Abstract
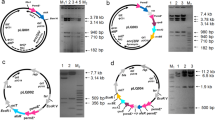
Analysis of the α-lipomycin biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces aureofaciens Tü117 led to the identification of five putative regulatory genes, which are congregated into a subcluster. Analysis of the lipReg1–4 and lipX1 showed that they encode components of two-component signal transduction systems (LipReg1 and LipReg2), multiple antibiotics resistance-type regulator (LipReg3), large ATP-binding regulators of the LuxR family-type regulator (LipReg4), and small ribonuclease (LipRegX1), respectively. A combination of targeted gene disruptions, complementation experiments, lipomycin production studies, and gene expression analysis via RT-PCR suggests that all regulatory lip genes are involved in α-lipomycin production. On the basis of the obtained data, we propose that LipReg2 controls the activity of LipReg1, which in its turn govern the expression of the α-lipomycin pathway-specific regulatory gene lipReg4. The ribonuclease gene lipX1 and the transporter regulator lipReg3 appear to work independently of genes lipReg1, lipReg2, and lipReg4.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigle B, Pang X, Decaris B, Leblond P (2005) Involvement of AlpV, a new member of the Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein family, in regulation of the duplicated type II polyketide synthase alp gene cluster in Streptomyces ambofaciens. J Bacteriol 187:2491–2500
Alekshun M, Levy S, Mealy T, Seaton B, Head J (2001) The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2, 3 A resolution. Nat Struct Biol 8:710–714
Bate N, Stratigopoulos G, Cundliffe E (2002) Differential roles of two SARP-encoding regulatory gene during tylosin biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol 43:449–458
Bate N, Bignell DRD, Cundliffe E (2006) Regulation of tylosin biosynthesis involving ‘SARP- helper’ activity. Mol Microbiol 62:148–156
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brein K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Bihlmaier C, Welle E, Hofmann C, Welzel K, Vente A, Breitling E, Muller M, Glaser S, Bechthold A (2006) Biosynthesis of the acyclic polyene antibiotic lipomycin in Streptomyces aureofaciens Tü117. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:2113–2121
Blondelet-Rouault M-H, Weiser Y, Lebrihi A, Branny P, Pernodet J (1997) Antibiotic resistance gene cassettes derived from the U` interposon for use in Escherichia coli and Streptomyces. Gene 190:315–317
Bolard J (1986) How do the polyene macrolide antibiotics affect the cellular membrane properties? Biochim Biophys Acta 864:257–304
Boos W, Shuman H (1998) Maltose/maltodextrin system of Escherichia coli: transport, metabolism and regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:204–229
Chen Y, Wendt-Pienkowski E, Shen B (2008) Identification and utility of FdmR1 as a Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein activator for fredericamycin production in Streptomyces griseus ATCC 49344 and heterologous hosts. J Bacteriol 190:5587–5596
Dylan C, Jensen A (1998) Investigation of the Streptomyces clavuligerus cephamycin C gene cluster and its regulation by the CcaR protein. J Bacteriol 180:4068–4079
Esser V, Elefson D (1970) Experiences with the Kirby–Bauer method of antibiotic susceptibility testing. Am J Clin Pathol 54:193–198
Fernandez-Moreno M, Caballero J, Hopwood D, Malpartida F (1991) The act-cluster contains regulatory and antibiotic export genes, direct targets for translational control by the bld-tRNA gene of Streptomyces. Cell 66:769–780
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith C (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155:223–229
Folcher M, Gaillard H, Nguyen L, Nguyen K, Lacroix K, Bamas-Jacques N, Rinkel M, Ch T (2001) Pleiotropic function of a Streptomyces pristinaespiralis autoregulator receptor in development, antibiotic biosynthesis, and expression of a superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 276:44297–44306
Gravenbeek M, Jones G (2008) The endonuclease activity of RNase III is required for the regulation of antibiotic production by Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 154:3547–3555
Grkovich S, Brown M, Skurray R (2002) Regulation of bacterial drug export systems. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:671–701
Gust B, Kieser T, Chater K (2002) PCR targeting system in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Guzmann LM, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J (1995) Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 177:4121–4130
Hopwood D (2007) How do antibiotic-producing bacteria ensure their self-resistance before antibiotic biosynthesis incapacitates them? Mol Microbiol 63:937–940
