Abstract
Purpose
The ATP-binding cassette transporter G2 (ABCG2) plays an important role in the disposition of rosuvastatin. Telmisartan, a selective angiotension-II type 1 (AT1) receptor blocker, inhibits the transport capacity of ABCG2, which may result in drug interactions. This study investigated the pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and telmisartan and the potential mechanism.
Methods
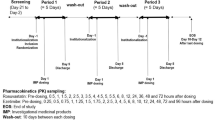
In this two-phase fixed-order design study, healthy subjects received single doses of 10 mg rosuvastatin at baseline and after telmisartan 40 mg daily for 14 days. Patients with hyperlipidaemia who had been taking rosuvastatin 10 mg daily for at least 4 weeks were given telmisartan 40 mg daily for 14 days together with rosuvastatin. Plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin were measured over 24 h before and after telmisartan administration. In vitro experiments using a bidirectional transport assay were performed to investigate the involvement of ABCG2 in the interaction.
Results
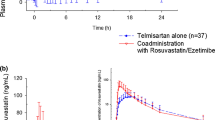
Co-administration of telmisartan significantly increased the maximum plasma concentration (C max) and the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) of rosuvastatin by 71 and 26 %, respectively. The T max values were reduced after administration of telmisartan. There was no significant difference in the interaction of rosuvastatin with telmisartan between healthy volunteers and patients receiving long-term rosuvastatin therapy or among subjects with the different ABCG2 421 C>A genotypes. The in vitro experiment demonstrated that telmisartan inhibited ABCG2-mediated efflux of rosuvastatin.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated that telmisartan significantly increased the systemic exposure to rosuvastatin after single and multiple doses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Escobar C, Barrios V (2013) An evaluation of the latest evidence relating to renin-angiotensin system inhibitors. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 9(7):847–858
Benson SC, Pershadsingh HA, Ho CI, Chittiboyina A, Desai P, Pravenec M, Qi N, Wang J, Avery MA, Kurtz TW (2004) Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension 43(5):993–1002
Weiss J, Sauer A, Divac N, Herzog M, Schwedhelm E, Boger RH, Haefeli WE, Benndorf RA (2010) Interaction of angiotensin receptor type 1 blockers with ATP-binding cassette transporters. Biopharm Drug Dispos 31(2–3):150–161
Kamiyama E, Nakai D, Mikkaichi T, Okudaira N, Okazaki O (2010) Interaction of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers with P-gp substrates in Caco-2 cells and hMDR1-expressing membranes. Life Sci 86(1–2):52–58
Mogi M, Yang J, Lambert JF, Colvin GA, Shiojima I, Skurk C, Summer R, Fine A, Quesenberry PJ, Walsh K (2003) Akt signaling regulates side population cell phenotype via Bcrp1 translocation. J Biol Chem 278(40):39068–39075
Takada T, Suzuki H, Gotoh Y, Sugiyama Y (2005) Regulation of the cell surface expression of human BCRP/ABCG2 by the phosphorylation state of Akt in polarized cells. Drug Metab Dispos: Biol Fate Chem 33(7):905–909
Bleau AM, Hambardzumyan D, Ozawa T, Fomchenko EI, Huse JT, Brennan CW, Holland EC (2009) PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates the side population phenotype and ABCG2 activity in glioma tumor stem-like cells. Cell Stem Cell 4(3):226–235
To KK, Tomlinson B (2013) Targeting the ABCG2-overexpressing multidrug resistant (MDR) cancer cells by PPARgamma agonists. Br J Pharmacol 170(5):1137–1151
Frampton JE (2011) Telmisartan: a review of its use in cardiovascular disease prevention. Drugs 71(6):651–677
Hu M, Tomlinson B (2014) Evaluation of the pharmacokinetics and drug interactions of the two recently developed statins, rosuvastatin and pitavastatin. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 10(1):51–65
Hu M, To KK, Mak VW, Tomlinson B (2011) The ABCG2 transporter and its relations with the pharmacokinetics, drug interaction and lipid-lowering effects of statins. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7(1):49–62
Chasman DI, Giulianini F, MacFadyen J, Barratt BJ, Nyberg F, Ridker PM (2012) Genetic determinants of statin-induced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction: the justification for the use of statins in prevention: an intervention trial evaluating rosuvastatin (JUPITER) trial. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 5(2):257–264
Lee HK, Hu M, Lui S, Ho CS, Wong CK, Tomlinson B (2013) Effects of polymorphisms in ABCG2, SLCO1B1, SLC10A1 and CYP2C9/19 on plasma concentrations of rosuvastatin and lipid response in Chinese patients. Pharmacogenomics 14(11):1283–1294
Tomlinson B, Hu M, Lee VW, Lui SS, Chu TT, Poon EW, Ko GT, Baum L, Tam LS, Li EK (2010) ABCG2 polymorphism is associated with the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol response to rosuvastatin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87(5):558–562
Gallelli L, Ferraro M, Spagnuolo V, Rende P, Mauro GF, De Sarro G (2009) Rosuvastatin-induced rhabdomyolysis probably via CYP2C9 saturation. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 24(1):83–87
