Abstract
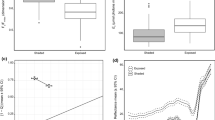
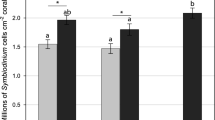
Corals harbouring genetically mixed communities of endosymbiotic algae (Symbiodinium) often show distribution patterns in accordance with differences in light climate across an individual colony. However, the physiology of these genetically characterised communities is not well understood. Single stranded conformation polymorphism (SSCP) and real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) analyses were used to examine the genetic diversity of the Symbiodinium community in hospite across an individual colony of Acropora valida at the spatial scale of single polyps. The physiological characteristics of the polyps were examined prior to sampling with a combined O2 microelectrode with a fibre-optic microprobe (combined sensor diameter 50–100 μm) enabling simultaneous measurements of O2 concentration, gross photosynthesis rate and photosystem II (PSII) quantum yield at the coral surface as a function of increasing irradiances. Both sun- and shade-adapted polyps were found to harbour either Symbiodinium clade C types alone or clades A and C simultaneously. Polyps were grouped in two categories according to (1) their orientation towardps light, or (2) their symbiont community composition. Physiological differences were not detected between sun- and shade-adapted polyps, but O2 concentration at 1,100 μmol photons m−2 s−1 was higher in polyps that harboured both clades A and C symbionts than in polyps that harboured clade C only. These results suggest that the acclimatisation of zooxanthellae of individual polyps of an A. valida colony to ambient light levels may not be the only determinant of the photosynthetic capacity of zooxanthellae. Here, we found that photosynthetic capacity is also likely to have a strong genetic basis and differs between genetically distinct Symbiodinium types.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker AC (2001) Reef corals bleach to survive change. Nature 411:765–766
Baker AC (2003) Flexibility and specificity in coral-algal symbiosis: diversity, ecology, and biogeography of Symbiodinium. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34:661–689
Berkelmans R (2002) Time-integrated thermal bleaching thresholds of reefs and their variation on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 229:73–82
Berkelmans R, van Oppen MJH (2006) The role of zooxanthellae in the thermal tolerance of corals: a ‘nugget of hope’ for coral reefs in an era of climate change. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 273:2305–2312
Bhagooli R, Hidaka M (2003) Comparison of stress susceptibility of in hospite and isolated zooxanthellae among five coral species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 291:181–197
Chang SS, Prezelin BB, Trench RK (1983) Mechanisms of photoadaption in three strains of the symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium microadriaticum. Mar Biol 76:219–229
Coffroth MA, Santos SR (2005) Genetic diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium. Protist 156:19–34
De Beer D, Kühl M, Stambler N, Vaki L (2000) A microsensor study of light enhanced Ca2+ uptake and photo-synthesis in the reef-building coral Favia sp. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 194:75–85
Enriquez S, Mendez ER, Iglesias-Prieto R (2005) Multiple scattering on coral skeletons enhances light absorption by symbiotic algae. Limnol Oceanogr 50:1025–1032
Fabricius KE, Mieog JC, Colin PL, Idip D, van Oppen MJH (2004) Identity and diversity of coral endosymbionts (zooxanthellae) from three Palauan reefs with contrasting bleaching, temperature and shading histories. Mol Ecol 13:2445–2458
Falkowski PG, Dubinsky Z (1981) Light-shade adaptation of Stylophora pistillata, a hermatypic coral from the Gulf of Eilat. Nature 289:172–174
Franklin LA, Badger MR (2001) A comparison of photosynthetic electron transport rates in macroalgae measured by pulse amplitude modulated chlorophyll fluorometry and mass spectrometry. J Phycol 37:756–767
Gates RD, Bil KY, Muscatine L (1999) The influence of an anthozoan ‘host factor’ on the physiology of a symbiotic dinoflagellate. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 232:241–259
Gates RD, Hoegh-Guldberg O, McFall-Ngai MJ, Bil K, Muscatine L (1995) Free amino acids exhibit anthozoan ‘host factor’ activity: they induce the release of photosynthates from symbiotic dinoflagellates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7434
