hyperkinetic disorder (AD-HKD) research. The role of other potential neuropsychological “risk factors”, such as recognition memory, remains understudied. Further, the impact of methylphenidate (MPH) on key neuropsychological processes in AD-HKD remains poorly understood.
Objectives
To compare the performance of boys with AD-HKD on a spatial working memory (SWM) task and on two non-working memory tasks [a simultaneous and delayed matching-to-sample task (DMtS) and a pattern-recognition task] with that of healthy boys, and to investigate the impact of acute and chronic MPH on performance of these tasks.
Methods
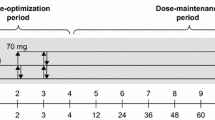
Baseline performance of 75 stimulant-naive boys with AD-HKD was compared with that of 70 healthy boys. The AD-HKD boys were then re-tested following the administration of acute and chronic challenges with MPH (0.3 mg/kg and 0.6 mg/kg) under randomised double-blind placebo controlled conditions.
Results
Compared with healthy boys, the AD-HKD boys demonstrated performance deficits on all neuropsychological tasks. A single dose of MPH restored performance on the DMtS task but had no impact on the SWM or pattern-recognition tasks. Chronic MPH administration did not alter performance on the SWM task but did improve performance on both the pattern-recognition and DMtS tasks. However, the acute restorative effect of MPH on DMtS diminished with repeated administration.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that current conceptualisations of the neuropsychological basis of AD-HKD and the proposed therapeutic mechanisms of MPH require broadening.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas MA, Sahakian BJ, Levy R (1990) Neuropsychological deficits and CT scan changes in elderly depressives. Psychol Med 20:507–520
August GJ (1987) Production deficiencies in free recall: a comparison of hyperactive, learning-disabled, and normal children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 15:429–440
Bachevalier J, Mishkin M (1986) Visual recognition impairment follows ventromedial but not dorsolateral prefrontal lesions in monkeys. Behav Brain Res 20:249–261
Baddeley A (1986) Working memory. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Baddeley A (1996) The fractionation of working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:13468–13472
Baddeley A (2003) Working memory and language: an overview. J Commun Disord 36:189–208
Barkley RA (1997) Behavioral inhibition, sustained attention, and executive functions: constructing a unifying theory of ADHD. Psychol Bull 121:65–94
Barnett R, Maruff P, Vance A, Luk ESL, Costin J, Wood C, Pantelis C (2001) Abnormal executive function in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: the effect of stimulant medication and age on spatial working memory. Psychol Med 31:1107–1115
Benezra E, Douglas VI (1988) Short-term serial recall in ADDH, normal, and reading-disabled boys. J Abnorm Child Psychol 16:511–525
Biederman J, Faraone SV, Keenan K, Benjamin J, Krifcher B, Moore C, Sprich-Buckminster S, Ugaglia K, Jellinek MS, Steingard R (1992) Further evidence for family-genetic risk factors in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Patterns of comorbidity in probands and relatives psychiatrically and pediatrically referred samples. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:728–738
Borcherding B, Thompson K, Kruesi M, Bartko J, Rapoport JL, Weingartner H (1988) Automatic and effortful processing in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 16:333–345
Castellanos FX, Tannock R (2002) Neuroscience of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: the search for endophenotypes. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:617–628
Castellanos FX, Lee PP, Sharp W, Jeffries NO, Greenstein DK, Clasen LS, Blumenthal JD, James RS, Ebens CL, Walter JM, Zijdenbos A, Evans AC, Giedd JN, Rapoport JL (2002) Developmental trajectories of brain volume abnormalities in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. JAMA 288:1740–1748
Chang HT, Klorman R, Shaywitz SE, Fletcher JM, Marchione KE, Holahan JM, Stuebing KK, Brumaghim JT, Shaywitz BA (1999) Paired-associate learning in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder as a function of hyperactivity–impulsivity and oppositional defiant disorder. J Abnorm Child Psychol 27:237–245
Chelonis JJ, Edwards MC, Schulz EG, Baldwin R, Blake DJ, Wenger A, Paule MG (2002) Stimulant medication improves recognition memory in children diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 10:400–407
Conte R, Kinsbourne M, Swanson J, Zirk H, Samuels M (1986) Presentation rate effects on paired associate learning by attention deficit disordered children. Child Dev 57:681–687
Curtis WJ, Lindeke LL, Georgieff MK, Nelson CA (2002) Neurobehavioural functioning in neonatal intensive care unit graduates in late childhood and early adolescence. Brain 125:1646–1659
Daneman M, Carpenter PA (1980) Individual differences in working memory and reading. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 19:450–466
Douglas VI (1988) Cognitive deficits in children with attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity. In: Bloomingdale LM, Sergeant J (eds) Attention deficit disorder; criteria, cognition, intervention. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 65–81
