Abstract
Rational
Neonatal anoxia-ischemia (AI) particularly affects the central nervous system. Despite the many treatments that have been tested, none of them has proven to be completely successful. Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) and oleoylethanolamide (OEA) are acylethanolamides that do not bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors and thus they do not present cannabinoid activity. These molecules are agonist compounds of peroxisome proliferator-activator receptor alpha (PPARα), which modulates the expression of different genes that are related to glucose and lipid metabolism, inflammation, differentiation and proliferation.
Objective
In the present study, we analyzed the effects that the administration of PEA or OEA, after a neonatal AI event, has over different areas of the hippocampus.
Methods
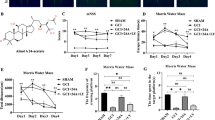
To this end, 7-day-old rats were subjected to AI and then treated with vehicle, OEA (2 or 10 mg/kg) or PEA (2 or 10 mg/kg). At 30 days of age, animals were subjected to behavioral tests followed by immunohistochemical studies.
Results
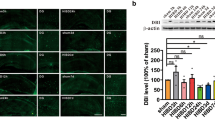
Results showed that neonatal AI was associated with decreased locomotion, as well as recognition and spatial memory impairments. Furthermore, these deficits were accompanied with enhanced neuroinflammation and astrogliosis, as well as a decreased PPARα expression. PEA treatment was able to prevent neuroinflammation, reduce astrogliosis and preserve cognitive functions.
Conclusions
These results indicate that the acylethanolamide PEA may play an important role in the mechanisms underlying neonatal AI, and it could be a good candidate for further studies regarding neonatal AI treatments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Genovese T, Impellizzeri D, Crupi R, Velardi E, Marino A, Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S (2012) Reduction of ischemic brain injury by administration of palmitoylethanolamide after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res 1477:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.006
Ahmad T, Laviolette SR (2017) Cannabinoid reward and aversion effects in the posterior ventral tegmental area are mediated through dissociable opiate receptor subtypes and separate amygdalar and accumbal dopamine receptor substrates. Psychopharmacology 234:2325–2336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4669-7
Almli CR, Levy TJ, Han BH, Shah AR, Gidday JM, Holtzman DM (2000) BDNF protects against spatial memory deficits following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Exp Neurol 166:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1006/exnr.2000.7492
Alonso-Alconada D, Alvarez A, Hilario E (2011) Cannabinoid as a neuroprotective strategy in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. Neurosci Bull 27:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-011-1008-6
Balduini W, De Angelis V, Mazzoni E, Cimino M (2000) Long-lasting behavioral alterations following a hypoxic/ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Brain Res 859:318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(00)01997-1
Barros CA, Ekuni R, Moro MA, Pereira FM, Dos Santos Pereira MA, Milani H (2009) The cognitive and histopathological effects of chronic 4-vessel occlusion in rats depend on the set of vessels occluded and the age of the animals. Behav Brain Res 197:378–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.10.023
Barry A, O'Halloran KD, McKenna JP, McCreary C, Harhen B, Kerr DM, Finn DP, Downer EJ (2018) Plasma N-acylethanolamine and endocannabinoid levels in burning mouth syndrome: potential role in disease pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med 47:440–442. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12692
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate—a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Royal Statist Soc, Series B (Methodological) 57:289–300. https://doi.org/10.2307/2346101
Bhateja DK, Dhull DK, Gill A, Sidhu A, Sharma S, Reddy BV, Padi SS (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α activation attenuates 3-nitropropionic acid induced behavioral and biochemical alterations in rats: possible neuroprotective mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 674:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.10.029
Blanco E, Galeano P, Holubiec MI, Romero JI, Logica T, Rivera P, Pavón FJ, Suarez J, Capani F, Rodríguez de Fonseca F (2015) Perinatal asphyxia results in altered expression of the hippocampal acylethanolamide/endocannabinoid signaling system associated to memory impairments in postweaned rats. Front Neuroanat 9:141. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00141
