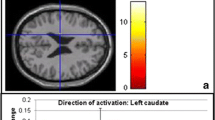
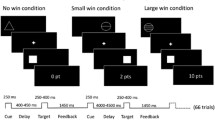
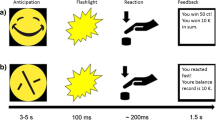
Abstract
Rationale
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies have reported increased activation of the mesolimbic system in response to anticipation of rewarding stimuli. The anticipation of uncertain outcomes evokes activation in the amygdala, orbitofrontal cortex, inferior frontal gyrus and insula. Drugs known to effect dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons also alter regional activation.
Objectives
Benzylpiperazine (BZP) and/or trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) have been recreationally used worldwide for more than a decade. BZP affects mainly dopaminergic neurons, while TFMPP has serotonergic effects.
Methods
We investigated the effects of an acute dose of BZP, TFMPP or a combination of BZP and TFMPP on the anticipation of reward in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study using fMRI. An event-related gambling paradigm was completed by healthy controls 90 min after taking an oral dose of either BZP (200 mg), TFMPP (either 50 or 60 mg), BZP + TFMPP (100 + 30 mg) or placebo.
Results
After giving BZP, the anticipation of a $4 reward decreased the activation of the inferior frontal gyrus, insula and occipital regions in comparison to placebo. TFMPP increased the activation of the putamen but decreased the activity in the insula relative to placebo. When BZP and TFMPP were given in combination, activation of the rolandic operculum occurred. The magnitude of reward also affected neural correlates.
Conclusion
We propose that the effects of BZP and TFMPP on dopaminergic and serotonergic circuitry, respectively, reflect regional changes. The dopaminergic effects of BZP appear to increase positive arousal and subsequently reduce the response to uncertainty, while TFMPP appears to alter the response to uncertainty by increasing emotional responses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adcock RA, Thangavel A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Knutson B, Gabrieli JDE (2006) Reward-motivated learning: mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron 50:507–517
Anselme P (2009) The effect of exposure to drugs on the processing of natural rewards. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:314–335
Antia U, Tingle MD, Russell BR (2010) Validation of an LC-MS method for the detection and quantification of BZP and TFMPP and their hydroxylated metabolites in human plasma and its application to the pharmacokinetic study of TFMPP in humans. J Forensic Sci 55:1311–1318
Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA (2004) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci 8:170–177
Baumann MH, Clark RD, Budzynski AG, Partilla JS, Blough BE, Rothman RB (2005) N-substituted piperazines abused by humans mimic the molecular mechanism of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or ‘Ecstasy’). Neuropsychopharmacology 30:550–560
Becerra L, Harter K, Gonzalez RG, Borsook D (2006) Functional magnetic resonance imaging measures of the effects of morphine on central nervous system circuitry in opioid-naive healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg 103:208–216
Bernabeu R, Bevilaqua L, Ardenghi P, Bromberg E, Schmitz P, Bianchin M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Involvement of hippocampal cAMP/cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathways in a late memory consolidation phase of aversively motivated learning in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7041–7046
Berridge KC, Robinson TE, Aldridge JW (2009) Dissecting components of reward: ‘liking’, ‘wanting’, and learning. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:65–73
Bertolino A, Rubino V, Sambataro F, Blasi G, Latorre V, Fazio L, Caforio G, Petruzzella V, Kolachana B, Hariri A, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Nardini M, Weinberger DR, Scarabino T (2006) Prefrontal-hippocampal coupling during memory processing is modulated by COMT val158met genotype. Biol Psychiatry 60:1250–1258