DSM IV (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. Washington, DC
Dunn L, Dunn L, Whetton C, Burley J (1997) British Picture Vocabulary Scale, 2nd edn. NFER-Nelson, London
Fray PJ, Robbins TW (1996) CANTAB battery: proposed utility in neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicol Teratol 18:499–504
Fuster JM (1989) The prefrontal cortex: anatomy, physiology, and neuropsychology of the frontal lobe, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York
Giedd JN, Blumenthal J, Molloy E, Castellanos FX (2001) Brain imaging of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Ann N Y Acad Sci 931:33–49
Gleitman H, Fridlund A, Reisberg D (1999) Memory. Psychology. W.W. Norton, New York, pp 260–299
Greenhill LL, Perel JM, Rudolph G, Feldman B, Curran S, Puig-Antich J, Gardner R (2001) Correlations between motor persistence and plasma levels in methylphenidate-treated boys with ADHD. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 4:207–215
Hughes C, Plumet MH, Leboyer M (1999) Towards a cognitive phenotype for autism: increased prevalence of executive dysfunction and superior spatial span amongst siblings of children with autism. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 40:705–718
ICD 10 (1992) The International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision edn. World Health Organisation, Geneva
Kaufman J, Birmaher B, Brent D, Rao U, Ryan N (1996) Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL), Version 1.0. Department of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh (unpublished work)
Kempton S, Vance A, Maruff P, Luk E, Costin J, Pantelis C (1999) Executive function and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: stimulant medication and better executive function performance in children. Psychol Med 29:527–538
Loge DV, Staton RD, Beatty WW (1990) Performance of children with ADHD on tests sensitive to frontal lobe dysfunction. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 29:540–545
Luciana M, Nelson CA (1998) The functional emergence of prefrontally-guided working memory systems in four- to eight-year-old children. Neuropsychologia 36:273–293
Mehta MA, Calloway P, Sahakian BJ (2000a) Amelioration of specific working memory deficits by methylphenidate in a case of adult attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Psychopharmacol 14:299–302
Mehta MA, Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Mavaddat N, Pickard JD, Robbins TW (2000b) Methylphenidate enhances working memory by modulating discrete frontal and parietal lobe regions in the human brain. J Neurosci 20:RC65:1–6
Mehta MA, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2001) Stimulant drugs and ADHD: basic and clinical neuroscience. In: Solanto MV, Arnsten AF, Castellanos FX (eds) Oxford University Press, New York, pp 303–331
Mishkin M (1982) A memory system in the monkey. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 298:83–95
Morgan AB, Lilienfeld SO (2000) A meta-analytic review of the relation between antisocial behavior and neuropsychological measures of executive function. Clin Psychol Rev 20:113–136
MTA Cooperative Group (1999) A 14-month randomized clinical trial of treatment strategies for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. The MTA Cooperative Group. Multimodal treatment study of children with ADHD. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:1073–1086
Nadder TS, Rutter M, Silberg JL, Maes HH, Eaves LJ (2002) Genetic effects on the variation and covariation of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and oppositional-defiant disorder/conduct disorder (ODD/CD) symptomatologies across informant and occasion of measurement. Psychol Med 32:39–53
Nelson CA, Monk CS, Lin J, Carver LJ, Thomas KM, Truwit CL (2000) Functional neuroanatomy of spatial working memory in children. Dev Psychol 36:109–116
Nigg JT, Blaskey LG, Huang-Pollock CL, Rappley MD (2002) Neuropsychological executive functions and DSM-IV ADHD subtypes. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41:59–66
NIMH (2000) National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39:182–193
Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Semple J, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995) Visuo-spatial short-term recognition memory and learning after temporal lobe excisions, frontal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 33:1–24
Owen AM, Morris RG, Sahakian BJ, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1996) Double dissociations of memory and executive functions in working memory tasks following frontal lobe excisions, temporal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Brain 119:1597–1615
Pennington BF, Ozonoff S (1996) Executive functions and developmental psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 37:57–87
Petrides M, Milner B (1982) Deficits on subject-ordered tasks after frontal- and temporal-lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 20:249–262
Robbins TW, James M, Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, McInnes L, Rabbitt P (1994) Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia 5:266–281