Blanco-Calvo E, Rivera P, Arrabal S, Vargas A, Pavón FJ, Serrano A, Castilla-Ortega E, Galeano P, Rubio L, Suárez J, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2014) Pharmacological blockade of either cannabinoid CB1 or CB2 receptors prevents both cocaine-induced conditioned locomotion and cocaine-induced reduction of cell proliferation in the hippocampus of adult male rat. Front Integr Neurosci 7:106. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnint.2013.00106
Bordet R, Ouk T, Petrault O, Gelé P, Gautier S, Laprais M, Deplanque D, Duriez P, Staels B, Fruchart JC, Bastide M (2006) PPAR: a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1341–1346. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0341341
Campolongo P, Roozendaal B, Trezza V, Cuomo V, Astarita G, Fu J, McGaugh JL, Piomelli D (2009) Fat-induced satiety factor oleoylethanolamide enhances memory consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:8027–8031. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0903038106
Carrera JM (2006) Protocolos de Obstetricia y Medicina Perinatal del Instituto Dexeus. Elsevier Masson, Barcelona
Cechetti F, Worm PV, Pereira LO, Siqueira IR, Netto AC (2010) The modified 2VO ischemia protocol causes cognitive impairment similar to that induced by the standard method, but with a better survival rate. Braz J Med Biol Res 43:1178–1183. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-879X2010007500124
Chen D, Dixon BJ, Doycheva DM, Li B, Zhang Y, Hu Q, He Y, Guo Z, Nowrangi D, Flores J, Filippov V, Zhang JH, Tang J (2018) IRE1α inhibition decreased TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation through miR-17-5p after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in rats. J Neuroinflammation 15:32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1077-9
Crews FT, Walter TJ, Coleman LG Jr, Vetreno RP (2017) Toll-like receptor signaling and stages of addiction. Psychopharmacology 234:1483–1498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4560-6
Cristiano L, Cimini A, Moreno S, Ragnelli AM, Paola Cerù M (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and related transcription factors in differentiating astrocyte cultures. Neuroscience 131:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.11.008
Cunha-Rodrigues MC, Balduci CTDN, Tenório F, Barradas PC (2018) GABA function may be related to the impairment of learning and memory caused by systemic prenatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol Learn Mem 149:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2018.01.004
D'Agostino G, Russo R, Avagliano C, Cristiano C, Meli R, Calignano A (2012) Palmitoylethanolamide protects against the amyloid-β25-35-induced learning and memory impairment in mice, an experimental model of Alzheimer disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1784–1792. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.25
Dai C, Liu Y, Dong Z (2017) Tanshinone I alleviates motor and cognitive impairments via suppressing oxidative stress in the neonatal rats after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Brain 10:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-017-0332-9
Davies M, Jacobs A, Brody DL, Friess SH (2018) Delayed hypoxemia after traumatic brain injury exacerbates long-term behavioral deficits. J Neurotrauma 35:790–801. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2017.5354
Deacon RM, Bannerman DM, Kirby BP, Croucher A, Rawlins JN (2002) Effects of cytotoxic hippocampal lesions in mice on a cognitive test battery. Behav Brain Res 133:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(01)00451-X
Di Marzo V, Skaper SD (2013) Palmitoylethanolamide: biochemistry, pharmacology and therapeutic use of a pleiotropic anti-inflammatory lipid mediator. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 12:4–6. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527311312010004
Domnick NK, Gretenkord S, De Feo V, Sedlacik J, Brockmann MD, Hanganu-Opatz IL (2015) Neonatal hypoxia-ischemia impairs juvenile recognition memory by disrupting the maturation of prefrontal-hippocampal networks. Exp Neurol 273:202–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.08.017
Driscoll DJO, Felice VD, Kenny LC, Boylan GB, O'Keeffe GW (2018) Mild prenatal hypoxia-ischemia leads to social deficits and central and peripheral inflammation in exposed offspring. Brain Behav Immun, in press 69:418–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2018.01.001
