Abstract
Background
Parkinson’s disease (PD) psychosis is encountered in as many as 50% of patients with advanced disease. Treatment options for PD psychosis are few. In fact, only clozapine and pimavanserin have shown efficacy in randomised controlled trials. Clinicians are often reluctant to prescribe the former, due to the risk of agranulocytosis, while the latter is not widely available yet. Because it is already clinically available and exhibits high affinity for serotonin 2A receptors, a target with which both clozapine and pimavanserin interact, we hypothesised that the anti-depressant mirtazapine might be effective to alleviate PD psychosis.
Methods
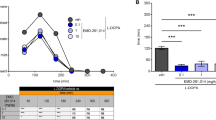
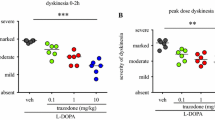
Here, we tested the anti-psychotic potential of mirtazapine in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned common marmoset. Five MPTP-lesioned marmosets exhibiting psychosis-like behaviours were administered L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) in combination with mirtazapine (0.1, 1 and 10 mg/kg) or vehicle. We also tested the effect of mirtazapine on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia.
Results
The addition of mirtazapine 10 mg/kg to L-DOPA reduced psychosis-like behaviours by 50% (P < 0.05) and dyskinesia by 29% (P < 0.01), when compared to L-DOPA/vehicle. Importantly, the antipsychotic and antidyskinetic effects of mirtazapine were achieved without hindering L-DOPA anti-parkinsonian action.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that mirtazapine may be effective to alleviate PD psychosis and, because the drug is clinically available, clinical trials that would assess its anti-psychotic efficacy in PD could be rapidly undertaken, hopefully leading to a new treatment option for this debilitating condition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvir JM, Lieberman JA, Safferman AZ, Schwimmer JL, Schaaf JA (1993) Clozapine-induced agranulocytosis. Incidence and risk factors in the United States N Engl J Med 329:162–167. doi:10.1056/NEJM199307153290303
Anttila SA, Leinonen EV (2001) A review of the pharmacological and clinical profile of mirtazapine. CNS Drug Rev 7:249–264
Cummings J et al (2014) Pimavanserin for patients with Parkinson’s disease psychosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 383:533–540. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62106-6
de Boer T (1996) The pharmacologic profile of mirtazapine. J Clin Psychiatry 57(Suppl 4):19–25
Delbressine LP et al (1998) Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation of mirtazapine in human volunteers. Clinical drug investigation 15:45–55
Durif F et al (2004) Clozapine improves dyskinesias in Parkinson disease: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 62:381–388
Fox SH, Visanji N, Reyes G, Huot P, Gomez-Ramirez J, Johnston T, Brotchie JM (2010) Neuropsychiatric behaviors in the MPTP marmoset model of Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 37:86–95
Fox SH, Visanji NP, Johnston TH, Gomez-Ramirez J, Voon V, Brotchie JM (2006) Dopamine receptor agonists and levodopa and inducing psychosis-like behavior in the MPTP primate model of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 63:1343–1344. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.9.1343
French Clozapine Parkinson Study Group (1999) Clozapine in drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. The French Clozapine Parkinson Study Group. Lancet 353:2041–2042
Friedman JH (2013) Parkinson disease psychosis: update. Behav Neurol 27:469–477. doi:10.3233/BEN-129016
Godschalx-Dekker JA, Siegers HP (2014) Reduction of parkinsonism and psychosis with mirtazapine. A Case Report Pharmacopsychiatry. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1367014
Goetz CG, Pappert EJ, Blasucci LM, Stebbins GT, Ling ZD, Nora MV, Carvey PM (1998) Intravenous levodopa in hallucinating Parkinson’s disease patients: high-dose challenge does not precipitate hallucinations. Neurology 50:515–517
Gordon PH, Pullman SL, Louis ED, Frucht SJ, Fahn S (2002) Mirtazapine in Parkinsonian tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 9:125–126
Hely MA, Morris JG, Reid WG, Trafficante R (2005) Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: non-L-dopa-responsive problems dominate at 15 years. Mov Disord 20:190–199. doi:10.1002/mds.20324
Huot P, Johnston TH, Gandy MN, Reyes MG, Fox SH, Piggott MJ, Brotchie JM (2012) The monoamine re-uptake inhibitor UWA-101 improves motor fluctuations in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. PLoS One 7:e45587. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045587
Huot P et al (2011) Characterization of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) enantiomers in vitro and in the MPTP-lesioned primate: R-MDMA reduces severity of dyskinesia, whereas S-MDMA extends duration of on-time. J Neurosci 31:7190–7198. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1171-11.2011
