Abstract
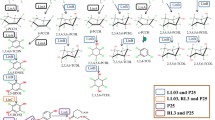
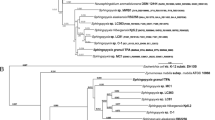
In silico analysis of nucleotide sequences flanking the recently found hydroquinone dioxygenase in Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3 revealed a gene cluster that encodes a hydroquinone catabolic pathway. In addition to the two open-reading frames encoding the recently characterized hydroquinone dioxygenase, the cluster consisted of six open-reading frames. We were able to express the three open-reading frames, hqdC, hqdD, and hqdE, and demonstrated that the three gene products, HqdC, HqdD, and HqdE had 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, maleylacetate reductase, and intradiol dioxygenase activity, respectively. Surprisingly, the gene cluster showed similarities to functionally related clusters found in members of the β- and γ-proteobacteria rather than to those found in other members of the genus Sphingomonas sensu latu.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addou S, Rentzsch R, Lee D, Orengo CA (2009) Domain-based and family-specific sequence identity thresholds increase the levels of reliable protein function transfer. J Mol Biol 387(2):416–430
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. doi:10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Bartels I, Knackmuss H-J, Reineke W (1984) Suicide inactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-halocatechols. Appl Environ Microbiol 47(3):500–505
Cai M, Xun L (2002) Organization and regulation of pentachlorophenol-degrading genes in Sphingobium chlorophenolicum ATCC 39723. J Bacteriol 184(17):4672–4680. doi:10.1128/jb.184.17.4672-4680.2002
Cerdan P, Wasserfallen A, Rekik M, Timmis KN, Harayama S (1994) Substrate specificity of catechol 2, 3-dioxygenase encoded by TOL plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida and its relationship to cell growth. J Bacteriol 176(19):6074–6081
Corvini PFX, Vinken R, Hommes G, Schmidt B, Dohmann M (2004) Degradation of the radioactive and non-labelled branched 4(3′,5′-dimethyl 3′-heptyl)-phenol nonylphenol isomer by Sphingomonas TTNP3. Biodegradation 15(1):9–18
Corvini PFX, Hollender J, Ji R, Schumacher S, Prell J, Hommes G, Priefer U, Vinken R, Schaffer A (2006a) The degradation of alpha-quaternary nonylphenol isomers by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3 involves a type II ipso-substitution mechanism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(1):114–122. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0080-0
Corvini PFX, Schaffer A, Schlosser D (2006b) Microbial degradation of nonylphenol and other alkylphenols—our evolving view. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72(2):223–243. doi:10.1007/s00253-006-0476-5
Endo R, Kamakura M, Miyauchi K, Fukuda M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M, Nagata Y (2005) Identification and characterization of genes involved in the downstream degradation pathway of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J Bacteriol 187(3):847–853. doi:10.1128/jb.187.3.847-853.2005
Gabriel FLP, Giger W, Guenther K, Kohler H-PE (2005a) Differential degradation of nonylphenol isomers by Sphingomonas xenophaga Bayram. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(3):1123–1129. doi:10.1128/aem.71.3.1123-1129.2005
Gabriel FLP, Heidlberger A, Rentsch D, Giger W, Guenther K, Kohler HPE (2005b) A novel metabolic pathway for degradation of 4-nonylphenol environmental contaminants by Sphingomonas xenophaga Bayram: ipso-hydroxylation and intramolecular rearrangement. J Biol Chem 280(16):15526–15533. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413446200
Gabriel FLP, Cyris M, Giger W, Kohler HPE (2007a) ipso-Substitution: a general biochemical and biodegradation mechanism to cleave alpha-quaternary alkylphenols and bisphenol A. Chem Biodivers 4(9):2123–2137
Gabriel FLP, Cyris M, Jonkers N, Giger W, Guenther K, Kohler HPE (2007b) Elucidation of the ipso-substitution mechanism for side-chain cleavage of alpha-quaternary 4-nonylphenols and 4-t-butoxyphenol in Sphingobium xenophagum Bayram. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(10):3320–3326. doi:10.1128/aem.02994-06
Gabriel FLP, Routledge EJ, Heidlberger A, Rentsch D, Guenther K, Giger W, Sumpter JP, Kohler HPE (2008) Isomer-specific degradation and endocrine disrupting activity of nonylphenols. Environ Sci Technol 42(17):6399–6408. doi:10.1021/es800577a