Ennaceur A (2010) One-trial object recognition in rats and mice: methodological and theoretical issues. Behav Brain Res 215:244–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.12.036
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(88)90157-X
Esposito E, Impellizzeri D, Mazzon E, Paterniti I, Cuzzocrea S (2012) Neuroprotective activities of palmitoylethanolamide in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 7:e41880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041880
Fidaleo M, Fanelli F, Ceru MP, Moreno S (2014) Neuroprotective properties of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and its lipid ligands. Curr Med Chem 21:2803–2821. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867321666140303143455
Franklin A, Parmentier-Batteur S, Walter L, Greenberg DA, Stella N (2003) Palmitoylethanolamide increases after focal cerebral ischemia and potentiates microglial cell motility. J Neurosci 23:7767–7775. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-21-07767.2003
Fu J, Gaetani S, Oveisi F, Lo Verme J, Serrano A, Rodríguez De Fonseca F, Rosengarth A, Luecke H, Di Giacomo B, Tarzia G, Piomelli D (2003) Oleylethanolamide regulates feeding and body weight through activation of the nuclear receptor PPAR-alpha. Nature 425:90–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01921
Galeano P, Blanco E, Logica Tornatore TM, Romero JI, Holubiec MI, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Capani F (2015) Life-long environmental enrichment counteracts spatial learning, reference and working memory deficits in middle-aged rats subjected to perinatal asphyxia. Front Behav Neurosci 8:406. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00406
Galeano P, Blanco Calvo E, Madureira de Oliveira D, Cuenya L, Kamenetzky GV, Mustaca AE, Barreto GE, Giraldez-Alvarez LD, Milei J, Capani F (2011) Long-lasting effects of perinatal asphyxia on exploration, memory and incentive downshift. Int J Dev Neurosci 29:609–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2011.05.002
Galinsky R, Lear CA, Dean JM, Wassink G, Dhillon SK, Fraser M, Davidson JO, Bennet L, Gunn AJ (2018) Complex interactions between hypoxia-ischemia and inflammation in preterm brain injury. Dev Med Child Neurol 60:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/dmcn.13629
Griva M, Lagoudaki R, Touloumi O, Nousiopoulou E, Karalis F, Georgiou T, Kokaraki G, Simeonidou C, Tata DA, Spandou E (2017) Long-term effects of enriched environment following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia on behavior, BDNF and synaptophysin levels in rat hippocampus: effect of combined treatment with G-CSF. Brain Res 1667:55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.05.004
Guida F, Luongo L, Boccella S, Giordano ME, Romano R, Bellini G, Manzo I, Furiano A, Rizzo A, Imperatore R, Iannotti FA, D'Aniello E, Piscitelli F, Sca Rossi F, Cristino L, Di Marzo V, de Novellis V, Maione S (2017) Palmitoylethanolamide induces microglia changes associated with increased migration and phagocytic activity: involvement of the CB2 receptor. Sci Rep 7:375. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00342-1
Halliwell B (1992) Reactive oxygen species and the central nervous system. J Neurochem 59:1609–1623. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10990.x
Hansen HS, Diep TA (2009) N-acylethanolamines, anandamide and food intake. Biochem Pharmacol 78:553–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.04.024
Ho WS, Barrett DA, Randall MD (2008) ‘Entourage’ effects of N-palmitoylethanolamide and N-oleoylethanolamide on vasorelaxation to anandamide occur through TRPV1 receptors. Br J Pharmacol 155:837–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.324
Holubiec MI, Romero JI, Blanco E, Tornatore TL, Suarez J, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Galeano P, Capani F (2017) Acylethanolamides and endocannabinoid signaling system in dorsal striatum of rats exposed to perinatal asphyxia. Neurosci Lett 653:269–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.06828579484
Kossatz E, Silva-Peña D, Suárez J, de Fonseca FR, Maldonado R, Robledo P (2018) Octadecylpropyl sulfamide reduces neurodegeneration and restores the memory deficits induced by hypoxia-ischemia in mice. Front Pharmacol 9:376. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00376
Kumar A, Gupta A, Talukdar B (2007) Clinico-etiological and EEG profile of neonatal seizures. Indian J Pediatr 74:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-007-0023-0