Huot P et al (2014) UWA-121, a mixed dopamine and serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, enhances L-DOPA anti-parkinsonian action without worsening dyskinesia or psychosis-like behaviours in the MPTP-lesioned common marmoset. Neuropharmacology 82:76–87. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.012
Jaquenoud Sirot E et al (2012) Multicenter study on the clinical effectiveness, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacogenetics of mirtazapine in depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 32:622–629. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3182664d98
Johnston TH et al (2011) Fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibition reduces L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced hyperactivity in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-lesioned non-human primate model of Parkinson’s disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 336:423–430. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.169532
Kannari K et al (2002) Tandospirone citrate, a selective 5-HT1A agonist, alleviates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. No To Shinkei 54:133–137
Lewitt PA et al (2012) Randomized clinical trial of fipamezole for dyskinesia in Parkinson disease (FJORD study). Neurology 79:163–169. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31825f0451
Maertens de Noordhout A, Delwaide PJ (1986) Open pilot trial of ritanserin in parkinsonism. Clin Neuropharmacol 9:480–484
Meco G, Fabrizio E, Di Rezze S, Alessandri A, Pratesi L (2003) Mirtazapine in L-dopa-induced dyskinesias. Clin Neuropharmacol 26:179–181
Meco G, Marini S, Linfante I, Modarelli F, Agnoli A (1988) Controlled single-blind crossover study of ritanserin and placebo in L-dopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Ther Res 43:262–270
Nagata T, Shinagawa S, Tagai K, Nakayama K (2012) A case in which mirtazapine reduced auditory hallucinations in a patient with Parkinson disease Int Psychogeriatr:1–3 doi:10.1017/S1041610212002037
Nagata T, Shinagawa S, Tagai K, Nakayama K (2013) A case in which mirtazapine reduced auditory hallucinations in a patient with Parkinson disease. Int Psychogeriatr 25:1199–1201. doi:10.1017/S1041610212002037
Normann C, Hesslinger B, Frauenknecht S, Berger M, Walden J (1997) Psychosis during chronic levodopa therapy triggered by the new antidepressive drug mirtazapine. Pharmacopsychiatry 30:263–265
Parkinson Study Group (1999) Low-dose clozapine for the treatment of drug-induced psychosis in Parkinson’s disease. The Parkinson Study Group. N Engl J Med 340:757–763
Rascol O et al (2001) Idazoxan, an alpha-2 antagonist, and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 16:708–713
Rouini MR, Lavasani H, Sheikholeslami B, Owen H, Giorgi M (2014) Pharmacokinetics of mirtazapine and its main metabolites after single intravenous and oral administrations in rats at two dose rates. Daru 22:13. doi:10.1186/2008-2231-22-13
Seppi K et al (2011) The movement disorder society evidence-based medicine review update: treatments for the non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(Suppl 3):S42–S80. doi:10.1002/mds.23884
Tagai K, Nagata T, Shinagawa S, Tsuno N, Ozone M, Nakayama K (2013) Mirtazapine improves visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s disease: a case report. Psychogeriatrics : the official journal of the Japanese Psychogeriatric Society 13:103–107. doi:10.1111/j.1479-8301.2012.00432.x
Vanover KE et al (2008) A 5-HT2A receptor inverse agonist, ACP-103, reduces tremor in a rat model and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in a monkey model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90:540–544. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.04.010
Visanji NP, Gomez-Ramirez J, Johnston TH, Pires D, Voon V, Brotchie JM, Fox SH (2006) Pharmacological characterization of psychosis-like behavior in the MPTP-lesioned nonhuman primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21:1879–1891. doi:10.1002/mds.21073
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Université de Montréal, Centre Hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal, Parkinson Society Canada, Fonds de Recherche Québec – Santé and the Weston Brain Institute.We would like to thank Drs Jonathan Brotchie and Tom Johnston for their advice during MPTP administration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Animals were cared for in accordance with a protocol approved by McGill University Animal Care Committee in accordance with the regulations defined by the Canadian Council on Animal Care.
Conflict of Interest
PH has received payments from Philippe Huot MD Inc. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamadjida, A., Nuara, S.G., Veyres, N. et al. The effect of mirtazapine on dopaminergic psychosis and dyskinesia in the parkinsonian marmoset. Psychopharmacology 234, 905–911 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4530-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4530-z