Hugo N, Armengaud J, Gaillard J, Timmis KN, Jouanneau Y (1998) A novel [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin from Pseudomonas putida mt2 promotes the reductive reactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. J Biol Chem 273(16):9622–9629
Hugo N, Meyer C, Armengaud J, Gaillard J, Timmis KN, Jouanneau Y (2000) Characterization of three XylT-like [2Fe-2S] ferredoxins associated with catabolism of cresols or naphthalene: evidence for their involvement in catechol dioxygenase reactivation. J Bacteriol 182(19):5580–5585. doi:10.1128/jb.182.19.5580-5585.2000
Hussain S, Devers-Lamrani M, El Azhari N, Martin-Laurent F (2011) Isolation and characterization of an isoproturon mineralizing Sphingomonas sp. strain SH from a French agricultural soil. Biodegradation 22(3):637–650
Kang J-H, Katayama Y, Kondo F (2006) Biodegradation or metabolism of bisphenol A: from microorganisms to mammals. Toxicology 217(2–3):81–90
Kaschabek SR, Reineke W (1995) Maleylacetate reductase of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13: specificity of substrate conversion and halide elimination. J Bacteriol 177(2):320–325
Klecka GM, Naylor CG, Staples CA, Losey B (2010) Occurrence of nonylphenol ethoxylates and their metabolites in municipal wastewater treatment plants and receiving waters. Water Environ Res 82:447–454
Kolvenbach B, Schlaich N, Raoui Z, Prell J, Zuhlke S, Schaffer A, Guengerich FP, Corvini PFX (2007) Degradation pathway of bisphenol A: does ipso substitution apply to phenols containing a quaternary alpha-carbon structure in the para position? Appl Environ Microbiol 73(15):4776–4784
Kolvenbach BA, Lenz M, Benndorf D, Rapp E, Vlcek C, Fouzek J, Gabriel FLP, Kohler H-PE, Schäffer A (2011) Purification and characterization of hydroquinone dioxygenase from Sphingonomas sp. strain TTNP3. AMB Express 1:8
Kweon O, Kim S-J, Baek S, Chae J-C, Adjei MA, Baek D-H, Kim Y-C, Cerniglia CE (2008) A new classification system for bacterial Rieske non-heme iron aromatic ring-hydroxylating oxygenases. BMC Biochem 9:11. doi:10.1186/1471-2091-9-11
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Leung KT, Tresse O, Errampalli D, Lee H, Trevors JT (1997) Mineralization of p-nitrophenol by pentachlorophenol-degrading Sphingomonas spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155(1):107–114
Leung KT, Campbell S, Gan Y, White DC, Lee HT, Trevors J (1999) The role of the Sphingomonas species UG30 pentachlorophenol-4-monooxygenase in p-nitrophenol degradation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 173(1):247–253
Lukashin AV, Borodovsky M (1998) GeneMark.hmm: new solutions for gene finding. Nucleic Acids Res 26(4):1107–1115
Manickam N, Reddy MK, Saini HS, Shanker R (2008) Isolation of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas sp. by dehalogenase assay and characterization of genes involved in γ-HCH degradation. J Appl Microbiol 104(4):952–960
Miyauchi K, Adachi Y, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1999) Cloning and sequencing of a novel meta-cleavage dioxygenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 181(21):6712–6719
Moonen MJH, Kamerbeek NM, Westphal AH, Boeren SA, Janssen DB, Fraaije MW, van Berkel WJH (2008) Elucidation of the 4-hydroxyacetophenone catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas fluorescens ACB. J Bacteriol 190(15):5190–5198. doi:10.1128/jb.01944-07
Nagata Y, Kamakura M, Endo R, Miyazaki R, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M (2006) Distribution of γ-hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading genes on three replicons in Sphingobium japonicum UT26. FEMS Microbiol Lett 256(1):112–118. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00096.x
Nagata Y, Endo R, Ito M, Ohtsubo Y, Tsuda M (2007) Aerobic degradation of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) in bacteria and its biochemical and molecular basis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76(4):741–752
Ohtsubo Y, Miyauchi K, Kanda K, Hatta T, Kiyohara H, Senda T, Nagata Y, Mitsui Y, Takagi M (1999) PcpA, which is involved in the degradation of pentachlorophenol in Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723, is a novel type of ring-cleavage dioxygenase. FEBS Lett 459(3):395–398
