Abstract
Purpose
Pharmacokinetic interaction of sunitinib with diclofenac, paracetamol, mefenamic acid and ibuprofen was evaluated due to their P450 mediated metabolism and OATP1B1, OATP1B3, ABCB1, ABCG2 transporters overlapping features.
Methods
Male and female mice were administered 6 sunitinib doses (60 mg/kg) PO every 12 h and 30 min before the last dose were administered vehicle (control groups), 250 mg/kg paracetamol, 30 mg/kg diclofenac, 50 mg/kg mefenamic acid or 30 mg/kg ibuprofen (study groups), euthanized 6 h post last administration and sunitinib plasma, liver, kidney, brain concentrations analyzed.
Results
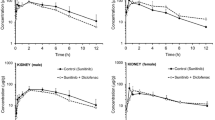
Ibuprofen halved sunitinib plasma concentration in female mice (p < 0.01) and showed 59 % lower concentration than male mice (p < 0.05). Diclofenac and paracetamol female mice showed 45 and 25 % higher plasma concentrations than male mice which were 27 % lower in mefenamic acid female mice. Paracetamol increased 2.2 (p < 0.05) liver and 1.4-fold (p < 0.05) kidney sunitinib concentrations in male mice that were lower in female mice (p < 0.01, p < 0.001, respectively). Ibuprofen increased 2.9-fold (p < 0.01) liver concentration in male mice that were higher than in female mice (p < 0.001). Female control mice had 35 % higher sunitinib brain concentration than male mice but the concentration decreased 37, 33, 10 and 57 % in the diclofenac, paracetamol, mefenamic acid and ibuprofen (p < 0.001), respectively. Tissue–plasma concentrations correlations were nonsignificant in control, paracetamol, mefenamic acid and ibuprofen groups but was significant in the diclofenac group in male mice (liver, brain) and female mice (liver, kidney).
Conclusions
These results portray gender-based sunitinib pharmacokinetic differences and NSAIDs selective effects on male or female mice, with potential clinical translatability.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Erp NP, Gelderblom H, Guchelaar H-J (2009) Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev 35:692–706. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2009.08.004
Kusuda Y, Miyake H, Terakawa T, Furukawa J, Muramaki M, Fujisawa M (2011) Treatment of brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma with sunitinib and radiotherapy: our experience and review of the literature. Int J Urol 18:326–329
Hatipoglu G, Hock SW, Weiss R, Fan Z, Sehm T, Ghoochani A, Buchfelder M, Savaskan NE, Eyüpoglu IY (2015) Sunitinib impedes brain tumor progression and reduces tumor-induced neurodegeneration in the microenvironment. Cancer Sci 106:160–170. doi:10.1111/cas.12580
Koutras AK, Krikelis D, Alexandrou N, Starakis I, Kalofonos HP (2007) Brain metastasis in renal cell cancer responding to sunitinib. Anticancer Res 27:4255–4257
Hu S, Chen Z, Franke R, Orwick S, Zhao M, Rudek MA, Sparreboom A, Baker SD (2009) Interaction of the multikinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib with solute carriers and ATP-binding cassette transporters. Clin Cancer Res 15:6062–6069. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0048
Zimmerman EI, Hu S, Roberts JL, Gibson AA, Orwick SJ, Li L, Sparreboom A, Baker SD (2013) Contribution of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 to the disposition of sorafenib and sorafenib-glucuronide. Clin Cancer Res 19:1458–1466. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3306
Tang SC, Lagas JS, Lankheet NAG, Poller B, Hillebrand MJ, Rosing H, Beijnen JH, Schinkel AH (2012) Brain accumulation of sunitinib is restricted by P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) and can be enhanced by oral elacridar and sunitinib coadministration. Int J Cancer 130:223–233. doi:10.1002/ijc.26000
Bowlin SJ, Xia F, Wang W, Robinson KD, Stanek EJ (2013) Twelve-month frequency of drug-metabolizing enzyme and transporter-based drug-drug interaction potential in patients receiving oral enzyme-targeted kinase inhibitor antineoplastic agents. Mayo Clin Proc 88:139–148. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.10.020
Lau CLL, Chan ST, Selvaratanam M, Khoo HW, Lim AYL, Modamio P, Mariño EL, Segarra I (2015) Sunitinib-ibuprofen drug interaction affects the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of sunitinib to brain, liver, and kidney in male and female mice differently. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 29:404–416. doi:10.1111/fcp.12126
Chee EL-C, Lim AYL, Modamio P, Fernandez-Lastra C, Segarra I (2015) Sunitinib tissue distribution changes after coadministration with ketoconazole in mice. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 41:309–319. doi:10.1007/s13318-015-0264-7
Segarra I, Modamio P, Fernández C, Mariño EL (2016) Sunitinib possible sex-divergent therapeutic outcomes. Clin Drug Investig. doi:10.1007/s40261-016-0428-5
