Abstract
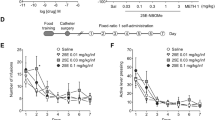
Eating disorders are frequently triggered by stress and are more prevalent in women than men. First signs often appear during early adolescence, but the biological basis for the sex-specific differences is unknown. Central administration of native relaxin-3 (RLN3) peptide or chimeric/truncated analogues produces differential effects on food intake and HPA axis activity in adult male and female rats, but the precise role of endogenous RLN3 signalling in metabolic and neuroendocrine control is unclear. Therefore, we examined the effects of microRNA-induced depletion (knock-down) of RLN3 mRNA/(peptide) production in neurons of the brainstem nucleus incertus (NI) in female rats on a range of physiological, behavioural and neurochemical indices, including food intake, body weight, anxiety, plasma corticosterone, mRNA levels of key neuropeptides in the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus (PVN) and limbic neural activity patterns (reflected by c-fos mRNA). Validated depletion of RLN3 in NI neurons of female rats (n = 8) produced a small, sustained (~ 2%) decrease in body weight, an imbalance in food intake and an increase in anxiety-like behaviour in the large open field, but not in the elevated plus-maze or light/dark box. Furthermore, NI RLN3 depletion disrupted corticosterone regulation, increased oxytocin and arginine-vasopressin, but not corticotropin-releasing factor, mRNA, in PVN, and decreased basal levels of c-fos mRNA in parvocellular and magnocellular PVN, bed nucleus of stria terminalis and the lateral hypothalamic area, brain regions involved in stress and feeding. These findings support a role for NI RLN3 neurons in fine-tuning stress and neuroendocrine responses and food intake regulation in female rats.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. American Psychiatric Association
Avery S, Clauss J, Blackford J (2016) The human BNST: functional role in anxiety and addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:126–141
Banerjee A, Shen P-J, Ma S, Bathgate RAD, Gundlach AL (2010) Swim stress excitation of nucleus incertus and rapid induction of relaxin-3 expression via CRF 1 activation. Neuropharmacology 58:145–155
Bathgate RAD, Samuel CS, Burazin TCD, Layfield S, Claasz AA, Reytomas IGT, Dawson NF, Zhao C, Bond C, Summers RJ (2002) Human relaxin gene 3 (H3) and the equivalent mouse relaxin (M3) gene novel members of the relaxin peptide family. J Biol Chem 277:1148–1157
Bathgate RAD, Zhang S, Hughes RA, Rosengren KJ, Wade JD (2012) The structural determinants of insulin-like peptide 3 activity. Front Endocrinol 3:11
Bathgate RAD, Oh MH, Ling WJ, Kaas Q, Hossain MA, Gooley PR, Rosengren KJ (2013) Elucidation of relaxin-3 binding interactions in the extracellular loops of RXFP3. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:13
Black DW, Grant JE (2014) DSM-5® Guidebook: The Essential Companion to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Association
Bourin M, Hascoët M (2003) The mouse light/dark box test. Eur J Pharmacol 463:55–65
Burazin TCD, Bathgate RAD, Macris M, Layfield S, Gundlach AL, Tregear GW (2002) Restricted, but abundant, expression of the novel rat gene-3 (R3) relaxin in the dorsal tegmental region of brain. J Neurochem 82:1553–1557
Callander GE, Ma S, Ganella DE, Wimmer VC, Gundlach AL, Thomas WG, Bathgate RAD (2012) Silencing relaxin-3 in nucleus incertus of adult rodents: a viral vector-based approach to investigate neuropeptide function. PLoS One 7:e42300
Calvez J, Lenglos C, de Avila C, Guèvremont G, Timofeeva E (2015) Differential effects of central administration of relaxin-3 on food intake and hypothalamic neuropeptides in male and female rats. Genes Brain Behav 14:550–563
Calvez J, de Avila C, Matte L-O, Guèvremont G, Gundlach AL, Timofeeva E (2016) Role of relaxin-3/RXFP3 system in stress-induced binge-like eating in female rats. Neuropharmacology 102:207–215