Breiter HC, Gollub RL, Weisskoff RM, Kennedy DN, Makris N, Berke JD, Goodman JM, Kantor HL, Gastfriend DR, Riorden JP, Mathew RT, Rosen BR, Hyman SE (1997) Acute effects of cocaine on human brain activity and emotion. Neuron 19:591–611
Bromberg-Martin ES, Matsumoto M, Hikosaka O (2010) Dopamine in motivational control: rewarding, aversive, and alerting. Neuron 68:815–834
Byrd KE, Romito LM, Dzemidzic M, Wong D, Talavage TM (2009) fMRI study of brain activity elicited by oral parafunctional movements. J Oral Rehabil 36:346–361
Carter CS, van Veen V (2007) Anterior cingulate cortex and conflict detection: an update of theory and data. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 7:367–379
Carter RM, Macinnes JJ, Huettel SA, Adcock RA (2009) Activation in the VTA and nucleus accumbens increases in anticipation of both gains and losses. Front Behav Neurosci 3:21
Copland DA, McMahon KL, Silburn PA, de Zubicaray GI (2009) Dopaminergic neuromodulation of semantic processing: a 4-T FMRI study with levodopa. Cereb Cortex 19:2651–2658
d'Acremont M, Lu Z-L, Li X, Van der Linden M, Bechara A (2009) Neural correlates of risk prediction error during reinforcement learning in humans. NeuroImage 47:1929–1939
Daw ND, Kakade S, Dayan P (2002) Opponent interactions between serotonin and dopamine. Neural Netw 15:603–616
Delgado MR, Nystrom LE, Fissell C, Noll DC, Fiez JA (2000) Tracking the hemodynamic responses to reward and punishment in the striatum. J Neurophysiol 84:3072–3077
Delgado MR, Locke HM, Stenger VA, Fiez JA (2003) Dorsal striatum responses to reward and punishment: effects of valence and magnitude manipulations. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3:27–38
Deroche-Gamonet V, Belin D, Piazza PV (2004) Evidence for addiction-like behavior in the rat. Science 305:1014–1017
Di Matteo V, Di Giovanni G, Di Mascio M, Esposito E (2000) Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence that RO 60–0175 inhibits mesolimbic dopaminergic function through serotonin(2C) receptors. Brain Res 865:85–90
Di Matteo V, De Blasi A, Di Giulio C, Esposito E (2001) Role of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the control of central dopamine function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:229–232
Dillon DG, Holmes AJ, Jahn AL, Bogdan R, Wald LL, Pizzagalli DA (2008) Dissociation of neural regions associated with anticipatory versus consummatory phases of incentive processing. Psychophysiology 45:36–49
Elliott R, Newman JL, Longe OA, William Deakin JF (2004) Instrumental responding for rewards is associated with enhanced neuronal response in subcortical reward systems. NeuroImage 21:984–990
Fantegrossi WE, Winger G, Woods JH, Woolverton WL, Coop A (2005) Reinforcing and discriminative stimulus effects of 1-benzylpiperazine and trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine in rhesus monkeys. Drug Alcohol Depend 77:161–168
Fekete MI, Szentendrei T, Herman JP, Kanyicska B (1980) Effects of reserpine and antidepressants on dopamine and DOPAC (3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid) concentrations in the striatum, olfactory tubercle and median eminence of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 64:231–238
Fink M, Wadsak W, Savli M, Stein P, Moser U, Hahn A, Mien L-K, Kletter K, Mitterhauser M, Kasper S, Lanzenberger R (2009) Lateralization of the serotonin-1A receptor distribution in language areas revealed by PET. NeuroImage 45:598–605
Fitzgerald DA, Posse S, Moore GJ, Tancer ME, Nathan PJ, Phan KL (2004) Neural correlates of internally-generated disgust via autobiographical recall: a functional magnetic resonance imaging investigation. Neurosci Lett 370:91–96
Gasbarri A, Sulli A, Innocenzi R, Pacitti C, Brioni JD (1996) Spatial memory impairment induced by lesion of the mesohippocampal dopaminergic system in the rat. Neuroscience 74:1037–1044
Grotewiel MS, Chu H, Sanders-Bush E (1994) m-Chlorophenylpiperazine and m-trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine are partial agonists at cloned 5-HT2A receptors expressed in fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1122–1126
