Abstract
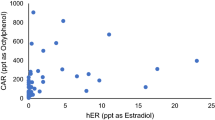
Synthetic polymers which can adsorb bisphenol A (BPA) and related compounds were prepared by a covalent molecular imprinting technique. BPA dimethacrylate, used as template molecule, was polymerized with a crosslinker, triethylene glycol dimethacrylate (TEGDMA) or trimethylol propane trimethacrylate (TRIM). After the polymerization treatment with dilute NaOH was used to cleave BPA from the polymers. For high recovery of BPA with low polymer matrix degradation, the hydrolysis conditions were determined to be treatment with 1.0 mol L−1 NaOH for 48 h. The binding sites generated by the hydrolysis were evaluated by determination of the retentivity of BPA, BPA analogues, and other endocrine disruptors. The polymers strongly adsorbed compounds with two hydroxyl groups at the 4,4′-positions. Generally the TEGDMA-based polymers had stronger affinity than the TRIM-based polymers, although the TRIM-based polymer adsorbed steroidal hormones with two hydroxyl groups, for example 17α-estradiol and 17β-estradiol, more strongly than the TEGDMA-based polymer, meaning that the crosslinkers affected the properties of the binding sites and, depending upon the target molecules, suitable crosslinkers should be chosen in this system.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Markey CM, Michaelson CL, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (2001) In: Manfred M (ed) The handbook of environmental chemistry, endocrine disruptors, part 1, alkylphenols and bisphenol A as environmental estrogens. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York 129–153
Komiyama M, Takeuchi T, Mukawa T, Asanuma H (2002) Molecular Imprinting. Wiley–VCH, Weinheim
Sellergren B (2001) (ed) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bartsch RA, Maeda M (1998) (eds) Molecular and ionic recognition with imprinted polymers, ACS Symp Ser 703. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Wulff G (1995) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 34:1812–1832
Takeuchi T, Haginaka J (1999) J Chromatogr B 728:1–20
Haupt K, Mosbach K (2000) Chem Rev 100:2495–2504
Tarbin JAM, Sharman M (1999) Anal Commun 36:105–107
Kanekiyo Y, Naganawa R, Tao H (2002) Chem Commun 2698–2699
Kubo T, Hosoya K, Watabe Y, Ikegami T, Tanaka N, Sano T, Kaya K (2003) J Chromatogr A 987:389–394
Sanbe H, Haginaka J (2003) J Pharm Biomed Anal 30:1835–1844
Umpleby II RJ, Bode M, Shimizu KD (2000) Analyst 125:1261–1265
Joshi VP, Karmalkar RN, Kulkarni MG, Mashelkar RA (1999) Ind Eng Chem Res 38:4417–4423
Ikegami T, Mukawa T, Nariai H, Takeuchi T (2004) Anal Chim Acta 504:131–135
Wulff G, Vietmeier J, Poll HG (1987) Makromol Chem 188:731–740
Ikegami T, Lee W-S, Nariai H, Takeuchi T (2004) J Chromatogr B, in press
Acknowledgments
This work has supported by Japan Society for the promotion of Science and Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikegami, T., Lee, WS., Nariai, H. et al. Synthetic polymers adsorbing bisphenol A and its analogues prepared by covalent molecular imprinting using bisphenol A dimethacrylate as a template molecule. Anal Bioanal Chem 378, 1898–1902 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2490-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-004-2490-8