Abstract
Background
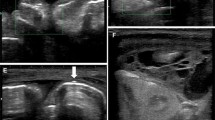
Intussusception (IS) is the most common cause of acute bowel obstruction in infants and young children. Ultrasonography is being increasingly used as the primary investigation for the diagnosis of IS and to guide air or hydrostatic enema reduction. However the accuracy of ultrasonography outside tertiary care settings in developed countries has not been assessed, particularly in Asia where the incidence of IS based on sonographic diagnosis has been reported as the highest in the world.
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of acute IS in infants less than 2 years of age in a paediatric hospital in Vietnam.
Materials and methods
A prospective study was conducted at the National Hospital for Paediatrics, Hanoi, Vietnam, over a 14-month period recruiting patients <2 years of age with IS. Abdominal ultrasonography was performed on each patient and the accuracy of the diagnosis was evaluated against the final diagnosis provided by air enema and/or surgery.
Results
A total of 640 infants <2 years of age presented with clinical symptoms and signs of IS. The diagnosis was confirmed in 533 patients via air enema or surgery. Abdominal ultrasonography was 97.5% (466/478) sensitive and 99% (106/107) specific in the detection of IS.
Conclusion
Ultrasonography is an accurate, safe and valuable clinical tool in the diagnosis of IS. The use of ultrasonography as a primary investigation for patients with suspected IS prevents unnecessary radiological or surgical procedures being performed, and reduces radiation exposure while maintaining a high level of diagnostic accuracy. These results validate the use of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of IS in a developing country setting.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce J, Huh YS, Cooney DR et al (1987) Intussusception: evolution of current management. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 6:663–674
Glover JM, Beasley SW, Phelan E (1991) Intussusception: effectiveness of gas enema. Pediatr Surg Int 6:195–197
Phelan E, de Campo JF, Malecky G (1988) Comparison of oxygen and barium reduction of ileocolic intussusception. AJR 150:1349–1352
Gu L, Alton DJ, Daneman A et al (1988) John Caffey Award. Intussusception reduction in children by rectal insufflation of air. AJR 150:1345–1348
Zheng JY, Frush DP, Guo JZ (1994) Review of pneumatic reduction of intussusception: evolution not revolution. J Pediatr Surg 29:93–97
Guo JZ, Ma XY, Zhou QH (1986) Results of air pressure enema reduction of intussusception: 6,396 cases in 13 years. J Pediatr Surg 21:1201–1203
Wang GD, Liu SJ (1988) Enema reduction of intussusception by hydrostatic pressure under ultrasound guidance: a report of 377 cases. J Pediatr Surg 23:814–818
Shanbhogue RL, Hussain SM, Meradji M et al (1994) Ultrasonography is accurate enough for the diagnosis of intussusception. J Pediatr Surg 29:324–327
del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D (1996) Intussusception: US findings with pathologic correlation – the crescent-in-doughnut sign. Radiology 199:688–692
Daneman A, Alton DJ (1996) Intussusception. Issues and controversies related to diagnosis and reduction. Radiol Clin North Am 34:743–756
Daneman A, Navarro O (2003) Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol 33:79–85
Vasavada P (2004) Ultrasound evaluation of acute abdominal emergencies in infants and children. Radiol Clin North Am 42:445–456
Verschelden P, Filiatrault D, Garel L et al (1992) Intussusception in children: reliability of US in diagnosis – a prospective study. Radiology 184:741–744
Bhisitkul DM, Listernick R, Shkolnik A et al (1992) Clinical application of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of intussusception. J Pediatr 121:182–186
Harrington L, Connolly B, Hu X et al (1998) Ultrasonographic and clinical predictors of intussusception. J Pediatr 132:836–839
Bines JE, Liem TN, Justice FA et al (2006) Risk factors for intussusception in Vietnam and Australia: adenovirus implicated, but not rotavirus. J Pediatr 149:452–460
Bines J, Ivanoff B (2002) Acute intussusception in infants and children: a global perspective. Vaccines and biologicals. WHO/V&B/02.19. World Health Organisation, Geneva
Bines JE, Ivanoff B, Justice F et al (2004) Clinical case definition for the diagnosis of acute intussusception. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 39:511–518
WHO (2000) Report of the meeting on future directions for rotavirus vaccine research in developing countries. Vaccines and biologicals. WHO/V&B/00.23. World Health Organisation, Geneva, 9–11 February
Swischuk LE, John SD, Swischuk PN (1994) Spontaneous reduction of intussusception: verification with US. Radiology 192:269–271
Kornecki A, Daneman A, Navarro O et al (2000) Spontaneous reduction of intussusception: clinical spectrum, management and outcome. Pediatr Radiol 30:58–63
Lim HK, Bae SH, Lee KH et al (1994) Assessment of reducibility of ileocolic intussusception in children: usefulness of color Doppler sonography. Radiology 191:781–785
Pracros JP, Tran-Minh VA, Morin de Finfe CH et al (1987) Acute intestinal intussusception in children. Contribution of ultrasonography (145 cases). Ann Radiol (Paris) 30:525–530
Murphy TV, Gargiullo PM, Massoudi MS et al (2001) Intussusception among infants given an oral rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med 344:564–572
Lee HC, Yeh HJ, Leu YJ (1989) Intussusception: the sonographic diagnosis and its clinical value. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 8:343–347
Woo SK, Kim JS, Suh SJ et al (1992) Childhood intussusception: US-guided hydrostatic reduction. Radiology 182:77–80
Wright JE, Slater S (1996) Suspected intussusception: is ultrasound a reliable diagnostic aid? Aust N Z J Surg 66:686–687
Acknowledgements
This project was made possible by a grant from the World Health Organization. We thank the infants and their families for their participation in this study. We would also like to acknowledge the staff from the Imaging, Surgical and Emergency Departments at the National Hospital of Paediatrics, Hanoi, for conducting this study and the staff of the Royal Children’s Hospital International (RCHI) for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Justice, F.A., de Campo, M., Liem, N.T. et al. Accuracy of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of intussusception in infants in Vietnam. Pediatr Radiol 37, 195–199 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0381-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0381-1