Mitra R, Jones S (2012) Adjuvant analgesics in cancer pain: a review. Am J Hosp Palliat Care 29:70–79. doi:10.1177/1049909111413256
Weise AM, Liu CY, Shields AF (2009) Fatal liver failure in a patient on acetaminophen treated with sunitinib malate and levothyroxine. Ann Pharmacother 43:761–766. doi:10.1345/aph.1L528
van der Veldt AA, Boven E, Helgason HH, van Wouwe M, Berkhof J, de Gast G, Mallo H, Tillier CN, van den Eertwegh AJ, Haanen JB (2008) Predictive factors for severe toxicity of sunitinib in unselected patients with advanced renal cell cancer. Br J Cancer 99:259–265. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604456
Lim AYL, Segarra I, Chakravarthi S, Akram S, Judson JP (2010) Histopathology and biochemistry analysis of the interaction between sunitinib and paracetamol in mice. BMC Pharmacol 10:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2210-10-14
Tan JR, Chakravarthi S, Judson JP, Haleagrahara N, Segarra I (2013) Potential protective effect of sunitinib after administration of diclofenac: biochemical and histopathological drug-drug interaction assessment in a mouse model. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386:619–633. doi:10.1007/s00210-013-0861-4
Tan SY, Kan E, Lim WY, Chay G, Law JHK, Soo GW, Bukhari NI, Segarra I (2011) Metronidazole leads to enhanced uptake of imatinib in brain, liver and kidney without affecting its plasma pharmacokinetics in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:918–925. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01296.x
Soo GW, Law JHK, Kan E, Tan SY, Lim WY, Chay G, Bukhari NI, Segarra I (2010) Differential effects of ketoconazole and primaquine on the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of imatinib in mice. Anticancer Drugs 21:695–703
Waxman DJ, Holloway MG (2009) Sex differences in the expression of hepatic drug metabolizing enzymes. Mol Pharmacol 76:215–228. doi:10.1124/mol.109.056705
Cui YJ, Cheng X, Weaver YM, Klaassen CD (2009) Tissue distribution, gender-divergent expression, ontogeny, and chemical induction of multidrug resistance transporter genes (Mdr1a, Mdr1b, Mdr2) in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 37:203–210. doi:10.1124/dmd.108.023721
Sarda S, Page C, Pickup K, Schulz-Utermoehl T, Wilson I (2012) Diclofenac metabolism in the mouse: novel in vivo metabolites identified by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Xenobiotica 42:179–194. doi:10.3109/00498254.2011.607865
Boelsterli UA (2003) Diclofenac-induced liver injury: a paradigm of idiosyncratic drug toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 192:307–322
Ohyama K, Murayama N, Shimizu M, Yamazaki H (2014) Drug interactions of diclofenac and its oxidative metabolite with human liver microsomal cytochrome P450 1A2-dependent drug oxidation. Xenobiotica 44:10–16. doi:10.3109/00498254.2013.806837
El-Sheikh AAK, van den Heuvel JJMW, Koenderink JB, Russel FGM (2007) Interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with multidrug resistance protein (MRP) 2/ABCC2- and MRP4/ABCC4-mediated methotrexate transport. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:229–235. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.110379
Jemnitz K, Heredi-Szabo K, Janossy J, Ioja E, Vereczkey L, Krajcsi P (2010) ABCC2/Abcc2: a multispecific transporter with dominant excretory functions. Drug Metab Rev 42:402–436. doi:10.3109/03602530903491741
Kindla J, Müller F, Mieth M, Fromm MF, König J (2011) Influence of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1- and OATP1B3-mediated drug transport. Drug Metab Dispos 39:1047–1053. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.037622
Slosky LM, Thompson BJ, Sanchez-Covarrubias L, Zhang Y, Laracuente M-L, Vanderah TW, Ronaldson PT, Davis TP (2013) Acetaminophen modulates P-glycoprotein functional expression at the blood-brain barrier by a constitutive androstane receptor-dependent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 84:774–786. doi:10.1124/mol.113.086298
McGill MR, Jaeschke H (2013) Metabolism and disposition of acetaminophen: recent advances in relation to hepatotoxicity and diagnosis. Pharm Res 30:2174–2187. doi:10.1007/s11095-013-1007-6
Novak A, Carpini GD, Ruiz ML, Luquita MG, Rubio MC, Mottino AD, Ghanem CI (2013) Acetaminophen inhibits intestinal p-glycoprotein transport activity. J Pharm Sci 102:3830–3837. doi:10.1002/jps.23673
Cimolai N (2013) The potential and promise of mefenamic acid. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 6:289–305. doi:10.1586/ecp.13.15
