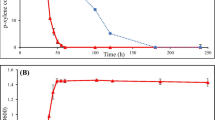
Abstract.
Pseudomonas putida CSV86 metabolizes 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene through distinct catabolic and detoxification pathways. In spite of the similarity in the steps involved in the methylnaphthalene detoxification and the toluene side-chain hydroxylation pathways, the strain failed to utilize toluene or xylenes. However, it could grow on benzyl alcohol, 2- and 4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol. Metabolic studies suggest that the benzyl alcohol metabolism proceeds via the benzaldehyde, benzoate, and catechol ortho-cleavage pathway, in contrast to the well established catechol meta-cleavage pathway. Carbon source-dependent enzyme activity studies suggest that the degradation of aromatic alcohol involves two regulons. Aromatic alcohol induces the upper regulon, which codes for aromatic alcohol- and aromatic aldehyde-dehydrogenase and converts alcohol into acid. The aromatic acid so generated induces the specific lower regulon and is metabolized via either the ortho- or the meta-cleavage pathway. CSV86 cells transform 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene to 1- and 2-hydroxymethyl naphthalene, which are further converted to the respective naphthoic acids due to the basal level expression and broad substrate specificity of the upper regulon enzymes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abril MA, Michan C, Timmis KN, Ramos JL (1989) Regulator and enzyme specificities of the TOL plasmid-encoded upper pathway for the degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons and expansion of the substrate range of the pathway. J Bacteriol 171:6782–6790
Assinder SJ, Williams PA (1990) The TOL plasmids: determinants of the catabolism of toluene and the xylenes. Adv Microb Physiol 31:1–69
Bestetti G, Bianchi D, Bosetti A, Gennaro P, Galli E, Leoni B, Pelizzoni F, Sello G (1995) Bioconversion of substituted naphthalenes to the corresponding 1,2-dihydro-1,2-dihydroxy derivative. Determination of the regio- and stereochemistry of the oxidation reactions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:306–313
Boylan DB, Tripp BW (1971) Determination of hydrocarbons in sea water extracts of crude oil and crude oil fractions. Nature 230:44–47
Bramucci M, Singh M, Nagarajan V (2002) Biotransformation of p-xylene and 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene by xylene monooxygenase cloned from a Sphingomonas isolate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:679–684
Cane PA, Williams PA (1982) The plasmid coded metabolism of naphthalene and 2-methylnaphthalene in Pseudomonas strains: phenotypic changes correlated with structural modification of the plasmid PWW-60. J Gen Microbiol 128:2281–2290
Cerniglia CE, Lambert KJ, Miller DW, Freeman JP (1984) Transformation of 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene by Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:111–118
Davis JL, Evans WC (1964) Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads: the ring fission mechanism. Biochem J 91:251–261
Dean-Raymond D, Bartha R (1975) Biodegradation of some polynuclear aromatic petroleum components by marine bacteria. Dev Ind Microbiol 16:97–110
Duetz WA, Marques S, De-Jong C, Ramos JL, Van-Andel JG (1994) Inductibility of the TOL catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas putida (pWW0) growing on succinate on continuous culture: evidence of carbon catabolites repression control. J Bacteriol 176:2354–2361
Franklin FC, Bagdasarian M, Bagdasarian MM, Timmis KN (1981) Molecular and functional analysis of the TOL plasmid pWWO from Pseudomonas putida and cloning of genes for the entire regulated aromatic ring meta cleavage pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7458–7462
Fujisawa H (1970) Protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase (Pseudomonas). Methods Enzymol 17a:526–529
Gibson DT, Zylstra GJ, Chauhan S (1990) Biotransformations catalyzed by toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida F1. In: Silver S, Chakrabarty AN, Iglewski B, Kaplan S (eds) Pseudomonas: biotransformations, pathogenesis and evolving biotechnology. ASM Press, Washington, D.C., pp 121–132
Harayama S, Leppik RA, Rekik M, Mermod N, Lehrbach PR, Reineke W, Timmis KN (1986) Gene order of the TOL catabolic plasmid upper pathway operon and oxidation of both toluene and benzyl alcohol by the xylA product. J Bacteriol 167:455–461
Harayama S, Rekik M, Wubbolts M, Rose K, Leppik RA, Timmis KN (1989) Characterization of five genes in the upper-pathway operon of TOL plasmid pWW0 from Pseudomonas putida and identification of the gene products. J Bacteriol 171:5048–5055
Holtel A, Marques S, Mohler I, Jakubzik U, Timmis KN (1994) Carbon source-dependent inhibition of xyl operon of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol 176:1773–1776
Johri AK, Dua M, Singh A, Sethunathan N, Legge RL (1999) Characterization and regulation of catabolic genes. Crit Rev Microbiol 25:245–273
