Abstract
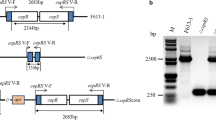
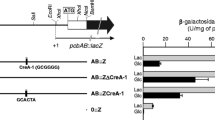
The effect of the CcaR regulatory protein on expression of the cephamycin C gene cluster is studied. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) expression analysis of the cephamycin biosynthesis genes in the ccaR-disrupted strain, S. clavuligerus ccaR::aph, revealed that in the absence of CcaR, the lat and cmcI genes expression was reduced 2,200- and 1,087-fold compared with the wild type. Expression of pcbAB–pcbC–cefD–cefE–cmcJ–cmcH and blp was 225- to 359-fold lower, while expression of pcbR–pbpA–bla and orf10 was only slightly affected if at all, indicating that resistance and regulatory genes are not under CcaR control as opposed to pathway biosynthetic genes. In the intergenic cmcH–ccaR region, a small messenger RNA (mRNA) overlaps with the cmcH transcription terminator. Deletion of 688 bp of the intergenic region results in a strain, S. clavuligerus ΔRI, still able to produce cephamycin C and clavulanic acid but at levels 30–40 % lower than the parental strain. Therefore, specific sequences in the intergenic region upstream of ccaR enhance the expression of ccaR but are not essential for its expression. Strains containing an additional ccaR gene integrated in the chromosome, S. clavuligerus pSET-PC, or multiple copies of ccaR expressed from the P glpF promoter, S. clavuligerus pAK23, were constructed. Fermentations of the pAK23 strain resulted in a 6.1-fold increase in specific cephamycin C production relative to the wild type. In the same experiments, qRT-PCR analysis of the cephamycin biosynthesis genes showed a 5.1-fold increase in ccaR expression and similar increases in expression of lat and cmcI, while expression of other cluster genes were increased in the order of 2- to 3-fold.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigle B, Wietzorrek A, Takano E, Bibb MJ (2000) A single amino acid substitution in region 1.2 of the principal sigma factor of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) results in pleiotropic loss of antibiotic production. Mol Microbiol 37:995–1004
Alexander DC, Brumlik MJ, Lee L, Jensen SE (2000) Early cephamycin biosynthetic genes are expressed from a polycistronic transcript in Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 182:348–356
Alexander DC, Jensen SE (1998) Investigation of the Streptomyces clavuligerus cephamycin C gene cluster and its regulation by the CcaR protein. J Bacteriol 180:4068–4079
Baggaley KH, Brown AG, Schofield CJ (1997) Chemistry and biosynthesis of clavulanic acid and other clavams. Nat Prod Rep 14:309–333
Baños S, Pérez-Redondo R, Koekman B, Liras P (2009) Glycerol utilization gene cluster in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(9):2991–2995
Burton K (1968) Determination of DNA concentration with diphenylamine. Methods Enzymol 12:163–166
Derveaux S, Vandesompele J, Hellemans J (2010) How to do successful gene expression analysis using real time PCR. Methods 50:227–230
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith CP (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155:223–229
Hobbs G, Frazer CM, Gardner DCJ, Cullum JA, Oliver SG (1989) Dispersed growth of Streptomyces in liquid culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:272–277
Hung TV, Malla S, Park BC, Liou KY, Lee HC, Sohng JK (2007) Enhancement of clavulanic acid by replicative and integrative expression of ccaR and cas2 in Streptomyces clavuligerus NRRL3585. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 17(9):1538–1545
Ishida K, Hung TV, Liou K, Lee HC, Shin CH, Sohng JK (2006) Characterization of pbpA and pbp2 encoding penicillin-binding proteins located on the downstream of clavulanic acid gene cluster in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Biotechnol Lett 28(6):409–417
Kim HS, Lee YJ, Lee CK, Choi SU, Yeo S, Hwang YI, Yu TS, Kinoshita H, Nihira T (2004) Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding the gamma-butyrolactone autoregulator receptor from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Arch Microbiol 182:44–50
Kovacevic S, Tobin MB, Miller JR (1990) The beta-lactam biosynthesis genes for isopenicillin N epimerase and deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase are expressed from a single transcript in Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 172:3952–3958
Li B, Walsh CT (2010) Identification of the gene cluster for the dithiolopyrrolone antibiotic holomycin in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Proc Nat Acad Sci 107(46):19731–19735
Liras P, Santamarta I, Pérez-Redondo R (2011) Clavulanic acid and clavams biosynthesis and regulation. In: Dyson P (ed) Streptomyces: Molecular biology and biotechnology. Horizon, Norwich
Liras P, Demain AL (2009) β-Lactam compounds with cephem structure produced by actinomycetes. In: Hopwood DA (ed) Complex enzymes in microbial natural product biosynthesis. Methods in enzymology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 401–429
López-García MT, Santamarta I, Liras P (2010) Morphological differentiation and clavulanic acid formation are affected in a Streptomyces clavuligerus adpA-deleted mutant. Microbiol 156:2354–2365
Martín JF, Liras P (1989) Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. Ann Rev Microbiol 43:173–206