Polissi A, Harayama S (1993) In vivo reactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase mediated by a chloroplast-type ferredoxin: a bacterial strategy to expand the substrate specificity of aromatic degradative pathways. EMBO J 12(8):3339–3347
Raecker T, Thiele B, Boehme RM, Guenther K (2011) Endocrine disrupting nonyl- and octylphenol in infant food in Germany: considerable daily intake of nonylphenol for babies. Chemosphere 82(11):1533–1540
Rieble S, Joshi DK, Gold MH (1994) Purification and characterization of a 1, 2, 4-trihydroxybenzene 1, 2-dioxygenase from the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol 176(16):4838–4844
Sakai K, Yamanaka H, Moriyoshi K, Ohmoto T, Ohe T (2007) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and related compounds by Sphingomonas sp. strain BP-7 isolated from seawater. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(1):51–57. doi:10.1271/bbb.60351
Sasaki M, Maki J, Oshiman K, Matsumura Y, Tsuchido T (2005) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by cells and cell lysate from Sphingomonas sp. strain AO1. Biodegradation 16(5):449–459. doi:10.1007/s10532-004-5023-4
Schuler L, Jouanneau Y, Ní Chadhain S, Meyer C, Pouli M, Zylstra G, Hols P, Agathos S (2009) Characterization of a ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase from phenanthrene-degrading Sphingomonas sp. strain LH128 able to oxidize benz[a]anthracene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(3):465–475. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-1858-2
Shen W, Liu W, Zhang J, Tao J, Deng H, Cao H, Cui Z (2010) Cloning and characterization of a gene cluster involved in the catabolism of p-nitrophenol from Pseudomonas putida DLL-E4. Bioresource Tech 101(19):7516–1522
Shimojo M, Kawakami M, Amada K (2009) Analysis of genes encoding the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading enzyme from Sphingomonas agrestis 58–1. J Biosci Bioeng 108(1):56–59
Soares A, Guieysse B, Jefferson B, Cartmell E, Lester JN (2008) Nonylphenol in the environment: a critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ Int 34(7):1033–1049
Spain JC, Gibson DT (1991) Pathway for biodegradation of p-nitrophenol in a Moraxella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(3):812–819
Stolz A (2009) Molecular characteristics of xenobiotic-degrading sphingomonads. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(5):793–811. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1752-3
Tanghe T, Dhooge V, Verstraete W (1999) Isolation of a bacterial strain able to degrade branched nonylphenol. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(2):746–751
vom Saal FS, Hughes C (2005) An extensive new literature concerning low-dose effects of bisphenol A shows the need for a new risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 113(8):926–933. doi:10.1289/ehp.7713
Wei Q, Liu H, Zhang J-J, Wang S-H, Xiao Y, Zhou N-Y (2010) Characterization of a para-nitrophenol catabolic cluster in Pseudomonas sp. strain NyZ402 and construction of an engineered strain capable of simultaneously mineralizing both para- and ortho-nitrophenols. Biodegradation 21(4):575–584
Yang C-F, Lee C-M, Wang C-C (2006) Isolation and physiological characterization of the pentachlorophenol degrading bacterium Sphingomonas chlorophenolica. Chemosphere 62(5):709–714
Zhang J-J, Liu H, Xiao Y, Zhang X-E, Zhou N-Y (2009) Identification and characterization of catabolic para-nitrophenol 4-monooxygenase and para-benzoquinone reductase from Pseudomonas sp. strain WBC-3. J Bacteriol 191(8):2703–2710. doi:10.1128/jb.01566-08
Zhao H-P, Wang L, Ren J-R, Li Z, Li M, Gao H-W (2008) Isolation and characterization of phenanthrene-degrading strains Sphingomonas sp. ZP1 and Tistrella sp. ZP5. J Hazard Mater 152(3):1293–1300
Acknowledgments
BAK and FLPG were funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation grant SNF-200021-120547. JF and CV were funded by the EC Grant Agreement 265946. We thank Dr. Stefan Kaschabek (University Freiberg) for generously providing a sample of cis-butenolide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolvenbach, B.A., Dobrowinski, H., Fousek, J. et al. An unexpected gene cluster for downstream degradation of alkylphenols in Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 1315–1324 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3451-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3451-8