Abstract
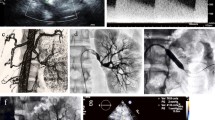
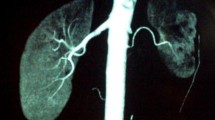
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) describes a group of conditions which cause nonatheromatous arterial stenoses, most commonly of the renal and carotid arteries, typically in young women. We report a rare case of bilateral segmental renal infarction secondary to FMD in a young male patient. His initial presentation with loin pain and pyrexia resulted in a delay in the definitive diagnosis of FMD. He was successfully treated with bilateral balloon angioplasty. The delayed diagnosis in this patient until the condition had progressed to bilateral renal infarcts highlights the need for prompt investigation and diagnosis of suspected cases of FMD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lüscher TF, Lie JT, Stanson AW et al (1987) Arterial fibromuscular dysplasia. Mayo Clin Proc 62(10):931–952
Slovut DP, Olin JW (2004) Fibromuscular dysplasia. N Engl J Med 350(18):1862–7181
Salifu MO, Gordon DH, Friedman EA et al (2000) Bilateral renal infarction in a black man with medial fibromuscular dysplasia. Am J Kidney Dis 36(1):184–189
Stinchcombe SJ, Manhire AR, Bishop MC et al (1992) Renal arterial fibromuscular dysplasia: acute renal infarction in three patients with angiographic evidence of medial fibroplasia. Br J Radiol 65(769):81–84
Siegelbaum MH, Weiss JP (1990) Renal infarction secondary to fibrous dysplasia and aneurysm formation of renal artery. Urology 35(1):73–75
Barbey F, Matthieu C, Nseir G et al (2003) A young man with a renal colic. J Intern Med 254(6):605–608
Stewart BH, Dustan HP, Kiser WS et al (1970) Correlation of angiography and natural history in evaluation of patients with renovascular hypertension. J Urol 104(2):231–238
Harrison EG Jr, McCormack LJ (1971) Pathologic classification of renal arterial disease in renovascular hypertension. Mayo 46(3):161–167
Kincaid OW, Davis GD, Hallermann FJ et al (1968) Fibromuscular dysplasia of the renal arteries. Arteriographic features, classification, and observations on natural history of the disease. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 104(2):271–282
Begelman SM, Olin JW (2000) Fibromuscular dysplasia. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12(1):41–47
Stanley JC, Gewertz BL, Bove EL et al (1975) Arterial fibrodysplasia. Histopathologic character and current etiologic concepts. Arch Surg 110(5):561–566
Stanley JC (1996) Renal artery fibrodysplasia. In: Novick AC, Scable J, Hamilton G (eds) Renal vascular disease. WB Saunders, London, pp 21–23
Alimi Y, Mercier C, Péllissier JF et al (1992) Fibromuscular disease of the renal artery: a new histopathologic classification. Ann Vasc Surg 6(3):220–224
Safian RD, Textor SC (2001) Renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 344(6):431–442
Goncharenko V, Gerlock AJ Jr, Shaff MI et al (1981) Progression of renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia in 42 patients as seen on angiography. Radiology 139(1):45–51
Sinnamon K, McNally D, Harty J (2007) Fibromuscular dysplasia presenting as renal infarction. Kidney Int 72(10):1295–1296
Domanovits H, Paulis M, Nikfardjam M et al (1999) Acute renal infarction. Clinical characteristics of 17 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 78(6):386–394
Chu P, Wei Y, Huang J et al (2006) Clinical characteristics of patients with segmental renal infarction. Nephrology 11(4):336–340
Sabharwal R, Viatica P, Coleman P (2007) Multidetector spiral CT renal angiography in the diagnosis of renal artery fibromuscular dysplasia. Eur J Radiol 61(3):520–527
de Fraissinette B, Garcier JM, Dieu V et al (2003) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of dysplastic stenoses of the renal artery: results on 70 adults. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 26(1):46–51
Tanaka R, Higashi M, Naito H (2007) Angioplasty for non-arteriosclerotic renal artery stenosis: the efficacy of cutting balloon angioplasty versus conventional angioplasty. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 30(4):601–606
Tanemoto M, Abe T, Chaki T et al (2005) Cutting balloon angioplasty of resistant renal artery stenosis caused by fibromuscular dysplasia. J Vasc Surg 41(5):898–901
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doody, O., Adam, W.R., Foley, P.T. et al. Fibromuscular Dysplasia Presenting with Bilateral Renal Infarction. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 329–332 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9363-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9363-z