Liaury K, Miyaoka T, Tsumori T, Furuya M, Hashioka S, Wake R, Tsuchie K, Fukushima M, Limoa E, Tanra AJ, Horiguchi J (2014) Minocycline improves recognition memory and attenuates microglial activation in Gunn rat: a possible hyperbilirubinemia-induced animal model of schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 50:184–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.017
López-Aguilera F, Plateo-Pignatari MG, Biaggio V, Ayala C, Seltzer AM (2012) Hypoxic preconditioning induces an AT2-R/VEGFR-2(Flk-1) interaction in the neonatal brain microvasculature for neuroprotection. Neuroscience 216:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.070
Lowin T, Apitz M, Anders S, Straub RH (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of N-acylethanolamines in rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells are mediated by TRPV1 and TRPA1 in a COX-2 dependent manner. Arthritis Res Ther 17:321. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0845-5
Mallard C, Tremblay ME, Vexler ZS (2018) Microglia and neonatal brain injury. Neuroscience, in press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.023
Ming-Yan H, Luo YL, Zhang XC, Liu H, Gao R, Wu JJ (2012) Hypoxic-ischemic injury decreases anxiety-like behavior in rats when associated with loss of tyrosine-hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons of the substantia nigra. Braz J Med Biol Res 45:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-879X2011007500161
Mirahmadi SM, Shahmohammadi A, Rousta AM, Azadi MR, Fahanik-Babaei J, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2017) Soy isoflavone genistein attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairments in the rat via exerting anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. Cytokine, in press 104:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.10.008
Mishima K, Ikeda T, Yoshikawa T, Aoo N, Egashira N, Xia YX, Ikenoue T, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2004) Effects of hypothermia and hyperthermia on attentional and spatial learning deficits following neonatal hypoxia-ischemic insult in rats. Behav Brain Res 151:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2003.08.018
Moran E, Ding L, Wang Z, Cheng R, Chen Q, Moore R, Takahashi Y, Ma JX (2014) Protective and antioxidant effects of PPARα in the ischemic retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 55:4568–4576. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.13-13127
Naccarato M, Pizzuti D, Petrosino S, Simonetto M, Ferigo L, Grandi FC, Pizzolato G, Di Marzo V (2010) Possible anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide involvement in human stroke. Lipids Health Dis 9:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-9-47
Okamoto Y, Tsuboi K, Ueda N (2009) Enzymatic formation of anandamide. Vitam Horm 81:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0083-6729(09)81001-7
Parrella E, Porrini V, Iorio R, Benarese M, Lanzillotta A, Mota M, Fusco M, Tonin P, Spano P, Pizzi M (2016) PEA and luteolin synergistically reduce mast cell-mediated toxicity and elicit neuroprotection in cell-based models of brain ischemia. Brain Res 1648:409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.014
Pasquarelli N, Porazik C, Hanselmann J, Weydt P, Ferger B, Witting A (2015) Comparative biochemical characterization of the monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitor KML29 in brain, spinal cord, liver, spleen, fat and muscle tissue. Neuropharmacology 91:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.12.001
Paterniti I, Impellizzeri D, Di Paola R, Navarra M, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E (2013) A new co-ultramicronized composite including palmitoylethanolamide and luteolin to prevent neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation 10:91. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-10-91
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Pei B, Sun J (2018) Pinocembrin alleviates cognition deficits by inhibiting inflammation in diabetic mice. J Neuroimmunol 314:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.11.006
Pereira LO, Arteni NS, Petersen RC, da Rocha AP, Achaval M, Netto CA (2007) Effects of daily environmental enrichment on memory deficits and brain injury following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2006.07.003
Petrosino S, Di Marzo V (2017) The pharmacology of palmitoylethanolamide and first data on the therapeutic efficacy of some of its new formulations. Br J Pharmacol 174:1349–1365. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13580
Romero JI, Hanschmann EM, Gellert M, Eitner S, Holubiec MI, Blanco-Calvo E, Lillig CH, Capani F (2015) Thioredoxin 1 and glutaredoxin 2 contribute to maintain the phenotype and integrity of neurons following perinatal asphyxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:1274–1285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.02.015