Son M, Kim Y, Lee D, Roh H, Son H, Guk J, Jang SB, Nam SY, Park K (2014) Pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and telmisartan in healthy Korean male volunteers: a randomized, open-label, two-period, crossover, multiple-dose study. Clin Ther 36(8):1147–1158
Lee HK, Ho CS, Hu M, Tomlinson B, Wong CK (2013) Development and validation of a sensitive method for simultaneous determination of rosuvastatin and N-desmethyl rosuvastatin in human plasma using liquid chromatography/negative electrospray ionization/tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr
Deppe S, Boger RH, Weiss J, Benndorf RA (2010) Telmisartan: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 6(7):863–871
Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, Schumacher H, Dagenais G, Sleight P, Anderson C (2008) Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med 358(15):1547–1559
AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP. Crestor (rosuvastatin calcium) Package Insert: Revised 01/07. Wilmington, DE, USA. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2010/021366s016lbl.pdf. Accessed 13 Sept 2016
Lee E, Ryan S, Birmingham B, Zalikowski J, March R, Ambrose H, Moore R, Lee C, Chen Y, Schneck D (2005) Rosuvastatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics in white and Asian subjects residing in the same environment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(4):330–341
Liu Z, Zhao Y, Wei F, Ye L, Lu F, Zhang H, Diao Y, Song H, Qi Z (2014) Treatment with telmisartan/rosuvastatin combination has a beneficial synergistic effect on ameliorating Th17/Treg functional imbalance in hypertensive patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 233(1):291–299
Deppe S, Ripperger A, Weiss J, Ergun S, Benndorf RA (2014) Impact of genetic variability in the ABCG2 gene on ABCG2 expression, function, and interaction with AT1 receptor antagonist telmisartan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443(4):1211–1217
Tamura A, Watanabe M, Saito H, Nakagawa H, Kamachi T, Okura I, Ishikawa T (2006) Functional validation of the genetic polymorphisms of human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter ABCG2: identification of alleles that are defective in porphyrin transport. Mol Pharmacol 70(1):287–296
Huang L, Wang Y, Grimm S (2006) ATP-dependent transport of rosuvastatin in membrane vesicles expressing breast cancer resistance protein. Drug Metab Dispos: Biol Fate Chem 34(5):738–742
Erbe DV, Gartrell K, Zhang YL, Suri V, Kirincich SJ, Will S, Perreault M, Wang S, Tobin JF (2006) Molecular activation of PPARgamma by angiotensin II type 1-receptor antagonists. Vasc Pharmacol 45(3):154–162
Roh H, Son H, Lee D, Chang H, Yun C, Park K (2014) Pharmacokinetic interaction between rosuvastatin and olmesartan: a randomized, open-label, 3-period, multiple-dose crossover study in healthy Korean male subjects. Clin Ther 36(8):1159–1170
Jung JA, Lee SY, Kim JR, Ko JW, Jang SB, Nam SY, Huh W (2015) A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interaction between rosuvastatin and valsartan in healthy subjects. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:745–752
Takeuchi K, Sugiura T, Matsubara K, Sato R, Shimizu T, Masuo Y, Horikawa M, Nakamichi N, Ishiwata N, Kato Y (2014) Interaction of novel platelet-increasing agent eltrombopag with rosuvastatin via breast cancer resistance protein in humans. Drug Metab Dispos: Biol Fate Chem 42(4):726–734
Allred AJ, Bowen CJ, Park JW, Peng B, Williams DD, Wire MB, Lee E (2011) Eltrombopag increases plasma rosuvastatin exposure in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 72(2):321–329
Acknowledgment
We thank the other members of the research team especially Ms. Swen Ip and Ms. Evelyn Chau for their excellent assistance. We also thank the volunteers for their participation in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol and statement of informed consent were approved by the Joint Clinical Research Ethics Committee of The Chinese University of Hong Kong and New Territories East Cluster (CUHK-NTEC), and this trial was registered at the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (WHO-ICTRP) as ChiCTR-ONC-13,003,006. All the subjects gave written informed consent.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
The plasma concentration–time profiles of rosuvastatin before and after telmisartan in the study subjects stratified by the ABCG2 421C>A genotypes (DOC 107 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
The plasma concentration–time profiles of rosuvastatin before and after telmisartan in the healthy volunteers and in patients receiving long-term rosuvastatin therapy (DOC 116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, M., Lee, HK., To, K.K.W. et al. Telmisartan increases systemic exposure to rosuvastatin after single and multiple doses, and in vitro studies show telmisartan inhibits ABCG2-mediated transport of rosuvastatin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 72, 1471–1478 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2130-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-016-2130-1