Haase L, Cerf-Ducastel B, Buracas G, Murphy C (2007) On-line psychophysical data acquisition and event-related fMRI protocol optimized for the investigation of brain activation in response to gustatory stimuli. J Neurosci Methods 159:98–107
Herndon JL, Pierson ME, Glennon RA (1992) Mechanistic investigation of the stimulus properties of 1-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:739–748
Hsu M, Bhatt M, Adolphs R, Tranel D, Camerer CF (2005) Neural systems responding to degrees of uncertainty in human decision-making. Science 310:1680–1683
Huettel SA, Song AW, McCarthy G (2005) Decisions under uncertainty: probabilistic context influences activation of prefrontal and parietal cortices. J Neurosci 25:3304–3311
Huettel SA, Stowe CJ, Gordon EM, Warner BT, Platt ML (2006) Neural signatures of economic preferences for risk and ambiguity. Neuron 49:765–775
Jan RK, Lin JC, Lee H, Sheridan JL, Kydd RR, Kirk IJ, Russell BR (2010) Determining the subjective effects of TFMPP in human males. Psychopharmacology 211:347–353
Jay TM (2003) Dopamine: a potential substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 69:375–390
Knutson B, Cooper JC (2005) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr Opin Neurol 18:411–417
Knutson B, Peterson R (2005) Neurally reconstructing expected utility. Games Econ Behav 52:305–315
Knutson B, Westdorp A, Kaiser E, Hommer D (2000) FMRI visualization of brain activity during a monetary incentive delay task. NeuroImage 12:20–27
Knutson B, Adams CM, Fong GW, Hommer D (2001a) Anticipation of increasing monetary reward selectively recruits nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 21:RC159
Knutson B, Fong GW, Adams CM, Varner JL, Hommer D (2001b) Dissociation of reward anticipation and outcome with event-related fMRI. Neuroreport 12:3683–3687
Knutson B, Fong GW, Bennett SM, Adams CM, Hommer D (2003) A region of mesial prefrontal cortex tracks monetarily rewarding outcomes: characterization with rapid event-related fMRI. NeuroImage 18:263–272
Knutson B, Bjork JM, Fong GW, Hommer D, Mattay VS, Weinberger DR (2004) Amphetamine modulates human incentive processing. Neuron 43:261–269
Knutson B, Taylor J, Kaufman M, Peterson R, Glover G (2005) Distributed neural representation of expected value. J Neurosci 25:4806–4812
Koyama T, McHaffie JG, Laurienti PJ, Coghill RC (2005) The subjective experience of pain: where expectations become reality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12950–12955
Kuhnen CM, Knutson B (2005) The neural basis of financial risk taking. Neuron 47:763–770
Leon MI, Shadlen MN (1999) Effect of expected reward magnitude on the response of neurons in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the macaque. Neuron 24:415–425
Lin JC, Bangs N, Lee H, Kydd RR, Russell BR (2009) Determining the subjective and physiological effects of BZP on human females. Psychopharmacology 207:439–446
Liu Z, Richmond BJ, Murray EA, Saunders RC, Steenrod S, Stubblefield BK, Montague DM, Ginns EI (2004) DNA targeting of rhinal cortex D2 receptor protein reversibly blocks learning of cues that predict reward. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:12336–12341
Mazaika P, Hoeft F, Glover G, Reiss A (2009) Methods and software for fMRI analysis for clinical subjects. In: 15th annual meeting of the Organization for Human Brain Mapping, San Francisco
McCabe C, Huber A, Harmer CJ, Cowen PJ (2011) The D2 antagonist sulpiride modulates the neural processing of both rewarding and aversive stimuli in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 217:271–278
McLaren DG, Ph.D. Postdoctoral Research Fellow (2011) Customised script for SPM. Department of Neurology, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School
Meririnne E, Kajos M, Kankaanpaa A, Seppala T (2006) Rewarding properties of 1-benzylpiperazine, a new drug of abuse, in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 98:346–350
Miranda F, Orozco G, Velazquez-Martinez DN (2002) Full substitution of the discriminative cue of a 5-HT(1A/1B/2C) agonist with the combined administration of a 5-HT(1B/2C) and a 5-HT(1A) agonist. Behav Pharmacol 13:303–311
