Abstract
Purpose
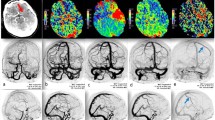
Cortical vein opacification is not routinely assessed in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke (AIS), and the value of temporal assessment of venous outflow is not known. We evaluated the utility of assessing cortical venous drainage over time using multiphase CT angiography (mCTA).
Methods
Cortical venous drainage was assessed in patients from the Precise and Rapid Assessment of Collaterals Using Multi-Phase CTA in the Triage of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke for IA Therapy prospective multicenter cohort study of patients with symptoms of AIS with ICA and/or middle cerebral artery occlusion on baseline mCTA. Opacification of vein of Labbe, sphenoparietal sinus, superficial middle cerebral vein, and vein of Trolard of the affected hemisphere was graded as no (0), partial (1), or full (2) opacification in each mCTA phase. The venous opacification scores for each phase were added to generate a total venous score (TVS) (range 0–24). Primary outcome was 90-day modified Rankin score. Repeated measures analysis was used to assess the effect of phase timing on venous score on outcome.
Results
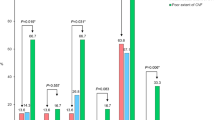
Of 432 patients, 284 (65.7%) had proximal arterial occlusions. Median venous opacification score per phase (range 0–8) was 3 (IQR 1–6) in the first phase and increased in the second and third phases [median (IQR): 6 (5–8) and 8 (6–8), respectively] of the mCTA. In a multivariable analysis adjusting for age, baseline National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, and Alberta stroke program early CT score, a significant association between TVS and 90-day mRS was noted ([adjusted cOR for TVS 6–11: 0.16 (95% CI 0.05–0.51); TVS 12–17: 0.18 (95% CI 0.06–0.57); TVS 18–24: 0.20 (0.06–0.63)]. Repeated measures analysis of venous scores from all three phases showed a significant effect of time/phase on TVS (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
This study concludes that venous opacification over time on multiphase CTA is associated with 90-day clinical outcome. There was however no added benefit of venous scoring vis-a-vis arterial collateral assessment in predicting outcome.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Code availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Nambiar V, Sohn SI, Almekhlafi MA et al (2014) CTA collateral status and response to recanalization in patients with acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:884–890
Campbell BC, Christensen S, Tress BM et al (2013) Failure of collateral blood flow is associated with infarct growth in ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33:1168–1172
Menon BK, Qazi E, Nambiar V et al (2015) Differential effect of baseline computed tomographic angiography collaterals on clinical outcome in patients enrolled in the Interventional Management of Stroke III Trial. Stroke 46:1239–1244
Román LS, Menon BK, Blasco J et al (2018) Imaging features and safety and efficacy of endovascular stroke treatment: a meta-analysis of individual patient-level data. Lancet Neurol 17:895–904
Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Churilov L et al (2020) Effect of intravenous tenecteplase dose on cerebral reperfusion before thrombectomy in patients with large vessel occlusion ischemic stroke: the EXTEND-IA TNK Part 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 323:1257–1265
Jansen IGH, van Vuuren AB, van Zwam WH et al (2018) Absence of cortical vein opacification is associated with lack of intra-arterial therapy benefit in stroke. Radiology 286:643–650
Menon BK, Bai HD, Modi J, Demchuk AM, Hudon M, Goyal M, Watson TWJ (2013) The ICV sign as a marker of increased cerebral blood transit time. Can J Neurol Sci 40:187–191
Parthasarathy R, Kate M, Rempel JL, Liebeskind DS, Jeerakathil T, Butcher KS, Shuaib A (2013) Prognostic evaluation based on cortical vein score difference in stroke. Stroke 44:2748–2754
Parthasarathy R, Sohn S-I, Jeerakathil T, Kate MP, Mishra SM, Nambiar VK, Ahmad A, Menon BK, Shuaib A (2015) A combined arterial and venous grading scale to predict outcome in anterior circulation ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging 25:969–977
van den Wijngaard IR, Wermer MJH, Boiten J, Algra A, Holswilder G, Meijer FJA, Dippel DWJ, Velthuis BK, Majoie CBLM, van Walderveen MAA (2016) Cortical venous filling on dynamic computed tomographic angiography: a novel predictor of clinical outcome in patients with acute middle cerebral artery stroke. Stroke 47:762–767
Menon B, Ospel J, Volny O, Mohamed Najm, Moiz H Impact of current imaging selection criteria for endovascular treatment decision-making on outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Circulation (under review)
Menon BK, d’Esterre CD, Qazi EM, Almekhlafi M, Hahn L, Demchuk AM, Goyal M (2015) Multiphase CT angiography: a new tool for the imaging triage of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Radiology 275:510–520
Tong L-S, Guo Z-N, Ou Y-B, Yu Y-N, Zhang X-C, Tang J, Zhang JH, Lou M (2018) Cerebral venous collaterals: a new fort for fighting ischemic stroke? Prog Neurobiol 163–164:172–193
Neuberger U, Möhlenbruch MA, Herweh C, Ulfert C, Bendszus M, Pfaff J (2017) Classification of bleeding events: comparison of ECASS III (European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study) and the New Heidelberg Bleeding Classification. Stroke 48:1983–1985
Yu AYX, Zerna C, Assis Z et al (2016) Multiphase CT angiography increases detection of anterior circulation intracranial occlusion. Neurology 87:609–616
Nigron A, Bourgois N, Dao S et al (2019) Anterior ischemic stroke: comparison of two clinical outcome prediction scores through the investigation of cerebral collaterals using multiphase CT angiography. J Neuroradiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurad.2019.03.016
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Disclosures
Dr Fouzi Bala is supported by La Société Française de Neuroradiologie and La Société Française de Radiologie.
Mayank Goyal received personal fees (Mentice, Medtronic, MicroVention, and Stryker outside the submitted work) and patent (systems of acute stroke diagnosis).
Andrea Zini received consulting fees from Stryker, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Alexion and speaker honoraria from Cerenovus.
Others: none
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
All participants consented for being a part of the study.
Consent to publication
All participants consented for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Bala, F., Kim, B.J. et al. Time-resolved assessment of cortical venous drainage on multiphase CT angiography in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 64, 897–903 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02837-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-021-02837-1