Abstract
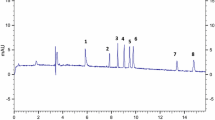
A method based on capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection (CE–ED) has been developed for the determination of hesperidin (HP) and synephrine (SP) in the Chinese traditional herbal drug, Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae, the dried rind of the ripe fruits of Citrus reticulata Blanco (mandarin orange). The effects of some important factors such as the acidity and concentration of running buffer, separation voltage, and detection potential were investigated to determine the optimum conditions. The working electrode was a 300 µm diameter carbon disc electrode positioned opposite the outlet of the capillary. Both analytes could be well separated within 5 min in a 40 cm long capillary at a separation voltage of 12 kV in 50 mmol L–1 borate buffer (pH 9.0). Excellent linearity was observed for the dependence of peak current on analyte concentration in the range from 2.5×10–6 to 1.0×10–3 mol L–1 for SP and from 5.0×10–6 to 1.0×10–3 mol L–1 for HP. The detection limits (S/N=3) for SP and HP were 4.96×10–7 mol L–1 and 6.54×10–7 mol L–1, respectively. This method has been successfully applied for the analysis of real samples, with satisfactory results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Zhang, L., Zhao, J. et al. Determination of hesperidin and synephrine in Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 373, 169–173 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1300-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1300-4