Dallman MF, la Fleur SE, Pecoraro NC, Gomez F, Houshyar H, Akana SF (2004) Minireview: glucocorticoids - food intake, abdominal obesity, and wealthy nations in 2004. Endocrinology 145:2633–2638
De Ávila C, Chometton S, Lenglos C, Calvez J, Gundlach AL, Timofeeva E (2018) Differential effects of relaxin-3 and a selective relaxin-3 receptor agonist on food and water intake and hypothalamic neuronal activity in rats. Behav Brain Res 336:135–144
Gafford GM, Guo J-D, Flandreau EI, Hazra R, Rainnie DG, Ressler KJ (2012) Cell-type specific deletion of GABA(A) α1 in corticotropin-releasing factor-containing neurons enhances anxiety and disrupts fear extinction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:16330–16335
Ganella DE, Ma S, Gundlach AL (2013) Relaxin-3/RXFP3 signalling and neuroendocrine function - a perspective on extrinsic hypothalamic control. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 4:128
Gjerstad JK, Lightman SL, Spiga F (2018) Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 21:403–416
Gundlach AL, Ma S, Sang Q, Shen PJ, Piccenna LP, Sedaghat K, Smith CM, Bathgate RAD, Lawrence AJ, Tregear GW (2009) Relaxin family peptides and receptors in mammalian brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1160:226–235
Haugaard-Kedstrom LM, Shabanpoor F, Hossain MA, Clark RJ, Ryan PJ, Craik DJ, Gundlach AL, Wade JD, Bathgate RAD, Rosengren KJ (2011) Design, synthesis, and characterization of a single-chain peptide antagonist for the relaxin-3 receptor RXFP3. J Am Chem Soc 133:4965–4974
Herman JP, Cullinan WE (1997) Neurocircuitry of stress: central control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Trends Neurosci 20:78–84
Hida T, Takahashi E, Shikata K, Hirohashi T, Sawai T, Seiki T, Tanaka H, Kawai T, Ito O, Arai T (2006) Chronic intracerebroventricular administration of relaxin-3 increases body weight in rats. J Recept Signal Transduct 26:147–158
Hoek HW, Van Hoeken D (2003) Review of the prevalence and incidence of eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord 34:383–396
Hudson JI, Hiripi E, Pope HG, Kessler RC (2007) The prevalence and correlates of eating disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Biol Psychiatry 61:348–358
Kania A, Gugula A, Grabowiecka A, de Ávila C, Blasiak T, Rajfur Z, Lewandowski MH, Hess G, Timofeeva E, Gundlach AL, Blasiak A (2017) Inhibition of oxytocin and vasopressin neuron activity in rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus by relaxin-3/RXFP3 signalling. J Physiol 595:3425–3447
Krahn DD, Gosnell BA, Grace M, Levine AS (1986) CRF antagonist partially reverses CRF-and stress-induced effects on feeding. Brain Res Bull 17:285–289
Kuei C, Sutton S, Bonaventure P, Pudiak C, Shelton J, Zhu J, Nepomuceno D, Wu J, Chen J, Kamme F, Seierstad M, Hack MD, Bathgate RAD, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Atack J, Lovenberg TW, Liu C (2007) R3 (BΔ23-27) R/I5 chimeric peptide, a selective antagonist for GPCR135 and GPCR142 over relaxin receptor LGR7 in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Biol Chem 282:25425–25435
Kumar JR, Rajkumar R, Jayakody T, Marwari S, Hong JM, Ma S, Gundlach AL, Lai MK, Dawe GS (2017) Relaxin’ the brain: a case for targeting the nucleus incertus network and relaxin-3/RXFP3 system in neuropsychiatric disorders. Br J Pharmacol 174:1061–1076
Laitinen J, Ek E, Sovio U (2002) Stress-related eating and drinking behavior and body mass index and predictors of this behavior. Prev Med 34:29–39
Lawther AJ, Flavell A, Ma S, Kent S, Lowry CA, Gundlach AL, Hale MW (2018) Involvement of serotonergic and relaxin-3 neuropeptide systems in the expression of anxiety-like behavior. Neuroscience 390:88–103
Lee Y, Fitz S, Johnson PL, Shekhar A (2008) Repeated stimulation of CRF receptors in the BNST of rats selectively induces social but not panic-like anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2586–2594
