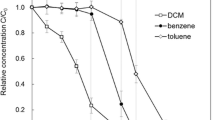
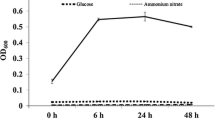
Abstract
Persistent use of the diphenyl ether herbicides oxyfluorfen may seriously increase the health risks and ecological safety problems. A newly bacterium R-21 isolated from active soil was able to degrade and utilize oxyfluorfen as the sole carbon source. R-21 was identified as Chryseobacterium aquifrigidense by morphology, physiobiochemical characteristics, and genetic analysis. Under the optimum cultural conditions (pH 6.9, temperature 33.4 °C, and inoculum size 0.2 g L−1), R-21 could degrade 92.1 % of oxyfluorfen at 50 mg L−1 within 5 days. During oxyfluorfen degradation, six metabolites were detected and identified by atmospheric pressure gas chromatography coupled to quadrupole–time of flight mass spectrometry and ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole–time of flight mass spectrometry, and a plausible degradation pathway was deduced. Strain R-21 is a promising potential in bioremediation of oxyfluorfen-contaminated environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arulkumar M, Sathishkumar P, Palvannan T (2011) Optimization of Orange G dye adsorption by activated carbon of Thespesia populnea pods using response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 186(1):827–834
Brown J, Brown R (2012) Process optimization of an auger pyrolyzer with heat carrier using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 103(1):405–414
Chakraborty S, Bhattacharyya A, Chowdhury A (2002) Degradation of oxyfluorfen by Azotobacter chroococcum (Beijerink). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69(2):203–209
Chen S, Dong YH, Chang C, Deng Y, Zhang XF, Zhong G, Song H, Hu M, Zhang L-H (2013a) Characterization of a novel cyfluthrin-degrading bacterial strain Brevibacterium aureum and its biochemical degradation pathway. Bioresour Technol 132:16–23
Chen S, Dong YH, Chang C, Deng Y, Zhang XF, Zhong G, Song H, Hu M, Zhang L-H (2013b) Characterization of a novel cyfluthrin-degrading bacterial strain Brevibacterium aureum and its biochemical degradation pathway. Bioresour Technol 132:16–23
Chen S, Hu M, Liu J, Zhong G, Yang L, Rizwan-ul-Haq M, Han H (2011a) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a novel Ochrobactrum lupini DG-S-01. J Hazard Mater 187(1):433–440
Chen S, Hu W, Xiao Y, Deng Y, Jia J, Hu M (2012) Degradation of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid by a Bacillus sp. PLoS One 7(11):e50456
Chen S, Lai K, Li Y, Hu M, Zhang Y, Zeng Y (2011b) Biodegradation of deltamethrin and its hydrolysis product 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde by a newly isolated Streptomyces aureus strain HP-S-01. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(4):1471–1483
Feng ZZ, Li QF, Zhang J, Zhang J, Huang X, Lu P, Li SP (2012) Microbial degradation of fomesafen by a newly isolated strain Pseudomonas zeshuii BY-1 and the biochemical degradation pathway. J Agric Food Chem 60(29):7104–7110
Gangadharan D, Sivaramakrishnan S, Nampoothiri KM, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2008) Response surface methodology for the optimization of alpha amylase production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4597–4602
Hassanein HM (2002) Toxicological effects of the herbicide oxyfluorfen on acetylcholinesterase in two fish species: Oreochromis niloticus and Gambusia affinis. J Environ Sci Health A 37(4):521–527
He J, Zhen Q, Qiu N, Liu Z, Wang B, Shao Z, Yu Z (2009) Medium optimization for the production of a novel bioflocculant from Halomonas sp. V3astimization for the production of a. Bioresour Technol 100(23):5922–5927
Hiratsuka N, Wariishi H, Tanaka H (2001) Degradation of diphenyl ether herbicides by the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Coriolus versicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57(4):563–571
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PH, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) International edition: Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Co.
Kamei I, Kondo R (2006) Simultaneous degradation of commercially produced CNP herbicide and of contaminated dioxin by treatment using the white-rot fungus Phlebia brevispora. Chemosphere 65(7):1221–1227
Keum YS, Lee YJ, Kim J-H (2008) Metabolism of nitrodiphenyl ether herbicides by dioxin-degrading bacterium Sphingomonas wittichii RW1. J Agric Food Chem 56(19):9146–9151
Liang B, Lu P, Li H, Li R, Li S, Huang X (2009) Biodegradation of fomesafen by strain Lysinibacillus sp. ZB-1 isolated from soil. Chemosphere 77(11):1614–1619
Liang B, Zhao Y-k LP, S-p L, Huang X (2010) Biotransformation of the diphenyl ether herbicide lactofen and purification of a lactofen esterase from Brevundimonas sp. LY-2. J Agric Food Chem 58(17):9711–9715
Luong J (1987) Generalization of Monod kinetics for analysis of growth data with substrate inhibition. Biotechnol Bioeng 29(2):242–248
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Qiu J, Zheng J, Zhang J, Li S, He J (2010) Isolation, identification and characteristics of a fluoroglycofen-ethyl-degrading bacterium YF1. Chinese J App Environ Biol 2009(5):686–691
Rio B, Parent-Massin D, Lautraite S, Hoellinger H (1997) Effects of a diphenyl-ether herbicide, oxyfluorfen, on human BFU-E/CFU-E development and haemoglobin synthesis. Hum Exp Toxicol 16(2):115–122
Roberts T, Hutson D, Lee P, Nicholls P (1998) Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals: Pt. 1, Herbicides and plant growth regulators. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry
Schmidt S, Wittich R, Erdmann D, Wilkes H, Francke W, Fortnagel P (1992) Biodegradation of diphenyl ether and its monohalogenated derivatives by Sphingomonas sp. strain SS3. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(9):2744–2750
Shen X-H, Zhou N-Y, Liu S-J (2012) Degradation and assimilation of aromatic compounds by Corynebacterium glutamicum: another potential for applications for this bacterium? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(1):77–89
Singh BK, Walker A, Wright DJ (2006) Bioremedial potential of fenamiphos and chlorpyrifos degrading isolates: influence of different environmental conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 38(9):2682–2693
Song J, Gu J, Zhai Y, Wu W, Wang H, Ruan Z, Shi Y, Yan Y (2013) Biodegradation of nicosulfuron by a Talaromyces flavus LZM1. Bioresour Technol 140:243–248
Tomlin CDS (2001) The e-pesticide manual, 15th edition. version 5.0. British Crop Protection Council
Vidali M (2001) Bioremediation. An overview. Pure Appl Chem 73(7):1163–1172
Villarreal DT, Turco RF, Konopka A (1991) Propachlor degradation by a soil bacterial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(8):2135–2140
Xiao Y, Chen S, Gao Y, Hu W, Hu M, Zhong G (2015) Isolation of a novel beta-cypermethrin degrading strain Bacillus subtilis BSF01 and its biodegradation pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(6):2849–2859
Xu J, Li X, Xu Y, Qiu L, Pan C (2009) Biodegradation of pyrazosulfuron-ethyl by three strains of bacteria isolated from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 74(5):682–687
Yen J-H, Sheu W-S, Wang Y-S (2003) Dissipation of the herbicide oxyfluorfen in subtropical soils and its potential to contaminate groundwater. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 54(2):151–156
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171879, 31371968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 410 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Xu, J., Dong, F. et al. Characterization of a novel oxyfluorfen-degrading bacterial strain Chryseobacterium aquifrigidense and its biochemical degradation pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 6837–6845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7504-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7504-x