Romero JI, Holubiec MI, Tornatore TL, Rivière S, Hanschmann EM, Kölliker-Frers RA, Tau J, Blanco E, Galeano P, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Lillig CH, Capani F (2017) Neuronal damage induced by perinatal asphyxia is attenuated by postinjury glutaredoxin-2 administration. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:4162465. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4162465
Salter MW, Stevens B (2017) Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat Med 23:1018–1027. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4397
Saraceno GE, Bertolino ML, Galeano P, Romero JI, Garcia-Segura LM, Capani F (2010) Estradiol therapy in adulthood reverses glial and neuronal alterations caused by perinatal asphyxia. Exp Neurol 223:615–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.02.010
Saraceno GE, Castilla R, Barreto GE, Gonzalez J, Kölliker-Frers RA, Capani F (2012) Hippocampal dendritic spines modifications induced by perinatal asphyxia. Neural Plast 2012:873532. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/873532
Sayd A, Antón M, Alén F, Caso JR, Pavón J, Leza JC, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, García-Bueno B, Orio L (2014) Systemic administration of oleoylethanolamide protects from neuroinflammation and anhedonia induced by LPS in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:pyu111. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyu111
Schwartz PH, Massarweh WF, Vinters HV, Wasterlain CG (1992) A rat model of severe neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke 23:539–546
Schoch H, Huerta MY, Ruiz CM, Farrell MR, Jung KM, Huang JJ, Campbell RR, Piomelli D, Mahler SV (2018) Adolescent cannabinoid exposure effects on natural reward seeking and learning in rats. Psychopharmacology 235:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4749-8
Schomacher M, Müller HD, Sommer C, Schwab S, Schäbitz WR (2008) Endocannabinoids mediate neuroprotection after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1240:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2008.09.019
Scuderi C, Bronzuoli MR, Facchinetti R, Pace L, Ferraro L, Broad KD, Serviddio G, Bellanti F, Palombelli G, Carpinelli G, Canese R, Gaetani S, Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Cassano T (2018) Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide rescues learning and memory impairments in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease by exerting anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Transl Psychiatry 8:32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-017-0076-4
Scuderi C, Esposito G, Blasio A, Valenza M, Arietti P, Steardo L Jr, Carnuccio R, De Filippis D, Petrosino S, Iuvone T, Di Marzo V, Steardo L (2011) Palmitoylethanolamide counteracts reactive astrogliosis induced by β-amyloid peptide. J Cell Mol Med 15:2664–2274. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01267.x
Scuderi C, Stecca C, Valenza M, Ratano P, Bronzuoli MR, Bartoli S, Steardo L, Pompili E, Fumagalli L, Campolongo P, Steardo L (2014) Palmitoylethanolamide controls reactive gliosis and exerts neuroprotective functions in a rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Dis 5:e1419. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.376
Sebetseba KN, Ramdin T, Ballot D (2017) The use of therapeutic hypothermia in neonates with perinatal asphyxia at Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg academic hospital: a retrospective review. Ther Hypothermia Temp Manag, in press. https://doi.org/10.1089/ther.2017.0040
Sedláčková N, Krajčiová M, Koprdová R, Ujházy E, Brucknerová I, Mach M (2014) Subchronic perinatal asphyxia increased anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in the rat offspring. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 35(Suppl 2):214–220
Serrano A, Rivera P, Pavon FJ, Decara J, Suárez J, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, Parsons LH (2012) Differential effects of single versus repeated alcohol withdrawal on the expression of endocannabinoid system-related genes in the rat amygdala. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36:984–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01686.x
Siracusa R, Paterniti I, Impellizzeri D, Cordaro M, Crupi R, Navarra M, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E (2015) The association of palmitoylethanolamide with luteolin decreases neuroinflammation and stimulates autophagy in Parkinson’s disease model. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 14:1350–1365. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527314666150821102823
