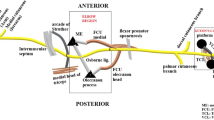
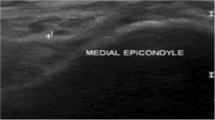
Abstract
Impingement/entrapment of the ulnar nerve by the intermuscular septum at the distal arm is a common cause of recurrent or recalcitrant ulnar neuropathy following ulnar nerve decompression or anterior transposition. Primary entrapment/impingement of the ulnar nerve along the intermuscular septum may also occur. Evaluation with both ultrasound (US) and MRI can identify entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the intermuscular septum, while dynamic assessment with US can also identify dynamic subluxation of the ulnar nerve over the intermuscular septum.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assmus H, Antoniadis G, Bischoff C, Hoffmann R, Martini AK, Preissler P, et al. Cubital tunnel syndrome - a review and management guidelines. Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2011;72(2):90–8.
Novak CB, Mackinnon SE. Selection of operative procedures for cubital tunnel syndrome. Hand (N Y). 2009;4(1):50–4.
Zhong S, Zhong Z, Yu Y, Yang L, Gao Y, Song J, et al. Ultrasonic observation and clinical application of Arcade of Struthers in the mid-arm. World Neurosurg. 2016;91:560-6.e1.
Kholinne E, Alsharidah MM, Almutair O, Aljasser S, Alhothali W, Kwak JM, et al. Revision surgery for refractory cubital tunnel syndrome: a systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2019;105(5):867–76.
Hanandeh A, Mani VR, Bauer P, Ramcharan A, Donaldson B. Identification and surgical management of upper arm and forearm compartment syndrome. Cureus. 2019;11(10):e5862.
Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. In: Lewis WH, editor. IV. Myology, 7d. The Muscles and Fasciæ of the Arm. New York: Bartleby .com; 2000. https://www.bartleby.com/107/124.html.
Nakajima M, Ono N, Kojima T, Kusunose K. Ulnar entrapment neuropathy along the medial intermuscular septum in the midarm. Muscle Nerve. 2009;39(5):707–10.
Dellon AL. Musculotendinous variations about the medial humeral epicondyle. J Hand Surg Br. 1986;11(2):175–81.
Tubbs RS, Deep A, Shoja MM, Mortazavi MM, Loukas M, Cohen-Gadol AA. The arcade of Struthers: an anatomical study with potential neurosurgical significance. Surg Neurol Int. 2011;2:184.
Chadwick N, Morag Y, Smith BW, Yablon C, Kim SM, Yang LJ. Imaging appearance following surgical decompression of the ulnar nerve. Br J Radiol. 2019;92(1094):20180757.
Green JR Jr, Rayan GM. The cubital tunnel: anatomic, histologic, and biomechanical study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;8(5):466–70.
Felder JM 3rd, Mackinnon SE, Patterson MM. The 7 structures distal to the elbow that are critical to successful anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve. Hand (N Y). 2019;14(6):776–81.
Dellon AL. Techniques for successful management of ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1991;2(1):57–73.
Caetano EB, Sabongi Neto JJ, Vieira LA, Caetano MF. The arcade of Struthers: an anatomical study and clinical implications. Rev Bras Ortop. 2017;52(3):331–6.
Tang P, Hoellwarth JS, Chauhan A. Recurrent cubital tunnel syndrome: a critical analysis review. JBJS Rev. 2016. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.O.00022.
Sivak WN, Hagerty SE, Huyhn L, Jordan AC, Munin MC, Spiess AM. Diagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment at the arcade of struthers with electromyography and ultrasound. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2016;4(3):e648.
von Schroeder HP, Scheker LR. Redefining the “Arcade of Struthers”. J Hand Surg Am. 2003;28(6):1018–21.
Siqueira MG, Martins RS. The controversial arcade of Struthers. Surg Neurol. 2005;64(Suppl 1:S1):17–20 (discussion S1:-1).
de Ruiter GCW, de Jonge JGH, Vlak MHM, van Loon-Felter AE. Ulnar neuropathy caused by muscular Arcade of Struthers. World Neurosurg. 2020;142:128–30.
Karatas A, Apaydin N, Uz A, Tubbs R, Loukas M, Gezen F. Regional anatomic structures of the elbow that may potentially compress the ulnar nerve. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(4):627–31.
Ochiai N, Hayashi T, Ninomiya S. High ulnar nerve palsy caused by the arcade of Struthers. J Hand Surg Br. 1992;17(6):629–31.
O’Hara JJ, Stone JH. Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow caused by a prominent medial head of the triceps and an anconeus epitrochlearis muscle. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(1):133–5.
Novak CB, Mehdian H, von Schroeder HP. Laxity of the ulnar nerve during elbow flexion and extension. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(6):1163–7.
Wright TW, Glowczewskie F Jr, Cowin D, Wheeler DL. Ulnar nerve excursion and strain at the elbow and wrist associated with upper extremity motion. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26(4):655–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (M4V 1540 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morag, Y., Popadich, M., Chang, K. et al. Imaging the intermuscular septum in the context of ulnar neuropathy. Skeletal Radiol 51, 505–511 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-021-03835-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-021-03835-3