Gladfelter EH, Michel G, Sanfelici A (1989) Metabolic gradients along a branch of the reef coral Acropora palmata. Bull Mar Sci 44:1166–1173
Glynn PW, Mate JL, Baker AC (2001) Coral bleaching and mortality in Panama and Equador during the 1997–1998 El Nino-Southern Oscillation event: Spatial/temporal patterns and comparisons with the 1982–1983 event. Bull Mar Sci 69:79–109
Gorbunov MY, Koler ZS, Lesser MP, Falkowski PG (2001) Photosynthesis and photoprotection in symbiotic corals. Limnol Oceanogr 46:75–85
Goulet TL (2006) Most corals may not change their symbionts. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 321:1–7
Grant AJ, Remond M, People J, Hinde R (1997) Effects of host-tissue homogenate of the scleractinian coral Plesiastrea versipora on glycerol metabolism in isolated symbiotic dinoflagellates. Mar Biol 128:665–670
Hill R, Schreiber U, Gademann R, Larkum AWD, Kühl M, Ralph PJ (2004) Spatial heterogeneity of photosynthesis and the effect of temperature-induced bleaching conditions in three species of coral. Mar Biol 144:633–640
Iglesias-Prieto R, Trench RK (1994) Acclimation and adaptation to irradiance in symbiotic dinoflagellates. I. Responses of the photosynthetic unit to changes in photon flux density. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 113:163–175
Iglesias-Prieto R, Beltran VH, LaJeunesse TC, Reyes-Bonilla H, Thomé PE (2004) Different algal symbionts explain the vertical distribution of dominant reef corals in the eastern Pacific. Proc R Soc Lond B 271:1757–1763
Jones RJ, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Larkum AWD, Schreiber U (1998) Temperature-induced bleaching of corals begins with impairment of the CO2 mechanism in zooxanthellae. Plant Cell Environ 21:1219–1230
Kühl M (2005) Optical microsensors for analysis of microbial communities. Meth Enzymol 397:166–199
Kühl M, Cohen Y, Dalsgaard T, Jørgensen BB, Revsbech NP (1995) Microenvironment and photosynthesis of zooxanthellae in scleractinian corals studies with microsensors for O2, pH and light. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 117:159–172
Kühl M, Glud RN, Borum J, Roberts R, Rysgaard S (2001) Photosynthetic performance of surface associated algae below sea ice as measured with a pulse amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorometer and O2 microsensors. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 223:1–14
LaJeunesse TC (2001) Investigating the biodiversity, ecology, and phylogeny of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates in the genus Symbiodinium using the ITS region: in search of a ‘species’ level marker. J Phycol 377:886–880
LaJeunesse TC, Loh WKW, van Woesik R (2003) Low symbiont diversity in southern Great Barrier Reef corals, relative to those of the Caribbean. Limnol Oceanogr 48:2046–2054
Lavaud J, van Gorkom H, Etienne A (2002) Photosystem II electron transfer cycle and chlororespiration in planktonic diatoms. Photosynth Res 74:51–59
Little AF, van Oppen MJH, Willis BL (2004) Flexibility in algal endosymbioses shapes growth in reef corals. Science 304:1492–1494
Longstaff BJ, Kildea T, Runcie JW, Cheshire A, Dennison WC, Hurd C, Kana T, Raven JA, Larkum AWD (2002) An in situ study of photosynthetic oxygen exchange and electron transport rate in the marine macroalga Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta). Photosynth Res 74:281–293
Mieog JC, van Oppen MJH, Cantin NE, Stam WT, Olsen JL (2007) Real-time PCR reveals a high incidence of Symbiodinium clade D at low levels in four scleractinian corals across the Great Barrier Reef: implications for symbiont shuffling. Coral Reefs (DOI 10.1007/s00338–007-0244-8)
Muscatine L (1990) The role of symbiotic algae in carbon and energy flux in reef corals. In: Dubinsky Z (ed) Ecosystems of the World 25: coral reefs. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 75–87
Platt T, Gallegos CL, Harrison WG (1980) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38:687–701
Porter JW, Muscatine L, Dubinsky Z, Falkowski PG (1984) Primary production and photoadaptation in light and shade-adapted colonies of the symbiotic coral, Stylophora pistillata. Proc R Soc Lond B 222:161–180
Ralph PJ, Gademann R (2005) Rapid light curves: a powerful tool for the assessment of photosynthetic activity. Aquat Bot 82:222–237
Ralph PJ, Gademann R, Larkum AWD, Kühl M (2002) Spatial heterogeneity in active chlorophyll fluorescence and PSII activity of coral tissues. Mar Biol 141:639–646
