Abstract
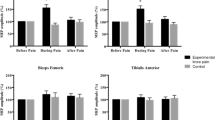
Musculoskeletal pains are often characterised by referred pain and hyperalgesia. The aim of the present study was to examine the sensitivity to pressure and pinprick at sites ipsi- and contralateral to capsaicin-induced pain in the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle. Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores of the sensation to sub- and supra-pain threshold stimuli by pressure and pinprick were recorded before, during and after experimental muscle pain. It was found that pressure stimulation (120% of baseline pain threshold) delivered over the ipsilateral deep peroneal nerve between the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones showed a significant increase in VAS scores during muscle pain. The referred pain did not overlap this hyperalgesic site. Ipsilateral test sites at the TA muscle, great toe and between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal bones did not show any changes in response to pressure stimulation during pain. In contrast, test sites at the ipsilateral ankle showed hypoalgesia to pressure during muscle pain. In the contralateral leg hypoalgesia to pressure was found at all sites during pain. The decreased sensitivity to pressure was confirmed with both sub- and supra-pressure pain-threshold stimuli. VAS scores to pinprick were either decreased or unchanged during pain compared to before pain. Naloxone administrated in a placebo-controlled manner had no effect on hypoalgesia to pressure or pinprick during muscle pain. Thus, the generalised decreased sensitivity may reflect activation of non-opioid endogenous pain inhibitory systems. The lack of change in sensitivity at some sites could indicate a competitive balance between excitatory and inhibitory mechanisms. The deep peroneal nerve specifically innervates both the TA muscle and the only site of hyperalgesia indicating spatial summation of afferent activity from these structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by The Danish National Research Foundation
Meda A/S, Søborg, Denmark kindly donated Narcanti® to the present study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graven-Nielsen, T., Gibson, S.J., Laursen, R.J. et al. Opioid-insensitive hypoalgesia to mechanical stimuli at sites ipsilateral and contralateral to experimental muscle pain in human volunteers. Exp Brain Res 146, 213–222 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1169-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1169-7