Abstract
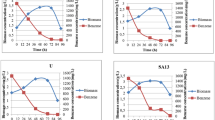
Streptomycetes resistant to the herbicide alachlor [2-chloro-2′,6′-diethyl-N-(methoxymethyl) acetanilide] were used in degradation assays to characterize the products of alachlor biodegradation. Of six strains tested, Streptomyces sp. LS166, LS177, and LS182 were able to grow at an alachlor concentration of 144 mg l−1 and degraded approximately 60–75% of the alachlor in 14 days, as evaluated by high performance liquid chromatography. The alachlor biodegradation products were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry based on mass spectral data and fragmentation patterns. All compounds detected in these assays were similar for all streptomycetes strains tested, and involved dechlorination with subsequent N-dealkylation and cyclization of the remaining N-substituent with one of the ethyl groups to produce indole and quinoline derivatives. The enzymatic pathway used by Streptomyces sp. LS182 did not generate DEA (2′,6′-diethylaniline), a carcinogenic derivative of alachlor reported in other studies. Given the high degradation rates observed here, the Streptomyces strains tested may be useful in the degradation/detoxification processes of alachlor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aga DS, Thurman EM (2001) Formation and transport of the sulfonic acid metabolites of alachlor and metalachlor in soil. Environ Sci Technol 35: 2455–2460
Aislabie J, Bej AK, Hurst H, Rothenburger S, Atlas RM (1990) Microbial degradation of quinoline and methylquinolines. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:345–351
Buzan J, Guichard N, Lebbe J, Prévot A, Serpinet J, Tranchant J (1969) In: Tranchant J (ed) Practical manual of gas chromatography. , Elsevier, London, pp 228
Capri E, Walker A (1993) Biodegradation of liquid and microencapsulated formulations of alachlor in clay loam soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 50:506–513
Coleman S, Liu S, Linderman R, Hodgson E, Rose RL (1999) In vitro metabolism of alachlor by human liver microsomes and human cytochrome P450 isoforms. Chem-Biol Inter 122:27–39
Coleman S, Linderman R, Hodgson E, Rose RL (2000) Comparative metabolism of chloroacetamide herbicides and selected metabolites in human and rat liver microsomes. Environ Health Perspect 108:1151–1157
De Schrijver A, de Mot R (1999) Degradation of pesticides by actinomycetes. Crit Rev Microbiol 25:85–119
Draper PM, MacLean DB (1968) Mass spectra of alkylquinolines. Can J Chem 46:1487–1497
Ferrey ML, Koskinen WC, Blanchette RA, Burnes TA (1994) Mineralization of alachlor by lignin-degrading fungi. Can J Microbiol 40:795–798
Fetzner S (1998) Bacterial degradation of pyridine, indole, quinoline, and their derivatives under different redox conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:237–250
Hanioka N, Watanabe K, Yoda R, Ando M (2002) Effect of alachlor on hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes in rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 25: 25–37
Hanzlik RP, Shaffer CL, Morton MD (2001) N-dealkylation of an N-cyclopropylamine by horseradish. Fate of the cyclopropyl group. J Am Chem Soc 123: 8502–8508
Kaiser JP, Feng Y, Bollag JM (1996) Microbial metabolism of pyridine, quinoline, acridine, and their derivatives under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Microbiol Rev 60:483–498
Konopka A (1994) Anaerobic degradation of chloroacetanilide herbicides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:440–445
Licht D, Johansen SS, Arvin E, Ahring BK (1997) Transformation of indol and quinoline by Desulfobacterium indolicum (DSM 3383). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:167–172
Mangiapan S, Benfenati E, Grasso P, Terreni M, Pregnolato M, Pagani G, Barcelo D (1997) Metabolites of alachlor in water: identification by mass spectrometry and chemical synthesis. Environ Sci Technol 31:3637–3646
Marx M, Djerassi C (1968) Mass spectrometry in structural and stereochemical problems. The question of ring expansion in the fragmentation of 13C-labeled nitrogen heterocycles. J Am Chem Soc 90:678–681
McCarthy AJ, Williams ST (1992). Actinomycetes as agents of biodegradation in the environment—a review. Gene 115: 189–192
Monteiro RT (1997). Degradação de pesticidas. In: Melo, IS, Azevedo, JL (eds) Microbiologia Ambiental. pp.107–124. Jaguariúna (SP), EMBRAPA-CNPMA
Novick NJ, Alexander M (1985) Cometabolism of low concentrations of propachlor, alachlor, and cycloate in sewage and lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:737–743
Novick NJ, Mukherjee R, Alexander M (1986) Metabolism of alachlor and propachlor in suspensions of pretreated soils and in samples from ground water aquifers. J Agric Food Chem 34:721–725
Osano O, Admiraal W, Klamer HJC, Pastor D, Bleeker EAJ (2002) Comparative toxic and genotoxic effects of chloroacetanilides, formamidines and their degradation products on Vibrio fischeri and Chironomus riparius. Environ Pollut 119:195–202
Pothuluri JV, Freeman JP, Evans FE, Moorman TB, Cerniglia CE (1993) Metabolism of alachlor by the fungus Cunninghamella elegans. J Agric Food Chem 41:483–488
Sette LD (2001). Isolamento e sistemática de actinomicetos degradadores de herbicidas. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas (SP), Brazil
Shelton D, Khader S, Karns JS, Pogell BM (1996) Metabolism of twelve herbicides by Streptomyces. Biodegradation 7:129–136
Shukla OP (1986) Microbial transformation of quinoline by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:1332–1342
Smith AE, Phillips DV (1975) Degradation of alachlor by Rhizoctonia solani. Agron J 67:347
Stamper DM, Tuovinen OH (1998) Biodegradation of the acetanilide herbicides alachlor, metolachlor, and propachlor. Crit Rev Microbiol 24:1-22
Sun HL, Sheets TS, Corbin FT (1990) Transformation of alachlor by soil microbial comunities. Weed Sci 38:416
Tiedje JM, Hagedorn ML (1975) Degradation of alachlor by a soil fungus, Chaetomium globosun. J Agric Food Chem 23:77–81
Yen PY, Koskinen WC, Schweizer EE (1994) Dissipation of alachlor in four soils as influenced by degradation and sorption process. Weed Sci 42:233–240
Zagorc-Koncan J (1996) Effects of atrazine and alachlor on self-purification processes in receiving streams. Water Sci Technol 6:181–187
Acknowledgements
LDS and LAMAC were supported by fellowships from FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil) and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil), respectively, and by a research grant from FAPESP. We declare that the study was conduct according to Brazilian current legislation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durães Sette, L., Mendonça Alves da Costa, L.A., Marsaioli, A.J. et al. Biodegradation of alachlor by soil streptomycetes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64, 712–717 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1494-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1494-1