Murphy K, Garavan H (2004) An empirical investigation into the number of subjects required for an event-related fMRI study. NeuroImage 22:879–885
Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:1151–1159
Nitschke JB, Dixon GE, Sarinopoulos I, Short SJ, Cohen JD, Smith EE, Kosslyn SM, Rose RM, Davidson RJ (2006) Altering expectancy dampens neural response to aversive taste in primary taste cortex. Nat Neurosci 9:435–442
Oberlander C, Euvrard C, Dumont C, Boissier JR (1979) Circling behaviour induced by dopamine releasers and/or uptake inhibitors during degeneration of the nigrostriatal pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 60:163–170
O'Doherty J, Dayan P, Schultz J, Deichmann R, Friston K, Dolan RJ (2004) Dissociable roles of ventral and dorsal striatum in instrumental conditioning. Science 304:452–454
Ogawa H, Wakita M, Hasegawa K, Kobayakawa T, Sakai N, Hirai T, Yamashita Y, Saito S (2005) Functional MRI detection of activation in the primary gustatory cortices in humans. Chem Senses 30:583–592
Paulus MP, Rogalsky C, Simmons A, Feinstein JS, Stein MB (2003) Increased activation in the right insula during risk-taking decision making is related to harm avoidance and neuroticism. NeuroImage 19:1439–1448
Preuschoff K, Quartz SR, Bossaerts P (2008) Human insula activation reflects risk prediction errors as well as risk. J Neurosci 28:2745–2752
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2000) The psychology and neurobiology of addiction: an incentive-sensitization view. Addiction 95(Suppl 2):S91–S117
Rode C, Cosmides L, Hell W, Tooby J (1999) When and why do people avoid unknown probabilities in decisions under uncertainty? Testing some predictions from optimal foraging theory. Cognition 72:269–304
Rolls ET, McCabe C, Redoute J (2008) Expected value, reward outcome, and temporal difference error representations in a probabilistic decision task. Cereb Cortex 18:652–663
Schlosser RGM, Nenadic I, Wagner G, Zysset S, Koch K, Sauer H (2009) Dopaminergic modulation of brain systems subserving decision making under uncertainty: a study with fMRI and methylphenidate challenge. Synapse 63:429–442
Schmitz Y, Lee CJ, Schmauss C, Gonon F, Sulzer D (2001) Amphetamine distorts stimulation-dependent dopamine overflow: effects on D2 autoreceptors, transporters, and synaptic vesicle stores. J Neurosci 21:5916–5924
Schoeffter P, Hoyer D (1989) Interaction of arylpiperazines with 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1C and 5-HT1D receptors: do discriminatory 5-HT1B receptor ligands exist? Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 339:675–683
Seymour B, Daw N, Dayan P, Singer T, Dolan R (2007) Differential encoding of losses and gains in the human striatum. J Neurosci 27:4826–4831
Tekes K, Tothfalusi L, Malomvolgyi B, Herman F, Magyar K (1987) Studies on the biochemical mode of action of EGYT-475, a new antidepressant. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 39:203–211
Volkow ND, Fowler JS (2000) Addiction, a disease of compulsion and drive: involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:318–325
Wong D, Dzemidzic M, Talavage TM, Romito LM, Byrd KE (2011) Motor control of jaw movements: an fMRI study of parafunctional clench and grind behavior. Brain Res 1383:206–217
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Faculty Development Research Fund, School of Pharmacy, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, The University of Auckland. The authors would like to thank Dr. Donald McLaren for his fMRI guidance in the data analysis stage of this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curley, L.E., Kydd, R.R., Kirk, I.J. et al. Differential responses to anticipation of reward after an acute dose of the designer drugs benzylpiperazine (BZP) and trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine (TFMPP) alone and in combination using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Psychopharmacology 229, 673–685 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3128-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3128-3