Abstract
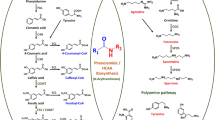
The strain of Mycobacterium sp. VKM Ac-1817D forms 9α-hydroxy-androst-4-ene-3,17-dione (9-OH-AD) as a major product from sitosterol. The formation of 9-OH-AD was accompanied with its partial destruction due to residual steroid-1-dehydrogenase (St1DH) activity. The activity was found to be induced by androst-4-ene-3,17-dione (AD), while other intermediates of sitosterol oxidation did not influence 1(2)-dehydrogenation. The enzyme is located mainly in the cytosolic fraction. The cytosolic St1DH (dimer, M r∼58 kDa) was partially purified by ammonium sulfate fractionation, ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-Sepharose and Phenyl-Sepharose, and gel filtration on Bio-Gel A-0.5M. It expressed the St1DH activity toward both AD and 9-OH-AD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhrem A, Titov Y (1970) Steroids and microorganisms (in Russian). Nauka, Moscow
Davis B (1964) Disc electrophoresis II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci 124:404–409
Donova MV, Gulevskaya SA, Dovbnya DV, Puntus IF (2005a) Mycobacterium sp. mutant strain producing 9α-hydroxyandrostenedione from sitosterol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:671–678
Donova MV, Dovbnya DV, Sukhodolskaya GV, Khomutov SM, Nikolayeva VM, Kwon I, Han K (2005b) Microbial conversion of sterol-containing soybean oil production waste. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:55–60
Drobnič K, Križaj I, Gubenšek F, Komel R (1993) Improved purification of steroid 1:2-dehydrogenase from Nocardia opaca and partial characterization of its cloned gene sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190:509–515
Groh H, Komel R, Deppmeyer V, Schade W, Horhold C (1980) Steroid transforming enzymes from microorganisms: the reverse reaction of the steroid 1-dehydrogenase from Nocardia. J Steroid Biochem 13:1413–1415
Itagaki E, Hatta T, Wakabayashi T, Suzuki K (1990a) Spectral properties of 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase from Nocardia corallina. Biochim Biophys Acta 1040:281–286
Itagaki E, Matushita T, Hatta T (1990b) Steroid transhydrogenase activity of 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase from Nocardia corallina. J Biochem 108:122–127
Kaufmann G, Schumann G, Wollweber L, Hueller E, Atrat P (1990) Steroid 1-dehydrogenase in nocardioform bacteria studied by electrophoresis and immunoblotting techniques. J Basic Microbiol 30:415–423
Kieslich K (1980) Steroid conversions. Econ Microbiol 5:370–467
Laemmli U (1970) Cleavage of structural protein assembly of heat of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lestrovaia NN (1981) Localization of 3-oxosteroid 1-dehydrogenase in Mycobacterium rubrum and Arthrobacter globiformis (in Russian). Mikrobiologiia 50:619–625
Medentsev AG, Arinbasarova AY, Koshcheyenko KA, Akimenko VK, Skryabin GK (1985) Regulation of 3-ketosteroid 1-en-dehydrogenase activity of Arthobacter globiformis cells by respiratory chain. J Steroid Biochem 23:365–368
Molnár I, Choi KP, Yamashita M, Murooka Y (1995) Molecular cloning, expression in Streptomyces lividans, and analysis of a gene cluster from Arthrobacter simplex encoding 3-ketosteroid-Δ1-dehydrogenase, 3-ketosteroid-Δ5-isomerase and a hypothetical regulatory protein. Mol Microbiol 15:895–905
Nikolayeva VM, Egorova OV, Dovbnya DV, Donova MV (2004) Extracellular 3β-hydroxysteroid oxidase of Mycobacterium vaccae VKM Ac-1815D. J Steroid Biochem 91:79–85
Sedlaczek L (1988) Biotransformation of steroids. Crit Rev Biotechnol 7:187–236
Seidel L, Horhold C (1992) Selection and characterisation of new microorganisms for the manufacture of 9-OH-AD from sterols. J Basic Microbiol 32:49–55
Sih CJ, Bennett RE (1962) Steroid-1-dehydrogenase of Nocardia restrictus. Biochim Biophys Acta 56:584–592
van der Geize R, Hessels GI, van Gerwen R, Vrijbloed JW, van der Meijden P, Dijkhuizen L (2000) Targeted disruption of the Kstd gene encoding a 3-ketosteroid-delta(1)-dehydrogenase isoenzyme of Rhodococcus erythropolis strain SQ1. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2029–2036
van der Geize R, Hessels GI, van Gerwen R, van der Meijden P, Dijkhuizen L (2001) Unmarked gene deletion mutagenesis of kstD, encoding 3-ketosteroid Δ1-dehydrogenase, in Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 using sacB as counter-selectable marker. FEMS Microbiol Lett 205:197–202
van der Geize R, Hessels GI, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Molecular and functional characterization of the kstD2 gene of Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 encoding a second 3-ketosteroid delta(1)-dehydrogenase isoenzyme. Microbiology 148:3285–3292
Wagner B, Atrat PG, Clark-Curtiss JE, Wagner M (1992a) Localization of the steroid 1-dehydrogenase in Rhodococcus erythropolis IMET 7030 by immunoelectorn microscopy. J Basic Microbiol 32:65–71
Wagner M, Atrat PG, Wagner B, Hanemann V, Clark-Curtiss JE (1992b) Overexpression of a Rhodococcus erythropolis protein in Escherichia coli with immunological identity to the Rhodococcus steroid 1-dehydrogenase. Immunoelectron microscopic localization and electrophoretic studies. J Basic Microbiol 32:269–277
Wovcha MG, Antosz FJ, Knight JC, Kominek LA, Pyke TR (1978) Bioconversion of sitosterol to useful steroidal intermediates by mutants of Mycobacterium fortuitum. Biochim Biophys Acta 531:308–321
Wovcha MG, Brooks KE, Kominek LA (1979) Evidence for two steroid 1,2-dehydrogenase activities in Mycobacterium fortuitum. Biochim Biophys Acta 574:471–479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sukhodolskaya, G.V., Nikolayeva, V.M., Khomutov, S.M. et al. Steroid-1-dehydrogenase of Mycobacterium sp. VKM Ac-1817D strain producing 9α-hydroxy-androst-4-ene-3,17-dione from sitosterol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 867–873 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0728-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0728-4