Horinouchi S (2007) Mining and polishing of the treasure trove in the bacterial genus Streptomyce. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:283–299
Hutchings M, Hoskisson P, Chandra G, Buttner M (2004) Sensing and responding to diverse extracellular signals? Analysis of the sensor kinase and response regulators of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiol 150:2795–2806
Kennel D (2002) Processing endoribonucleases and mRNA degradation in bacteria. J Bacteriol 184:4645–4657
Kieser T, Bibb M, Buttner M, Chater K, Hopwood D (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Köseoglu O, Kocagöz T (2004) A novel T-cloning vector system. Mikrobiyol Bul 38:239–243
Lee P, Umeyma T, Horinouchi S (2002) AfsS is a target of AfsR, a transcriptional factor with ATPase activity that globally controls secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 43:413–1430
Luzhetskyy A, Fedoryshyn M, Gromyko O, Ostash B, Rebets Y, Bechthold A, Fedorenko V (2006) IncP plasmids are most effective in mediating conjugation between Escherichia coli and Streptomyces. Genetica 42:595–601
McKenzie N, Nodwell J (2007) Phosphorylated AbsA2 negatively regulates antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor through interactions with pathway-specific regulatory gene promoters. J Bacteriol 189:5284–5292
Nuria A, Mendes M, Martin J, Aparacio J (2004) Identification of PimR as a positive regulator of pimaricin biosynthesis in Streptomyces natalensis. J Bacteriol 186:2567–2575
Nuria A, Santos-Aberturas J, Mendes M, Guerra S, Martin J, Aparacio J (2007) PimM, a PAS domain positive regulator of pimaricin biosynthesis in Streptomyces natalensis. J Bacteriol 153:3174–3183
Otten S, Ferguson J, Hutchinson R (1995) Regulation of daunorubicin production in Streptomyces peucetius by the dnrR2 locus. J Bacteriol 177:1216–1224
Pang X, Aigle B, Girardet M, Mangenot S, Pernodet L, Decaris B, Leblond P (2004) Functional angucyclin like antibiotic gene cluster in the terminal inverted repeats of Streptomyces ambofaciens liner chromosome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:575–588
Price B, Adamidis T, Kong R, Champness W (1999) A Streptomyces coelicolor antibiotic regulatory gene, absB, encodes an RNase III homolog. J Bacteriol 181:6142–6151
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Saridakis V, Shahinas D, Christendat D (2008) Structural insights on the mechanism of regulation of the MarR family of proteins: high resolution crystal structure of a transcriptional repressor from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Mol Biol 377:655–667
Sello J, Buttner M (2008) The gene encoding RNase III in Streptomyces coelicolor is transcribed during exponential phase and is required for antibiotic production and for proper sporulation. J Bacteriol 190:4079–4083
Sevcik J, Urbanikova L, Leland P, Raines R (2002) X-ray structure of two crystalline forms of a Streptomyces ribonuclease with cytotoxic activity. J Biol Chem 277:47325–47330
Sevcik J, Dauter Z, Wilson K (2004) Crystal structure reveals two alternative conformations in the active site of ribonuclease Sa2. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr D60:1198–1204
Sheldon P, Busarow S, Hutchinson R (2002) Mapping the DNA-binding domain and target sequences of the Streptomyces peucetius daunorubicin biosynthesis regulatory protein, DnrI. Mol Microbiol 44:449–460
Tahlan K, Ahn S, Sing A, Bodnaruk T, Willems A, Davidson A, Nodwell J (2007) Initiation of actinorhodin export in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 63:951–961
Wilson D, Xue Y, Reynolds K, Sherman D (2001) Characterization and analysis of the PikD regulatory factor in the picromycin biosynthetic pathway of Streptomyces venezuelae. J Bacteriol 183:3468–3475
Zhang Y, Muyrers JP, Rientjes J, Stewart AF (2003) Phage annealing proteins promote oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis in Escherichia coli and mouse ES cells. BMC Mol Biol 4:1
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the BMBF (genomic plus) grant to A.B and by the DAAD grant to L.H. (PKZ A/07/99406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Liliya Horbal and Yuriy Rebets equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horbal, L., Rebets, Y., Rabyk, M. et al. Characterization and analysis of the regulatory network involved in control of lipomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces aureofaciens Tü117. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 1069–1079 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2108-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2108-3