Abstract
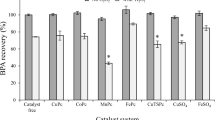
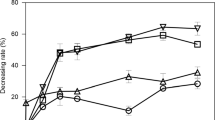
The oxidative degradation behavior of bisphenol A (BPA) using titanium dioxide (TiO2) in water was investigated. The main purposes were to clarify the relationship with estrogenic activity from the degradation pathways demonstrated by oxidation of BPA in water. Approximately 99% of the BPA decomposed within 300 min, and gas chromatography (GC) mass spectrometry (MS) and liquid chromatography (LC) MS analysis revealed many intermediates during the degradation process. Intermediates by decomposition of BPA, such as hydroxylated-BPA (OH-BPA), carboxylic intermediates, phenolic intermediates, and other intermediates produced by the cleavage of a benzene ring were identified and quantified. Estrogenic activities of the degradation pathways of the BPA in water were assessed by using a constructed yeast two-hybrid assay system for human estrogen receptor α (hERα) and Japanese medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) estrogen receptor α (medERα). Estrogenic activity for hERα and medERα was reduced to less than 20% of the initial activity for BPA after 240 min of UV irradiation. However, estrogenic activity for medERα was increased by 110% from the initial activity for BPA at 60 min of UV irradiation. It was estimated that medERα assay was more sensitive for BPA and the intermediates than was the hERα assay. From these findings, we estimate that the intermediates by the oxidation of BPA have the behaviors of xenoestrogen to the aquatic wildlife in the environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arulmozhiraja S, Shiraishi F, Okumura T, Iida M, Takigami H, Edmonds SJ, Morita M (2005) Structural requirements for the interaction of 91 hydroxylated polychlorinated biphenyls with estrogen and thyroid hormone receptors. Toxicol Sci 84:49–62
Atkinson A, Roy D (1995) In vivo DNA adduct formation by bisphenol A. Environ Molec Mutagen 26:60–66
Chiang K, Lim TM, Tsen L, Lee CC (2004) Photocatalytic degradation and mineralization of bisphenol A by TiO2 and platinized TiO2. Appl Catalysis A: General 261:225–237
Coleman HM, Chiang K, Amal R (2005) Effects of Ag and Pt on photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals in water. Chem Eng J 113:65–72
Fukahori S, Ichiyra H, Kitaoka T, Tanaka H (2003) Capturing of bisphenol A photodecomposition intermediates by composite TiO2-zeolite sheets. Appl Catalysis B: Environmental 46:453–462
Horikoshi S, Tokunaga A, Hidaka H, Serpone N (2004) Environmental remediation by an integrated microwave/UV-illumination technique VII. Thermal/non-thermal effects in the microwave-assisted photocatalyzed mineralization of bisphenol-A. J Photochem Photobiol A 162:33–40
Ishibashi H, Watanabe N, Matsumura N, Hirano M, Nagao Y, Shiratsuchi H, Kohra S, Yoshihara S, Arizono K (2005) Toxicity to early life stages and an estrogenic effect of a bisphenol A metabolite, 4-methyl-2,4-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)pent-1-ene on the medaka (Oryzias latipes). Life Sci 77:2643–2655
Kato K, Tsuzuki A, Torii Y, Taoda H, Butsugan Y (1995) Morphology of thin anatase coating prepared from alkoxide solutions containing organic polymer, affecting the photocatalytic decomposition of aqueous acetic acid. J Mater Sci 30:837–841
Krishnan AV, Stathis P, Permuth SF, Tokes L, Feldman D (1993) Bisphenol A: an estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 132:2279–2286
Nishikawa J, Saito K, Goto J, Dakeyama F, Matsuo M, Nishihara T (1999) New screening methods for chemicals with hormonal activities using interaction of nuclear hormone receptor with coactivator. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 154:76–83
Nomiyama K, Tanizaki T, Ishibashi H, Arizono K, Shinohara R (2005) Production mechanism of hydroxylated PCBs by oxidative degradation of selected PCBs using TiO2 in water and estrogenic activity of their intermediates. Environ Sci Technol 39:8762–8769
Nomura Y, Ishibashi H, Miyahara M, Shinohara R, Shiraishi F, Arizono K (2003) Effects of dental resin metabolites on estrogenic activity in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med 14:307–310
Ollis DF, Hsiao CY, Budiman L, Lee CL (1984) Heterogeneous photoassisted catalysis: conversion of perchloroethylene, dichloroethane, chloroacetic acids, and chlorobenzene. J CATAL (Journal of Catalysis) 88:89–96
Ohko Y, Ando I, Niwa C, Tatsuma T, Yamamura T, Nakashima T, Kubota Y, Fujishima A (2001) Degradation of bisphenol-A in water by TiO2 photocatalyst. Environ Sci Technol 35:2365–2368
Shiraishi F, Shiraishi H, Nishikawa J, Nishikawa T, Morita M (2000) Development of a simple operational estrogenicity assay system using the yeast two-hybrid system. J Environ Chem 10:57–64 [in Japanese]
Staples CA, Dorn PB, Klecka GM, Block ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36:2149–2173
Stewart JJP (1996) Application of localized molecular orbitales to the solution of semiempirical self-consistent field equations. J Quant Chem 58:133–146
Suzuki T, Nakagawa Y, Takano I, Yaguchi K, Yasuda K (2004) Environmental fate of bisphenol A and its biological metabolites in river water and their xeno-estrogenic activity. Environ Sci Technol 38:2389–2396
Tai C, Jiang G, Liu J, Zhou Q, Liu J (2005) Rapid degradation of bisphenol A using air as the oxidant catalyzed by polynuclear phthalicyanine complexes under visible light irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol A 172:275–282
Tanizaki T, Kadokami K, Shinohara R (2002) Catalytic photodegradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals using titanium dioxide photosemiconductor thin films. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:732–739
Terasaki M, Shiraishi F, Nishikawa T, Edmonds JS, Morita M, Makino M (2005) Estrogenic activity of impurities in industrial grade Bisphenol A. Environ Sci Technol 39:3703–3707
Watanabe N, Horikoshi S, Kawabe H, Sugie Y, Zhao J, Hidaka H (2003) Photodegradation mechanism for bisphenol A at the TiO2/H2O interfaces. Chemosphere 52:851–859
Yamaguchi A, Ishibashi H, Kohra S, Arizono K, Tominaga N (2005) Short-term effects of endocrine-disrupting chemicals on the expression of estrogen-responsive genes in male medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 30:239–249
Yoshihara S, Mizutare T, Makishima M, Suzuki N, Fujimoto N, Igarashi K, Ohta S (2004) Potent estrogenic metabolites of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B formed by rat liver S9 fraction: their structures and estrogenic potency. Toxicol Sci 78:50–59
Acknowledgments
This study was “High-Tech Research Center” projects for private universities: matching fund subsidy from NEXT (Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology), 2002−2006. The authors wish to thank Dr. F. Shiraishi of National Institute for Environmental Studies for the offer of the two-hybrid yeast. Fruitful discussions with Professor M. Koga of Prefectural University of Kumamoto, Japan are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nomiyama, K., Tanizaki, T., Koga, T. et al. Oxidative Degradation of BPA Using TiO2 in Water, and Transition of Estrogenic Activity in the Degradation Pathways. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52, 8–15 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0204-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0204-7