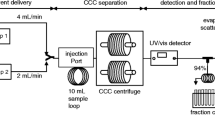
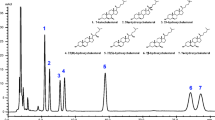
Abstract
Phytosterols are bioactive compounds which occur in low concentrations in plant oils. Due to their beneficial effects on human health, phytosterols have already been supplemented to food. Commercial phytosterol standards show insufficient purity and/or are very expensive. In this study, we developed a high-speed counter-current chromatography (HSCCC) method for the fractionation and analysis of a commercial crude β-sitosterol standard (purity ∼60% according to supplier). Different solvent systems were tested in shake-flask experiments, and the system n-hexane/methanol/aqueous silver nitrate solution (34/24/1, v/v/v) was finally used for HSCCC fractionation. About 50 mg phytosterols was injected and distributed into 57 fractions. Selected fractions were condensed and re-injected into the HSCCC system. This measure provided pure sitostanol (>99%) and β-sitosterol (∼99%), as well as a mixture of campesterol and stigmasterol without further phytosterols. An enriched HSCCC fraction facilitated the mass spectrometric analysis of further 11 minor phytosterols (after trimethylsilylation). It was also shown that the commercial product contained about 0.3% carotinoids which eluted without delay into an early HSCCC fraction and which were separated from the phytosterols.

Separation of a phytosterol mixture by means of counter-current chromatography provided pure phytosterols






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lagarda MJ, Llatas GG, Farré R (2006) Analysis of phytosterols in foods. J Pharma Biomed Anal 41:1486–1496
Kritchevsky D, Shirley CC (2005) Phytosterols—health benefits and potential concerns: a review. Nutr Res 25:413–428
Nguyen TT (1999) The cholesterol-lowering action of plant stanol esters. J Nutr 129:2109–2112
Fiebig HJ, Bruehl L, Aitzetmueller K (1998) Sterine—Isolierung und gaschromatographische Untersuchung. Lipid / Fett 100:422–428
Fernandes P, Cabral JMS (2007) Phytosterols: applications and recovery methods. Biores Technol 98:2335–2350
Zhou Y, Chen F, Zongcheng L (2002) Preparative separation of β-sitosterol by high speed countercurrent chromatography. J Liq Chrom Relat Technol 25:1693–1701
Ito Y (2005) Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1065:145–168
Ito Y, Bowman RL (1970) Countercurrent chromatography: liquid-liquid partition chromatography without solid support. Science 167:281–283
Du Q, Shu A, Ito Y (1996) Purification of fish oil ethyl esters by high-speed countercurrent chromatography using non-aqueous solvent systems. J Liq Chrom Relat Technol 19:1451–1457
Bousquet O, Goffic FL (1995) Counter-current chromatographic separation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Chromatogr A 704:211–216
Montilla EC, Hillebrand S, Butschbach D, Baldermann S, Watanabe N, Winterhalter P (2010) Preparative isolation of anthocyanins from Japanese purple sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) varieties by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 58:9899–9904
Du Q, Jerz G, Winterhalter P (2004) Isolation of two anthocyanin sambudiosides from bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1045:59–63
Jerz G, Skotzki T, Fiege K, Winterhalter P, Wybraniec S (2008) Separation of betalains from berries of Phytolacca Americana by ion-pair high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1190:63–73
Koehler N, Wray V, Winterhalter P (2008) Preparative isolation of procyanidins from grape seed extracts by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1177:114–125
Degenhardt A, Engelhardt UH, Lakenbrink C, Winterhalter P (2000) Preparative separation of polyphenols from tea by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 48:3425–3430
Kapp T, Vetter W (2009) Offline coupling of high-speed counter-current chromatography and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry generates a two-dimensional plot of toxaphene components. J Chromatogr A 1216:8391–8397
Cunha SS, Fernandes JO, Oliveira MB (2006) Quantification of free and esterified sterols in Portuguese olive oils by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1128:220–227
Dobson G, Christie WW, Nikolova-Damyanova B (1995) Silver ion chromatography of lipids and fatty acids. J Chromatogr B 671:197–222
Hoving EB, Muskiet FAJ, Christie WW (1991) Separation of cholesterol esters by silver ion chromatography using high-performance liquid chromatography or solid-phase extraction columns packed with a bonded sulphonic acid phase. J Chromatogr 565:103–110
Knights BA, Laurie W (1967) Application of combined gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry to the identification of sterols in oat seed. Phytochem 6:407–416
Pizzoferrato L, Nicoli S, Lintas C (1993) GC-MS characterization and quantification of sterols and cholesterol oxidation products. Chromatographia 35:269–274
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, M., Vetter, W. High-speed counter-current chromatographic separation of phytosterols. Anal Bioanal Chem 400, 3615–3623 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4995-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4995-2