Abstract
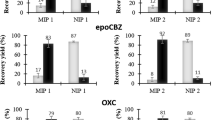
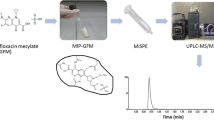
A novel water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP), prepared with enrofloxacin (ENR) as the template, has been optimised for the selective extraction of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in aqueous media. The results of a morphological characterisation and selectivity tests of the polymer material for ENR and related derivatives are reported. High affinity for the piperazine-based fluoroquinolones marbofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin was observed, whereas no retention was found for nonrelated antibiotics. Various parameters affecting the extraction efficiency of the polymer have been optimised to achieve selective extraction of the antibiotics from real samples and to reduce nonspecific interactions. These findings resulted in a MISPE/HPLC-FLD method allowing direct extraction of the analytes from aqueous samples with a selective wash using just 50% (v/v) organic solvent. The method showed excellent recoveries and precision when buffered urine samples fortified at five concentration levels (25–250 ng mL−1 each) of marbofloxacin, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, enrofloxacin and sarafloxacin were tested (53–88%, RSD 1–10%, n = 3). Moreover, the biological matrix of the aqueous samples did not influence the preconcentration efficiency of the fluoroquinolones on the MIP cartridges; no significant differences were observed between the recovery rates of the antibiotics in buffer and urine samples. The detection limits of the whole process range between 1.9 and 34 ng mL–1 when 5-mL urine samples are processed. The developed method has been successfully applied to preconcentration of norfloxacin in urine samples of a medicated patient, demonstrating the ability of the novel MIP for selective extraction of fluoroquinolones in urine samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIP:
-
molecularly imprinted polymer
- NIP:
-
nonimprinted polymer
- MAA:
-
methacrylic acid
- HEMA:
-
2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate
- EDMA:
-
ethylene glycol dimethacrylate
- ABDV:
-
2,2′-azobis(2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile)
- FQs:
-
fluoroquinolones
- ENR:
-
enrofloxacin
- MAR:
-
marbofloxacin
- SAR:
-
sarafloxacin
- CIP:
-
ciprofloxacin
- NOR:
-
norfloxacin
- OFL:
-
ofloxacin
- AMX:
-
amoxicillin
- PEG:
-
penicillin G
- CLX:
-
cloxacillin
- CEP:
-
cephapirin
- DAP:
-
dapsone
- BZ:
-
benzoic acid
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- FLD:
-
fluorescence detector
- DAD:
-
diode array detector
- LLE:
-
liquid–liquid extraction
- SFE:
-
supercritical fluid extraction
- PLE:
-
pressurised liquid extraction
- SPE:
-
solid-phase extraction
- MISPE:
-
molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction
- MI-MSPD:
-
molecularly imprinted matrix solid-phase dispersion
References
Debska J, Kot-Wasik A, Namiesnik J (2004) Crit Rev Anal Chem 67:34–51
Sanderson H, Johnson DJ, Rietsma T, Brain RA, Wilson CJ, Solomon KR (2004) Regul Toxicol Pharm 39:158–183
Commission of the European Communities (2000) The white paper on food safety. European Commission, Brussels. http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/health_consumer/library/pub/pub06_en.pdf. Accessed 29 Jun 2008
Botsoglou NA, Fletouris DJ (2000) Drug residues in foods: pharmacology, food safety and analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York
Marazuela MD, Moreno-Bondi MC (2004) J Chromatogr A 1034:25–32
Herranz S, Marazuela MD, Moreno-Bondi MC (2007) J Chromatogr A 1140:63–70
Cañada-Cañada F, Espinosa-Mansilla A, Muñoz de la Peña A (2007) J Sep Sci 30:1242–1249
Pena A, Chmielova D, Lino CM, Solich P (2007) J Sep Sci 30:2924–2928
Lolo M, Pedreira S, Fente C, Vázquez BI, Franco CM, Cepeda A (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:2849–52
Gratacós-Cubarsí M, García-Regueiro JA, Castellari M (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1991–1998
Turiel E, Bordin G, Rodríguez AR (2005) J Sep Sci 28:257–267
San Martín B, Cornejo J, Iragüen D, Hidalgo H, Anadón A (2007) J Food Prot 70:1952–1957
Morales-Muñoz S, Luque-García JL, de Castro L (2004) J Chromatogr A 1059:25–31
Schulte S, Ackermann T, Bertram N, Sauerbruch T, Paar WD (2006) J Chromatogr Sci 44:205–208
Siewert S (2006) J Pharm Biomed Anal 41:1360–1362
Shim JH, Shen JY, Kim MR, Lee CJ, Kim IS (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:7528–7532
Garcés A, Zerzanová A, Kucera R, Barrón D, Barbosa J (2006) J Chromatogr A 1137:22–29
Sellergren B (2001) Molecularly imprinted polymers. Man made mimics of antibodies and their applications in analytical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Piletsky S, Turner A (2006) Molecular imprinting of polymers. Landes Bioscience, Texas
Yan M, Ramström O (2005) Molecularly imprinted materials: science and technology. Marcel Dekker, New York
Caro E, Marcé Rosa M, Cormack Peter AG, Sherrington DC, Borrul F (2006) Anal Chim Acta 562:145–151
Urraca JL, Moreno-Bondi MC, Hall AJ, Sellergren B (2007) Anal Chem 79:695–701
Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A, Tadeo JL (2007) J Chromatogr A 1172:97–104
Guzmán-Vázquez de Prada A, Martínez-Ruiz P, Reviejo AJ, Pingarrón JM (2006) Anal Chim Acta 562:145–151
Yan H, Qiao F, Row KH (2007) Anal Chem 79:8242–8248
Xu Z, Kuang D, Liu L, Deng Q (2007) J Pharm Biomed Anal 45:54–61
Yan H, Row KH, Yang G (2008) Talanta 75:227–232
Benito-Peña E, Partal-Rodera AI, León-González ME, Moreno-Bondi MC (2006) Anal Chim Acta 556:415–422
Kim H, Kaczmarski K, Guiochon G (2005) Chem Eng Sci 60:5425–5444
Oral E, Peppas NA (2001) Polym Prepr 42:111–112
Dirion B, Cobb Z, Schillinger E, Andersson LI, Sellergren B (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:15101–15109
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Ding S, He F, Beier RC, Li J, Jiang H, Feng C, Wan Y, Zhang S, Kai Z, Yang X, Shen J (2007) Anal Chem 79:4471–4483
O´Mahony J, Molinelli A, Nolan K, Smyth MR, Mizaikoff B (2006) Biosensors Bioelec 21:1383–1392
García Calzón JA, Díaz García ME (2007) Sens Actuators B 123:1180–1194
Rampey AM, Umpleby RJ, Rushton GT, Iseman JC, Shah RN, Shimizu KD (2004) Anal Chem 76:1123–1133
Caro E, Marcé RM, Cormack PAG, Sherrington DC, Borrull F (2006) J Sep Sci 29:1230–1236
Acknowledgements
This work has been funded by the European Marie Curie Programme (MRTN-CT-2006–033873), the Spanish MEC (grant CTQ2006–15610-C02), the Madrid Regional Government (ref. S-0505/AMB/0374), the ESF, the ERDF and UCM (CCG07-UCM/AMB-2932). The authors thank Prof. M.J. Torralvo for the N2 adsorption studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benito-Peña, E., Martins, S., Orellana, G. et al. Water-compatible molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective recognition of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in biological samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 393, 235–245 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2405-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2405-1