Skaper SD, Facci L, Giusti P (2013) Glia and mast cells as targets for palmitoylethanolamide, an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective lipid mediator. Mol Neurobiol 48:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8487-6
Smith AL, Alexander M, Rosenkrantz TS, Sadek ML, Fitch RH (2014) Sex differences in behavioral outcome following neonatal hypoxia ischemia: insights from a clinical meta-analysis and a rodent model of induced hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol 254:54–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.01.003
Strackx E, Van den Hove DL, Prickaerts J, Zimmermann L, Steinbusch HW, Blanco CE, Gavilanes AW, Vles JS (2010) Fetal asphyctic preconditioning protects against perinatal asphyxia-induced behavioral consequences in adulthood. Behav Brain Res 208:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.11.040
Takada SH, Motta-Teixeira LC, Machado-Nils AV, Lee VY, Sampaio CA, Polli RS, Malheiros JM, Takase LF, Kihara AH, Covolan L, Xavier GF, Nogueira MI (2016) Impact of neonatal anoxia on adult rat hippocampal volume, neurogenesis and behavior. Behav Brain Res 296:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.08.039
Ueda N, Tsuboi K, Uyama T (2013) Metabolism of endocannabinoids and related N-acylethanolamines: canonical and alternative pathways. FEBS J 280:1874–1894. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12152
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ (2005) Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 27:81–86
Xu J, Chavis JA, Racke MK, Drew PD (2006) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and retinoid X receptor agonists inhibit inflammatory responses of astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 176:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.04.019
Yang LC, Guo H, Zhou H, Suo DQ, Li WJ, Zhou Y, Zhao Y, Yang WS, Jin X (2015) Chronic oleoylethanolamide treatment improves spatial cognitive deficits through enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Biochem Pharmacol 94:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2015.02.012
Zhou Y, Schwartz BI, Giza J, Gross SS, Lee FS, Kreek MJ (2017) Blockade of alcohol escalation and “relapse” drinking by pharmacological FAAH inhibition in male and female C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 234:2955–2970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4691-9
Zhou Y, Yang L, Ma A, Zhang X, Li W, Yang W, Chen C, Jin X (2012) Orally administered oleoylethanolamide protects mice from focal cerebral ischemic injury by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α. Neuropharmacology 63:242–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.03.008
Zhu H, Qiao L, Sun Y, Yin L, Huang L, Li J, Jiang L (2018) Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of neonatal rats following hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Neurosci Lett, in press 673:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.01.046
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Fundació “La Marató de TV3” (386/C/2011), European Regional Development Funds-European Union (ERDF-EU; Subprograma RETICS Red de Trastornos Adictivos RD16/0017/0001), Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad and ISCIII (PI16/01689) to FRF; Own Plan of the Andalucía TECH, International Campus of Excellence (ICE) to PG, and grants to EFE and FRF from Junta de Andalucía, Spain (EFE, group BIO-127; FRF, group BIO-339). JS holds a “Miguel Servet II” research contract from the National System of Health, ISCIII, EU-ERDF (CPII17/00024). Mariana I. Holubiec is a fellowship holder from Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT, Argentina). Eduardo Blanco is an associate professor of the Serra-Hunter Programme from the Catalan Government. Juan I. Romero and Pablo Galeano are research members from Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET, Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, corresponding authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 494 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holubiec, M.I., Romero, J.I., Suárez, J. et al. Palmitoylethanolamide prevents neuroinflammation, reduces astrogliosis and preserves recognition and spatial memory following induction of neonatal anoxia-ischemia. Psychopharmacology 235, 2929–2945 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4982-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4982-9