Jorgensen C, Nielsen B, Jensen BK, Mortensen E (1995) Transformation of o-xylene to o-methylbenzoic acid by a denitrifying enrichment culture using toluene as the primary substrate. Biodegradation 6:141–146
Kaubisch N, Daly JW, Jerina DM (1972) Arene oxides as intermediates in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds. Isomerization of methyl-substituted arene oxides. Biochemistry 11:3080–3088
Kojima Y, Fujisawa H, Nakazawa A, Nakazawa T, Kanetsuna F, Taniuchi H, Nozaki M, Hayaishi O (1967) Studies on pyrocatechase: purification and spectral properties. J Biol Chem 242:3270–3278
Lee CC, Craig WK, Smith PJ (1974) Water soluble hydrocarbons from crude oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 12:212–216
Lee K, Gibson DT (1996) Toluene and ethylbenzene oxidation by purified naphthalene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB 9816-4. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3101–3106
Lowry OH, Rosebrough MJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
MacKintosh RW, Fewson CA (1988) Benzyl alcohol dehydrogenase and benzaldehyde dehydrogenase II from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Substrate specificities and inhibition studies. Biochem J 255:653–661
Mahajan MC, Phale PS, Vaidyanathan CS (1994) Evidence for the involvement of multiple pathways in the biodegradation of 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene by Pseudomonas putida CSV86. Arch Microbiol 161:425–433
Mountfield RJ, Hopper DJ (1998) The formation of 1-hydroxymethyl naphthalene and 6-hydroxymethyl naphthalene by both oxidative and reductive routes in Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:379–383
Murray K, Duggleby CJ, Sala-Trepat M, Williams PA (1972) The metabolism of benzoate and methylbenzoate via the meta-cleavage pathway by Pseudomonas arvilla mt-2. Eur J Biochem 28:301–310
Nozaki M, Ono K, Nakazawa T, Kotani S, Hayaishi O (1968) Metapyrocatechase II. The role of iron and sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem 243:2682–2690
Phale PS, Mahajan MC, Vaidyanathan CS (1995) A pathway for biodegradation of 1-naphthoic acid by Pseudomonas maltophilia CSV 89. Arch Microbiol 163:42–47
Ramos JL, Marques S, Timmis KN (1997) Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid catabolic operons is achieved through an interplay of host factors and plasmid-encoded regulators. Annu Rev Microbiol 51:341–373
Robertson JB, Spain JC, Haddock JD, Gibson DT (1992) Oxidation of nitrotoluenes by toluene dioxygenase reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2643–2648
Selifonov SA, Grifoll M, Eaton RW, Chapman PJ (1996) Oxidation of naphthenoaromatic and methyl-substituted aromatic compounds by naphthalene 1,2-dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:507–514
Shaw JP, Harayama S (1990) Purification and characterization of TOL plasmid-encoded benzyl alcohol dehydrogenase and benzaldehyde dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem 191:705–714
Shaw JP, Harayama S (1992) Purification and characterization of the NADH: acceptor reductase component of xylene monooxygenase encoded by the TOL plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. Eur J Biochem 209:51–61
Shaw JP, Rekik M, Schwager F, Harayama S (1993) Kinetic studies on benzyl alcohol dehydrogenase encoded by TOL plasmid pWW0. A member of the zinc-containing long chain alcohol dehydrogenase family. J Biol Chem 268:10842–10850
Suzuki M, Hayakawa T, Shaw JP, Rekik M, Harayama S (1991) Primary structure of xylene monooxygenase: similarities to and differences from the alkane hydroxylation system. J Bacteriol 173:1690–1695
Wackett LP, Kwart LD, Gibson DT (1988) Benzylic monooxygenation catalyzed by toluene dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry 27:1360–1367
Williams PA, Catterall FA, Murray K (1975) Metabolism of naphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, salicylate and benzoate by Pseudomonas PG: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol 124:679–685
Winters K, O'Donnel R, Batterton JC, VanBaalen C (1976) Water soluble components of four fuel oils: chemical composition and effects on growth of microalgae. Mar Biol (NY) 36:269–276
Worsey M, Williams A (1975) Metabolism of toluene and xylenes by Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: evidence of a new function of the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol 124:7–13
Yen KM, Serdar CM (1988) Genetics of naphthalene catabolism in pseudomonads. Crit Rev Microbiol 15:247–256
Acknowledgements.
P.P. would like to thank the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, for a Research Grant and RSIC, IIT Bombay for providing a GC-MS facility. A UGC-Junior Research Fellowship to A.B. is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, A., Dixit, S.S. & Phale, P.S. Metabolism of benzyl alcohol via catechol ortho-pathway in methylnaphthalene-degrading Pseudomonas putida CSV86. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62, 579–585 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1305-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1305-8