Lenglos C, Mitra A, Guèvremont G, Timofeeva E (2013) Sex differences in the effects of chronic stress and food restriction on body weight gain and brain expression of CRF and relaxin-3 in rats. Genes Brain Behav 12:370–387
Lenglos C, Calvez J, Timofeeva E (2014) Sex-specific effects of relaxin-3 on food intake and brain expression of corticotropin-releasing factor in rats. Endocrinology 156:523–533
Liu C, Eriste E, Sutton S, Chen J, Roland B, Kuei C, Farmer N, Jörnvall H, Sillard R, Lovenberg TW (2003) Identification of relaxin-3/INSL7 as an endogenous ligand for the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor GPCR135. J Biol Chem 278:50754–50764
Lo SC, Ravaldi C, Cabras PL, Faravelli C, Ricca V (2007) Stress, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and eating disorders. Neuropsychobiology 57:95–115
Ma S, Shen P-J, Burazin TCD, Tregear GW, Gundlach AL (2006) Comparative localization of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor-7 (RXFP1) mRNA and [33P]-relaxin binding sites in rat brain: restricted somatic co-expression a clue to relaxin action? Neuroscience 141:329–344
Ma S, Bonaventure P, Ferraro T, Shen P-J, Burazin TCD, Bathgate RAD, Liu C, Tregear GW, Sutton SW, Gundlach AL (2007) Relaxin-3 in GABA projection neurons of nucleus incertus suggests widespread influence on forebrain circuits via G-protein-coupled receptor-135 in the rat. Neuroscience 144:165–190
Ma S, Blasiak A, Olucha-Bordonau FE, Verberne AJ, Gundlach AL (2013) Heterogeneous responses of nucleus incertus neurons to corticotrophin-releasing factor and coherent activity with hippocampal theta rhythm in the rat. J Physiol 591:3981–4001
Ma S, Smith CM, Blasiak A, Gundlach AL (2017) Distribution, physiology and pharmacology of relaxin-3/RXFP3 systems in brain. Br J Pharmacol 174:1034–1048
Ma S, Hangya B, Leonard CS, Wisden W, Gundlach AL (2018) Dual-transmitter systems regulating arousal, attention, learning and memory. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 85:21–33
Martin J, Timofeeva E (2010) Intermittent access to sucrose increases sucrose-licking activity and attenuates restraint stress-induced activation of the lateral septum. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R1383–R1398
McGowan BM, Stanley SS, Smith KL, White NE, Connolly MM, Thompson EL, Gardiner JV, Murphy KG, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2005) Central relaxin-3 administration causes hyperphagia in male Wistar rats. Endocrinology 146:3295–3300
McGowan BM, Stanley SA, Smith KL, Minnion JS, Donovan J, Thompson EL, Patterson M, Connolly MM, Abbott CR, Small CJ, Gardiner JV, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2006) Effects of acute and chronic relaxin-3 on food intake and energy expenditure in rats. Regul Pept 136:72–77
McGowan BM, Minnion JS, Murphy KG, Roy D, Stanley SA, Dhillo WS, Gardiner JV, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (2014) Relaxin-3 stimulates the neuro-endocrine stress axis via corticotrophin-releasing hormone. J Endocrinol 221:337–346
Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Cifani C, Lambertucci C, Volpini R, Cristalli G, Massi M (2012) A2A-Adenosine receptor agonists reduce both high-palatability and low-palatability food intake in female rats. Behav Pharmacol 23:567-74
Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Ciccocioppo R, Romano A, Bossert JM, Rice KC, Ubaldi M, St Laurent R, Gaetani S, Massi M, Shaham Y, Cifani C (2014) Role of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis corticotrophin-releasing factor receptors in frustration stress-induced binge-like palatable food consumption in female rats with a history of food restriction. J Neurosci 34:11316-11324
Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Ubaldi M, Giusepponi ME, Rice KC, Massi M, Ciccocioppo R, Cifani C (2017) Hypothalamic CRF1 receptor mechanisms are not sufficient to account for binge-like palatable food consumption in female rats. Int J Eat Disord 50:1194-1204