Takara K, Hayashi R, Kokufu M, Yamamoto K, Kitada N, Ohnishi N, Yokoyama T (2009) Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the expression and function of P-glycoprotein/MDR1 in Caco-2 cells. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:332–337. doi:10.1080/01480540903130658
Wiwattanawongsa K, Tantishaiyakul V, Lomlim L, Rojanasakul Y, Pinsuwan S, Keawnopparat S (2005) Experimental and computational studies of epithelial transport of mefenamic acid ester prodrugs. Pharm Res 22:721–727. doi:10.1007/s11095-005-2587-6
Mazaleuskaya LL, Theken KN, Gong L, Thorn CF, FitzGerald GA, Altman RB, Klein TE (2014) PharmGKB summary: ibuprofen pathways. Pharmacogenet Genomics. doi:10.1097/FPC.0000000000000113
Hou W-Y, Xu S-F, Zhu Q-N, Lu Y-F, Cheng X-G, Liu J (2014) Age- and sex-related differences of organic anion-transporting polypeptide gene expression in livers of rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:370–377. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.020
Maher JM, Slitt AL, Cherrington NJ, Cheng X, Klaassen CD (2005) Tissue distribution and hepatic and renal ontogeny of the multidrug resistance-associated protein (Mrp) family in mice. Drug Metab Dispos 33:947–955. doi:10.1124/dmd.105.003780
Breljak D, Brzica H, Sweet DH, Anzai N, Sabolic I (2013) Sex-dependent expression of Oat3 (Slc22a8) and Oat1 (Slc22a6) proteins in murine kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304:F1114–F1126. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00201.2012
Lankheet NA, Kloth JS, Gadellaa-van Hooijdonk CG, Cirkel GA, Mathijssen RH, Lolkema MP, Schellens JH, Voest EE, Sleijfer S, de Jonge MJ, Haanen JB, Beijnen JH, Huitema AD, Steeghs N (2014) Pharmacokinetically guided sunitinib dosing: a feasibility study in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 110:2441–2449. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.194
Lankheet NAG, Knapen LM, Schellens JHM, Beijnen JH, Steeghs N, Huitema ADR (2014) Plasma concentrations of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib, erlotinib, and sunitinib in routine clinical outpatient cancer care. Ther Drug Monit 36:326–334. doi:10.1097/FTD.0000000000000004
Gore ME, Szczylik C, Porta C, Bracarda S, Bjarnason GA, Oudard S, Lee S-H, Haanen J, Castellano D, Vrdoljak E, Schöffski P, Mainwaring P, Hawkins RE, Crinò L, Kim TM, Carteni G, Eberhardt WEE, Zhang K, Fly K, Matczak E, Lechuga MJ, Hariharan S, Bukowski R (2015) Final results from the large sunitinib global expanded-access trial in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 113:12–19. doi:10.1038/bjc.2015.196
Bamias A, Tzannis K, Beuselinck B, Oudard S, Escudier B, Diosynopoulos D, Papazisis K, Lang H, Wolter P, de Guillebon E, Stravodimos K, Chrisofos M, Fountzilas G, Elaidi R-T, Dimopoulos MA, Bamia C (2013) Development and validation of a prognostic model in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib: a European collaboration. Br J Cancer 109:332–341. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.341
Mizuno T, Fukudo M, Fukuda T, Terada T, Dong M, Kamba T, Yamasaki T, Ogawa O, Katsura T, Inui K-I, Vinks AA, Matsubara K (2014) The effect of ABCG2 genotype on the population pharmacokinetics of sunitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Ther Drug Monit 36:310–316. doi:10.1097/FTD.0000000000000025
Akaza H, Naito S, Ueno N, Aoki K, Houzawa H, Pitman Lowenthal S, Lee S-Y (2015) Real-world use of sunitinib in Japanese patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: efficacy, safety and biomarker analyses in 1689 consecutive patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45:576–583. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyv045
Sun T, Plutynski A, Ward S, Rubin JB (2015) An integrative view on sex differences in brain tumors. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:3323–3342. doi:10.1007/s00018-015-1930-2
Narjoz C, Cessot A, Thomas-Schoemann A, Golmard JL, Huillard O, Boudou-Rouquette P, Behouche A, Taieb F, Durand JP, Dauphin A, Coriat R, Vidal M, Tod M, Alexandre J, Loriot MA, Goldwasser F, Blanchet B (2015) Role of the lean body mass and of pharmacogenetic variants on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sunitinib in cancer patients. Invest New Drugs 33:257–268. doi:10.1007/s10637-014-0178-2
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the International Medical University for financial support: B1/07-Res(09)2010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, S.Y., Wong, M.M., Tiew, A.L.W. et al. Sunitinib DDI with paracetamol, diclofenac, mefenamic acid and ibuprofen shows sex-divergent effects on the tissue uptake and distribution pattern of sunitinib in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78, 709–718 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3120-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3120-9