Ralph PJ, Schreiber U, Gademann R, Kühl M, Larkum AWD (2005) Coral photobiology studied with a new imaging pulse amplitude modulated fluorometer. J Phycol 41:335–342
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB (1983) Photosynthesis of benthic microflora measured with high spatial resolution by the oxygen microprofile method: capabilities and limitations of the method. Limnol Oceanogr 28:749–756
Robison JD, Warner ME (2006) Differential impacts of photoacclimation and thermal stress on the photobiology of four different phylotypes of Symbiodinium (Pyrrhophyta). J Phycol 42:568–579
Rowan R, Knowlton N, Baker AC, Jara J (1997) Landscape ecology of algal symbionts creates variation in episodes of coral bleaching. Nature 388:265–269
Savage AM, Trapido-Rosenthal H, Douglas AE (2002) On the functional significant of molecular variation in Symbiodinium, the symbiotic algae of Cnidaria: photosynthetic responses to irradiance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 244:27–37
Schreiber U (2004) Pulse–amplitude–modulation (PAM) fluorometry and saturation pulse method: an overview. In: Papageorgiou GC, Govindjee (eds) Chlorophyll fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 279–319
Schreiber U, Kühl M, Klimant I, Reising H (1996) Measurement of chlorophyll fluorescence within leaves using a modified PAM fluorometer with a fiber-optic microprobe. Photosynth Res 47:103–109
Thornhill DJ, LaJeunesse TC, Kemp DW, Fitt WK, Schmidt DW (2006) Multi-year, seasonal genotypic surveys of coral–algal symbioses reveal prevalent stability or post-bleaching reversion. Mar Biol 148:711–722
Toller WW, Rowan R, Knowlton N (2001) Zooxanthellae of the Montastraea annularis species complex: patterns of distribution of four taxa of Symbiodinium on different reefs and across depths. Biol Bull 201:348–359
Ulstrup KE, van Oppen MJH (2003) Geographic and habitat partitioning of genetically distinct zooxanthellae (Symbiodinium) in Acropora corals on the Great Barrier Reef. Mol Ecol 12:3477–3484
Ulstrup KE, Berkelmans R, Ralph PJ, van Oppen MJH (2006a) Variation in bleaching sensitivity of two coral species across a latitudinal gradient on the Great Barrier Reef: the role of zooxanthellae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 314:135–148
Ulstrup KE, Ralph PJ, Larkum AWD, Kühl M (2006b) Intra-colonial variability in light acclimation of zooxanthellae in coral tissues of Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Biol 149:1325–1335
Ulstrup KE, Kühl M, Bourne D (2007) Zooxanthellae harvested by ciliates associated with brown band syndrome of corals remain photosynthetically competent. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1968–1975
van Oppen M, Palstra FP, Piquet AMT, Miller DJ (2001) Patterns of coral dinoflagellate associations in Acropora: significance of local availability and physiology of Symbiodinium strains and host–symbiont selectivity. Proc R Soc Lond B 268:1759–1767
van Oppen MJH, Mahiny AJ, Done TJ (2005) Geographic distribution of zooxanthella types in three coral species on the Great Barrier Reef sampled after the 2002 bleaching event. Coral Reefs 24:482–487
Visram S, Douglas AE (2006) Molecular diversity of symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) in scleractinian corals of Kenya. Coral Reefs 25:172–176
Warner ME, LaJeunesse TC, Robison JD, Thur RM (2006) The ecological distribution and comparative photobiology of symbiotic dinoflagellates from reef corals in Belize: potential implications for coral bleaching. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1887–1897
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank staff of Heron Island Research Station for facilitating scientific investigations. A Sigma Xi Grant-in-Aid of Research and the Winifred Violet Scott Foundation supported KEU. MvO was supported by Australian Institute of Marine Science, MK by the Danish Natural Science Research Council, and PJR by the Australian Research Council. Anni Glud manufactured microsensors used in this study. This work was conducted under GBRMPA permit no. G04/12776.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G.F. Humphrey.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulstrup, K.E., van Oppen, M.J.H., Kühl, M. et al. Inter-polyp genetic and physiological characterisation of Symbiodinium in an Acropora valida colony. Mar Biol 153, 225–234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0806-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0806-x