Mitra A, Lenglos C, Martin J, Mbende N, Gagne A, Timofeeva E (2011) Sucrose modifies c-fos mRNA expression in the brain of rats maintained on feeding schedules. Neuroscience 192:459–474
Moga MM, Saper CB, Gray TS (1989) Bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: cytoarchitecture, immunohistochemistry, and projection to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 283:315–332
Morton G, Cummings D, Baskin D, Barsh G, Schwartz M (2006) Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443:289–295
Muglia LJ, Jacobson L, Weninger SC, Karalis KP, Jeong K-H, Majzoub JA (2001) The physiology of corticotropin-releasing hormone deficiency in mice. Peptides 22:725–731
Neumann ID, Wigger A, Torner L, Holsboer F, Landgraf R (2000) Brain oxytocin inhibits basal and stress-induced activity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in male and female rats: partial action within the paraventricular nucleus. J Neuroendocrinol 12:235–243
Paxinos G, Watson C (2006) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Elsevier
Pich EM, Heinrichs SC, Rivier C, Miczek KA, Fisher DA, Koob GF (1993) Blockade of pituitary-adrenal axis activation induced by peripheral immunoneutralization of corticotropin-releasing factor does not affect the behavioral response to social defeat stress in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 18:495–507
Preti A, de Girolamo G, Vilagut G, Alonso J, de Graaf R, Bruffaerts R, Demyttenaere K, Pinto-Meza A, Haro JM, Morosini P (2009) The epidemiology of eating disorders in six European countries: results of the ESEMeD-WMH project. J Psychiatr Res 43:1125–1132
Pucci M, Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Giusepponi ME, Romano A, Filaferro M, Maccarrone M, Ciccocioppo R, Cifani C, D'Addario C (2016) Epigenetic regulation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ and corticotropin-releasing factor system genes in frustration stress-induced binge-like palatable food consumption. Addict Biol 21:1168-1185
Rodgers R, Dalvi A (1997) Anxiety, defence and the elevated plus-maze. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:801–810
Ryan PJ, Büchler E, Shabanpoor F, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Lawrence AJ, Gundlach AL (2013a) Central relaxin-3 receptor (RXFP3) activation decreases anxiety-and depressive-like behaviours in the rat. Behav Brain Res 244:142–151
Ryan PJ, Kastman HE, Krstew EV, Rosengren KJ, Hossain MA, Churilov L, Wade JD, Gundlach AL, Lawrence AJ (2013b) Relaxin-3/RXFP3 system regulates alcohol-seeking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:20789–20794
Ryan PJ, Krstew EV, Sarwar M, Gundlach AL, Lawrence AJ (2014) Relaxin-3 mRNA levels in nucleus incertus correlate with alcohol and sucrose intake in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 140:8–16
Saper CB, Chou TC, Elmquist JK (2002) The need to feed: homeostatic and hedonic control of eating. Neuron 36:199–211
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404:661–671
Shabanpoor F, Hossain MA, Ryan PJ, Belgi A, Layfield S, Kocan M, Zhang S, Samuel CS, Gundlach AL, Bathgate RAD, Separovic F, Wade JD (2012) Minimization of human relaxin-3 leading to high-affinity analogues with increased selectivity for relaxin-family peptide 3 receptor (RXFP3) over RXFP1. J Med Chem 55:1671–1681
Smagin GN, Howell LA, Redmann S, Ryan DH, Harris RB (1999) Prevention of stress-induced weight loss by third ventricle CRF receptor antagonist. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 276:R1461–R1468
Smith CM, Shen PJ, Banerjee A, Bonaventure P, Ma S, Bathgate RAD, Sutton SW, Gundlach AL (2010) Distribution of relaxin-3 and RXFP3 within arousal, stress, affective, and cognitive circuits of mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 518:4016–4045
