Abstract
Rational
In recent years, evidence suggests that modafinil may be useful for certain symptom domains of schizophrenia, especially for the negative and cognitive symptoms. However, the results are not consistent.
Objective
This study was designed to investigate the effect of modafinil added to risperidone in patients with chronic schizophrenia in a double blind and randomized clinical trial.
Methods
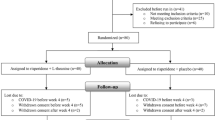
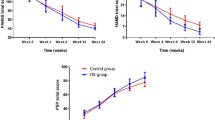
Participants were inpatients males (35) and females (11), ages 20–49 years at two teaching psychiatric hospital in Iran. All patients were in the active phase of the illness and met DSM-IV-TR criteria for schizophrenia. Patients were allocated in a random fashion 23 patients to risperidone 6 mg/day plus modafinil 200 mg/day and 23 patients to risperidone 6 mg/day plus placebo. The principal measure of outcome was the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS). Patients were assessed by a psychiatrist at baseline and after 2, 4, 6 and 8 weeks after the start of medication.
Results
The modafinil group had significantly greater improvement in the negative symptoms as well as PANSS total scores over the 8-week trial. Therapy with 200 mg/day of modafinil was well tolerated and no clinically important side effects were observed.
Conclusion
The present study indicates modafinil as a potential adjunctive treatment strategy for treatment of schizophrenia particularly the negative symptoms. Nevertheless, results of larger-controlled trials are needed before recommendation for broad clinical application can be made. This trial is registered with the Iranian Clinical Trials Registry (IRCT138903131556N16).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolfazli R, Hosseini M, Ghanizadeh A, Ghaleiha A, Tabrizi M, Raznahan M, Golalizadeh M, Akhondzadeh S (2011) Double-blind randomized parallel-group clinical trial of efficacy of the combination fluoxetine plus modafinil versus fluoxetine plus placebo in the treatment of major depression. Depress Anxiety 28:297–302
Akhondzadeh S (2006) Pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia: the past, present and future. Curr Drug Therapy 1:1–7
Akhondzadeh S, Rezaei F, Larijani B, Nejatisafa AA, Kashani L, Abbasi SH (2006) Correlation between testosterone, gonadotropins and prolactin and severity of negative symptoms in male patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 84:405–410
Akhondzadeh S, Tabatabaee M, Amini H, Ahmadi-Abhari SA, Abbasi SH, Behnam B (2007) Celecoxib as adjunctive therapy in schizophrenia: a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Res 90:179–185
Akhondzadeh S, Ghayyoumi R, Rezaei F, Salehi B, Modabbernia AH, Maroufi A, Esfandiari GR, Naderi M, Ghebleh F, Tabrizi M, Rezazadeh SA (2011) Sildenafil adjunctive therapy to risperidone in the treatment of the negative symptoms of schizophrenia: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Psychopharmacology 213:809–815
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn., text revision. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Amiri S, Mohammadi MR, Mohammadi M, Nouroozinejad GH, Kahbazi M, Akhondzadeh S (2008) Modafinil as a treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a double blind, randomized clinical trial. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:145–149
Ballon JS, Feifel D (2006) A systematic review of modafinil: potential clinical uses and mechanisms of action. J Clin Psychiatry 67:554–666
Buckley PF, Stahl SM (2007) Pharmacological treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia: therapeutic opportunity or cul-de-sac? Acta Psychiatr Scand 115:93–100
Chouinard G, Ross-Chouinard A, Annables L, Jones BD (1980) Extrapyramidal symptoms rating scale (abstract). Can J Neurol Sci 7:233
de Saint ZH, Martine O, Claude R, Gérard B, Stylianos N (2001) Variations in extracellular monoamines in the prefrontal cortex and medial hypothalamus after modafinil administration: a microdialysis study in rats. Neuroreport 12:3533–3537
Freudenreich O, Henderson DC, Macklin EA, Evins AE, Fan X, Cather C, Walsh JP, Goff DC (2009) Modafinil for clozapine-treated schizophrenia patie6nts: a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. J Clin Psychiatry 70:1674–1680
Ghaleiha A, Noorbala AA, Farnaghi F, Hajiazim M, Akhondzadeh S (2010) A double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled trial of buspirone added to risperidone in patients with chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 30:678–682
Kahbazi M, Ghoreishi A, Rahiminejad F, Mohammadi MR, Kamalipour A, Akhondzadeh S (2009) A randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial of modafinil in children and adolescents with attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Res 168:234–237
Kane JM, D’Souza DC, Patkar AA, Youakim JM, Tiller JM, Yang R, Keefe RS (2010) Armodafinil as adjunctive therapy in adults with cognitive deficits associated with schizophrenia: a 4-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry 71:1475–1481
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bull 13:261–276
Kumar R (2008) Approved and investigational uses of modafinil: an evidence-based review. Drugs 68:1803–1839
Mariani JJ, Hart CL (2005) Psychosis associated with modafinil and shift work. Am J Psychiatry 162:1983
Minzenberg MJ, Carter CS (2008) Modafinil: a review of neurochemical actions and effects on cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1477–1502
Mohammadi MR, Akhondzadeh S (2001) Schizophrenia: etiology and pharmacotherapy I. Drugs 4:1167–1172
Pierre JM, Peloian JH, Wirshing DA, Wirshing WC, Marder SR (2007) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil for negative symptoms in schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 68:705–710
Rosenthal MH, Bryant SL (2004) Benefits of adjunct modafinil in an open-label, pilot study in patients with schizophrenia. Clin Neuropharmacol 27:38–43
Saavedra-Velez C, Yusim A, Anbarasan D, Lindenmayer JP (2009) Modafinil as an adjunctive treatment of sedation, negative symptoms, and cognition in schizophrenia: a critical review. J Clin Psychiatry 70:104–112
Spence SA, Green RD, Wilkinson ID, Hunter MD (2005) Modafinil modulates anterior cingulate function in chronic schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 187:55–61
Tattan TM, Creed FH (2001) Negative symptoms of schizophrenia and compliance with medication. Schizophr Bull 27:149–155
Turner DC, Clark L, Pomarol-Clotet E, McKenna P, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2004) Modafinil improves cognition and attentional set shifting in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1363–1373
Wu P, Jones S, Ryan CJ, Michail D, Robinson TD (2008) Modafinil-induced psychosis. Intern Med J 38:677–678
Acknowledgments
This study was Dr. Mohaddeseh Bagheri’s postgraduate thesis toward the Iranian Board of Psychiatry. This study was supported by a grant from Tehran University of Medical Sciences to Prof. Shahin Akhondzadeh (grant no. 6157).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arbabi, M., Bagheri, M., Rezaei, F. et al. A placebo-controlled study of the modafinil added to risperidone in chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 220, 591–598 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2513-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2513-z