Medema MH, Trefzer A, Kovalchuk A, van den Berg M, Muller U, Heijne W, Wu L, Alam MT, Ronning CM, Nierman WC, Bovenberg RAL, Breitling R, Takano E (2010) The sequence of a 1.8-Mb bacterial linear plasmid reveals a rich evolutionary reservoir of secondary metabolic pathways. Genome Biol Evol 2:212–224
Paget MS, Chamberlin L, Atrih A, Foster SJ, Buttner MJ (1999) Evidence that the extracytoplasmic function sigma factor (E) is required for normal cell wall structure in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 181:204–211
Paradkar AS, Aidoo KA, Wong A, Jensen SE (1996) Molecular analysis of a beta-lactam resistance gene encoded within the cephamycin gene cluster of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 178:6266–6274
Pérez-Llarena JP, Rodríguez-García A, Enguita FJ, Martín JF, Liras P (1998) The pcd gene encoding piperideine-6-carboxylate dehydrogenase involved in biosynthesis of α-aminoadipic acid is located in the cephamycin cluster of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 180:4753–4756
Pérez-Llarena FJ, Liras P, Rodríguez-García A, Martín JF (1997a) A regulatory gene (ccaR) required for cephamycin and clavulanic acid production in Streptomyces clavuligerus: amplification results in overproduction of both beta-lactam compounds. J Bacteriol 179:2053–2059
Pérez-Llarena FJ, Martín JF, Coque JJ, Fuente JL, Galleni M, Frère JM, Liras P (1997b) The bla gene of the cephamycin cluster of Streptomyces clavuligerus encodes a class A β-lactamase of low enzymatic activity. J Bacteriol 179:6035–6040
Petrich AK, Leskiw BK, Paradkar AS, Jensen SE (1994) Transcriptional mapping of the genes encoding the early enzymes of the cephamycin biosynthetic pathway of Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene 142:41–48
Petrich AK, Wu X, Roy KL, Jensen SE (1992) Transcriptional analysis of the isopenicillin N synthase-encoding gene of Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene 111(1):77–84
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Robles-Reglero V, Santamarta I, Álvarez-Álvarez R, Martín JF, Liras P (2013) Transcriptional analysis and proteomics of the holomycin gene cluster in overproducer mutants of Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Biotechnol 163:69–76
Romero J, Liras P, Martín JF (1984) Dissociation of cephamycin and clavulanic acid biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20:318–325
Santamarta I, López-García MT, Kurt A, Nárdiz N, Álvarez-Álvarez R, Pérez-Redondo R, Martín JF, Liras P (2011) Characterization of DNA-binding sequences for CcaR in the cephamycin–clavulanic acid supercluster of Streptomyces clavuligerus. Mol Microbiol 81(4):968–981
Santamarta I, Lopez-Garcia MT, Pérez-Redondo R, Koekman B, Martín JF, Liras P (2007) Connecting primary and secondary metabolism: AreB, an IclR-like protein, binds the ARE(ccaR) sequence of S. clavuligerus and modulates leucine biosynthesis and cephamycin C and clavulanic acid production. Mol Microbiol 66(2):511–524
Santamarta I, Pérez-Redondo R, Lorenzana LM, Martín JF, Liras P (2005) Different proteins bind to the butyrolactone-receptor protein ARE sequence located upstream of the regulatory ccaR gene of S. clavuligerus. Mol Microbiol 57(4):1175–1176
Santamarta I, Rodríguez-García A, Pérez-Redondo R, Martín JF, Liras P (2002) CcaR is an autoregulatory protein that binds to the ccaR and cefD-cmcI promoters of the cephamycin C-clavulanic acid cluster in Streptomyces clavuligerus. J Bacteriol 184:3106–3113
Song JY, Jeong H, Yu DS, Fischbach MA, Park HS, Kim JJ, Seo JS, Jensen SE, Oh TK, Lee KJ, Kim JF (2010) Draft genome sequence of Streptomyces clavuligerus NRRL 3585, a producer of diverse secondary metabolites. J Bacteriol 192(23):6317–6318
Thai W, Paradkar AS, Jensen SE (2001) Construction and analysis of ss-lactamase-inhibitory protein (BLIP) non-producer mutants of Streptomyces clavuligerus. Microbiol-SGM 147:325–335
Wang L, Tahlan K, Kaziuk TL, Alexander DC, Jensen SE (2004) Transcriptional and translational analysis of the ccaR gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Microbiol-SGM 150(12):4137–4145
Ward JM, Hodgson JE (1993) The biosynthetic genes for clavulanic acid and cephamycin production occurs as a supercluster in three Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 110:239–242
Wilkinson CJ, Hughes-Thomas ZA, Martin CJ, Bohm I, Mironenko T, Deacon M, Wheatcroft M, Wirtz G, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (2002) Increasing the efficiency of heterologous promoters in actinomycetes. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 4(4):417–426
Acknowledgment
We gratefully acknowledge the Scientific and Technological Organization of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) grant number TBAG-109T962, for supporting this study. A.K. was supported by the METU Faculty Development Program (FDP). P.L. acknowledges the support of grant Bio2009-09820 from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitivity. R.A. was supported by a fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Education. We acknowledge Juan F. Martín and Jacqueline Piret for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 127 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurt, A., Álvarez-Álvarez, R., Liras, P. et al. Role of the cmcH–ccaR intergenic region and ccaR overexpression in cephamycin C biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 5869–5880 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4721-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4721-4