Smith CM, Chua BE, Zhang C, Walker AW, Haidar M, Hawkes D, Shabanpoor F, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Rosengren KJ, Gundlach AL (2014) Central injection of relaxin-3 receptor (RXFP3) antagonist peptides reduces motivated food seeking and consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res 268:117–126
Stuber GD, Wise RA (2016) Lateral hypothalamic circuits for feeding and reward. Nat Neurosci 19:198–205
Sutton SW, Bonaventure P, Kuei C, Roland B, Chen J, Nepomuceno D, Lovenberg TW, Liu C (2004) Distribution of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) 135 binding sites and receptor mRNA in the rat brain suggests a role for relaxin-3 in neuroendocrine and sensory processing. Neuroendocrinology 80:298–307
Sutton SW, Shelton J, Smith C, Williams J, Yun S, Motley T, Kuei C, Bonaventure P, Gundlach A, Liu C (2009) Metabolic and neuroendocrine responses to RXFP3 modulation in the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1160:242–249
Tanaka M (2010) Relaxin-3/insulin-like peptide 7, a neuropeptide involved in the stress response and food intake. FEBS J 277:4990–4997
Tanaka M, Iijima N, Miyamoto Y, Fukusumi S, Itoh Y, Ozawa H, Ibata Y (2005) Neurons expressing relaxin 3/INSL 7 in the nucleus incertus respond to stress. Eur J Neurosci 21:1659–1670
Timofeeva E, Calvez J (2014) Neuronal substrates of eating disorders. Brain Disord Ther 3:121–128
Walker DL, Toufexis DJ, Davis M (2003) Role of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis versus the amygdala in fear, stress, and anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 463:199–216
Watanabe Y, Miyamoto Y, Matsuda T, Tanaka M (2011) Relaxin-3/INSL7 regulates the stress-response system in the rat hypothalamus. J Mol Neurosci 43:169–174
Wilkinson TN, Speed TP, Tregear GW, Bathgate RAD (2005) Evolution of the relaxin-like peptide family. BMC Evol Biol 5:14
Zellner DA, Loaiza S, Gonzalez Z, Pita J, Morales J, Pecora D, Wolf A (2006) Food selection changes under stress. Physiol Behav 87:789–793
Zhang C, Chua BE, Yang A, Shabanpoor F, Hossain MA, Wade JD, Rosengren KJ, Smith CM, Gundlach AL (2015) Central relaxin-3 receptor (RXFP3) activation reduces elevated, but not basal, anxiety-like behaviour in C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res 292:125–132
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof Ross Bathgate and Dr Gabrielle Callander (The Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health) for providing the AAV(1/2)-EmGFP miR499 and AAV(1/2)- EmGFP miRC used in these studies.
Funding
This research was supported by NHMRC (Australia) project grant 1067522 (ALG), a NARSAD Independent Investigator Award (ALG), and a grant from the Dorothy Levien Foundation (ALG). CDÁ was supported by scholarships from the Centre thématique de recherche en neurosciences and Fonds de recherche du Québec - Santé, and by a Commonwealth Government (Australia) Endeavour Research Fellowship. We also acknowledge financial support from the Victorian State Government Infrastructure Program to The Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Experiments described were conducted with the approval of The Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health Animal Ethics Committee and according to ethical guidelines issued by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article is dedicated to Elena Timofeeva (deceased 28/09/2017), a fine scientist, colleague, supervisor and mentor
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Ávila, C., Chometton, S., Ma, S. et al. Effects of chronic silencing of relaxin-3 production in nucleus incertus neurons on food intake, body weight, anxiety-like behaviour and limbic brain activity in female rats. Psychopharmacology 237, 1091–1106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05439-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05439-1