Abstract
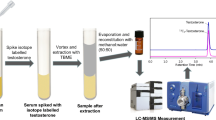
A rapid liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method has been developed and validated for the determination of α-trenbolone, β-trenbolone, α-nortestosterone, β-nortestosterone, zeranol, and taleranol in bovine liver. The impact of liquid–liquid extraction with methyl tert-butyl ether and optimized solid phase extraction on silica cartridges significantly reduced effort and time of sample preparation. Electrospray ionization gives a significant signal increase compared with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and atmospheric pressure photoionization. The HPLC gradient was optimized to separate isobaric analytes and matrix constituents from the hormone molecules. The optimized time and temperature of enzymatic hydrolysis of conjugated trenbolone was 4 h at 52 °C. The method validated in the range of 0.5–30 μg kg–1 for α-trenbolone, β-trenbolone, zeranol, taleranol, and 2–30 μg kg–1 for α-nortestosterone, β-nortestosterone. Combined uncertainty of measurements was in the range of 4 %–23 %. The matrix effect was negligible (1 %–5 %) for all analytes except of α-nortestosterone (19 %). The developed method with changes concerning sample size and hydrolysis was also applied for the analysis of meat, serum, and urine samples.

Determination of trenbolone, nortestosterone and zeranol in bovine liver




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Courtheyn D, Le Bizec B, Brambilla G, De Brabander HF, Cobbaert E, Van de Wiele M, Vercammen J, De Wasch K (2002) Recent developments in the use and abuse of growth promoters. Anal Chim Acta 473(1/2):71–82. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00753-5
Stephany R (2010) Hormonal growth promoting agents in food producing animals (pp. 355–367) Hormonal Growth Promoting Agents in Food Producing Animals. In: Thieme D, Hemmersbach P (Eds) Doping in sports: Biochemical principles, effects, and analysis, vol 195. Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-79088-4_16
Commission of the European Communities, Council Directive 96/22/EC (1996)
The Federal Assembly of Russia, Federal Law No. 29-FZ (2000)
Metzler M (1989) Metabolism of some anabolic agents: toxicological and analytical aspects. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 489(1):11–21. doi:10.1016/S0378-4347(00)82880-7
McEvoy JDG, McVeigh CE, Currie JW, Kennedy DG, McCaughey WJ (1998) Plasma, urinary and biliary residues in cattle following intramuscular injection of nortestosterone laurate. Vet Res Commun 22(7):479–491. doi:10.1023/a:1006179116231
Lone KP, van Ginkel LA (1997) Natural sex steroids and their xenobiotic analogs in animal production: growth, carcass quality, pharmacokinetics, metabolism, mode of action, residues, methods, and epidemiology. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 37(2):93–209. doi:10.1080/10408399709527771
Kaklamanos G, Theodoridis G, Dabalis T (2009) Determination of anabolic steroids in muscle tissue by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216(46):8072–8079. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.04.051
Noppe H, Le Bizec B, Verheyden K, De Brabander HF (2008) Novel analytical methods for the determination of steroid hormones in edible matrices. Anal Chim Acta 611(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.01.066
A Multi-Residue Method Using GC-MS for Determining Residues of Anabolic Agents in Animal Tissues (1994) In: Heitzman RJ (ed) Veterinary drug residues: residues in food producing animals and their products: Reference Materials and Methods; published on behalf of Commission of the European Communities by Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, pp. Cy1.2/1–Cy1.2/9
A modular method for the analysis of biological materials for residues of anabolic agents (steroid-like growth promoters) (1994) In: Heitzman RJ (ed) Veterinary drug residues: residues in food producing animals and their products: Reference Materials and Methods; Published on behalf of Commission of the European Communities by Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, pp. Cy1.1/1–Cy1.1/16
Horie M, Nakazawa H (2000) Determination of trenbolone and zeranol in bovine muscle and liver by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 882(1/2):53–62. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00205-3
Shao B, Zhao R, Meng J, Xue Y, Wu G, Hu J, Tu X (2005) Simultaneous determination of residual hormonal chemicals in meat, kidney, liver tissues, and milk by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 548(1/2):41–50. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2005.06.003
Yang Y, Shao B, Zhang J, Wu Y, Duan H (2009) Determination of the residues of 50 anabolic hormones in muscle, milk and liver by very high pressure liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 877(5/6):489–496. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.12.054
Wang H, Wang Z, Shao B, Liu Z, Liu S (2009) Determination of trenbolone residual in bovine liver by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82(4):415–418. doi:10.1007/s00128-008-9589-0
Commission Decision (EC) No. 2002/657/EC of 12 August 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results (2002) Off J Eur Communities L 221:8
Smeraglia J, Baldrey SF, Watson D (2002) Matrix effects and selectivity issues in LC-MS-MS. Chromatographia 55(1):S95–S99. doi:10.1007/bf02493363
Xu CL, Chu XG, Peng CF, Jin ZY, Wang LY (2006) Development of a faster determination of 10 anabolic steroids residues in animal muscle tissues by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 41(2):616–621. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.11.033
Kaklamanos G, Theodoridis G, Dabalis T (2009) Determination of anabolic steroids in bovine urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 877(23):2330–2336. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2009.03.033
Kaklamanos G, Theodoridis GA, Dabalis T, Papadoyannis I (2011) Determination of anabolic steroids in bovine serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879(2):225–229. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2010.11.029
MacNeil JD, Reid J, Fedeniuk RW (2008) Distribution of trenbolone residues in liver and various muscle groups of heifers that received multiple implants at the recommended site of application. J AOAC Int 91(3):670–674
Schmidt KS, Stachel CS, Gowik P (2009) In-house validation and factorial effect analysis of a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of steroids in bovine muscle. Anal Chim Acta 637(1/2):156–164. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.09.043
Vanhaecke L, Bussche JV, Wille K, Bekaert K, De Brabander HF (2011) Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in high-throughput confirmation and quantification of 34 anabolic steroids in bovine muscle. Anal Chim Acta 700(1/2):70–77. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2010.10.006
Guo T, Taylor RL, Singh RJ, Soldin SJ (2006) Simultaneous determination of 12 steroids by isotope dilution liquid chromatography-photospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta 372(1/2):76–82. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2006.03.034
Soldin SJ, Soldin OP (2009) Steroid hormone analysis by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 55(6):1061–1066. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2007.100008clinchem.2007.100008
EUROLAB Technical Report No. 1/2006: Guide to the Evaluation of Measurement Uncertainty for Quantitative Test Results (2006) EUROLAB
Ellison SLR, Williams A (eds) Eurachem/CITAC guide: quantifying uncertainty in analytical measurement, 3rd edition (2012) ISBN 978-0-948926-30-3 Available at: www.eurachem.org. Accessed Dec 2013
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ksenia Y. Osipova for technical contribution to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection on Hormone and Veterinary Drug Residue Analysis with guest editors Siska Croubels, Els Daeseleire, Sarah De Saeger, Peter Van Eenoo, and Lynn Vanhaecke.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yunin, M.A., Metalnikov, P.S., Komarov, A.A. et al. Development of a rapid method for the analysis of trenbolone, nortestosterone, and zeranol in bovine liver using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 4363–4371 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8346-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8346-y