Robbins TW, Semple J, Kumar R, Truman MI, Shorter J, Ferraro A, Fox B, McKay G, Matthews K (1997) Effects of scopolamine on delayed-matching-to-sample and paired associates tests of visual memory and learning in human subjects: comparison with diazepam and implications for dementia. Psychopharmacology 134:95–106
Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT (1998) Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease: a 15-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Donepezil Study Group. Arch Intern Med 158:1021–1031
Rothenberger A, Banaschewski T, Heinrich H, Moll GH, Schmidt MH, van’t Klooster B (2000) Comorbidity in ADHD-children: effects of coexisting conduct disorder or tic disorder on event-related brain potentials in an auditory selective-attention task. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 250:101–110
Sahakian BJ, Morris RG, Evenden JL, Heald A, Levy R, Philpot M, Robbins TW (1988) A comparative study of visuospatial memory and learning in Alzheimer-type dementia and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 111(Pt 3):695–718
Schachar R, Tannock R (2002) Syndromes of hyperactivity and attention deficit. In: Rutter M, Taylor E (eds) 418. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 399
Solanto MV, Abikoff H, Sonuga-Barke E, Schachar R, Logan GD, Wigal T, Hechtman L, Hinshaw S, Turkel E (2001) The ecological validity of delay aversion and response inhibition as measures of impulsivity in AD/HD: a supplement to the NIMH multimodal treatment study of AD/HD. J Abnorm Child Psychol 29:215–228
Sonuga-Barke EJ (2002) Psychological heterogeneity in AD/HD—a dual pathway model of behaviour and cognition. Behav Brain Res 130:29–36
Sonuga-Barke EJ, Taylor E, Sembi S, Smith J (1992) Hyperactivity and delay aversion. I. The effect of delay on choice. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 33:387–398
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Welcome SE, Henkenius AL, Toga AW, Peterson BS (2003) Cortical abnormalities in children and adolescents with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Lancet 362:1699–1707
Swanson J, Gupta S, Guinta D, Flynn D, Agler D, Lerner M, Williams L, Shoulson I, Wigal S (1999) Acute tolerance to methylphenidate in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. Clin Pharmacol Ther 66:295–305
Todd RD (2000) Genetics of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: are we ready for molecular genetic studies? Am J Med Genet 96:241–243
Todd RD, Rasmussen ER, Neuman RJ, Reich W, Hudziak JJ, Bucholz KK, Madden PA, Heath A (2001) Familiality and heritability of subtypes of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in a population sample of adolescent female twins. Am J Psychiatry 158:1891–1898
Uzbekov MG, Misionzhnik EY (2003) Changes in urinary monoamine excretion in hyperkinetic children. Hum Psychopharmacol 18:493–497
Vitiello B, Severe JB, Greenhill LL, Arnold LE, Abikoff HB, Bukstein OG, Elliott GR, Hechtman L, Jensen PS, Hinshaw SP, March JS, Newcorn JH, Swanson JM, Cantwell DP (2001) Methylphenidate dosage for children with ADHD over time under controlled conditions: lessons from the MTA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:188–196
Voelker SL, Carter RA, Sprague DJ, Gdowski CL, Lachar D (1989) Developmental trends in memory and metamemory in children with attention deficit disorder. J Pediatr Psychol 14:75–88
Volkow ND, Wang G, Fowler JS, Logan J, Gerasimov M, Maynard L, Ding Y, Gatley SJ, Gifford A, Franceschi D (2001a) Therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate significantly increase extracellular dopamine in the human brain. J Neurosci 21:RC121
Volkow ND, Wang G, Fowler JS, Logan J, Gerasimov M, Maynard L, Ding Y, Gatley SJ, Gifford A, Franceschi D (2001b) Therapeutic doses of oral methylphenidate significantly increase extracellular dopamine in the human brain. J Neurosci 21:RC121
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Bostic J, Prince J, Monuteaux MC, Soriano J, Fine C, Abrams A, Rater M, Polisner D (1999) A pilot controlled clinical trial of ABT-418, a cholinergic agonist, in the treatment of adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am J Psychiatry 156:1931–1937
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Wong J, Spencer TJ, Prince JB (2000) Adjunctive donepezil in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder youth: case series. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10:217–222
Williams D, Stott CM, Goodyer IM, Sahakian BJ (2000) Specific language impairment with or without hyperactivity: neuropsychological evidence for frontostriatal dysfunction. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:368–375
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a local trust through a TENOVUS-Scotland initiative. We thank M. Thrower, K. Antonson, A. Brown, J. Esperon, K. Walker and S. Trudu for assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhodes, S.M., Coghill, D.R. & Matthews, K. Methylphenidate restores visual memory, but not working memory function in attention deficit-hyperkinetic disorder. Psychopharmacology 175, 319–330 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1833-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1833-7