Abstract
Introduction
Central nervous system (CNS) relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is usually fatal. Risk stratification of patients has historically been poorly defined, and CNS prophylaxis with high-dose methotrexate (HDMTX) can be associated with multiple toxicities. The CNS International Prognostic Index (IPI) defines three patient risk groups for CNS disease. The aims of this study were to evaluate the toxicity of HDMTX and describe outcomes in HDMTX and non-HDMTX patients according to the CNS-IPI.
Methods
205 patients diagnosed with DLBCL between 2004 and 2014, initially treated with RCHOP-like chemotherapy and considered for HDMTX CNS prophylaxis were identified by pharmacy records at two teaching hospitals. Patient records were retrospectively reviewed for HDMTX toxicity, CNS-IPI calculation and CNS relapse.
Results
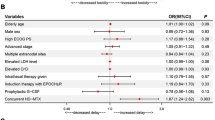
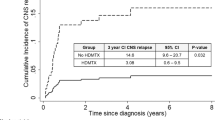
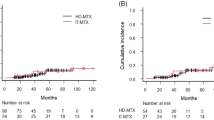
28 patients with DLBCL were selected for two doses of HDMTX. Two of 28 patients received only one dose, and three had their second dose reduced due to renal impairment. 28% of patients experienced nephrotoxicity. 24 HDMTX and 122 non-HDMTX patients were evaluable for the CNS-IPI. No significant difference in the CNS-IPI distribution between the two groups was identified (p = 0.695). Five patients had CNS relapse, two who received HDMTX and three who did not. No significant difference in CNS relapse rate was identified between 24 HDMTX patients propensity-matched to 24 non-HDMTX patients.
Conclusions
HDMTX was well-tolerated by patients. Application of the CNS-IPI identifies a different population of candidates for CNS prophylaxis compared to traditional criteria.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DLBCL:
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- HDMTX:
-
Systemic high-dose methotrexate
- ITMTX:
-
Intrathecal methotrexate
- IPI:
-
International Prognostic Index
- ECOG:
-
Eastern Collaborative Oncology Group
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- DSHNHL:
-
German high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma study group
- RCHOP:
-
Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisolone
- CTCAE:
-
Common terminology criteria for adverse events
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
References
Martelli M, Ferreri AJM, Agostinelli C, Di Rocco A, Pfreundschuh M, Pileri SA (2013) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 87(2):146–171
Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Glass B, Kaiser U, Cavallin-Stahl E, Wolf M et al (2012) CNS disease in younger patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma: an analysis of patients treated on the Mabthera International Trial and trials of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Study Group. Ann Oncol 23(5):1267–1273
Kridel R, Dietrich PY (2011) Prevention of CNS relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncol. 12(13):1258–1266
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Brière J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R et al (2002) CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. New Engl J Med 346(4):235–242
Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S et al (2010) Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d'Etudes des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. Blood 116(12):2040–2045
Ghose A, Kundu R, Latif T (2014) Prophylactic CNS directed therapy in systemic diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 91(3):292–303
Boehme V, Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Loeffler M, Pfreundschuh M (2009) CNS events in elderly patients with aggressive lymphoma treated with modern chemotherapy (CHOP-14) with or without rituximab: an analysis of patients treated in the RICOVER-60 trial of the German High-Grade Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Study Group (DSHNHL). Blood 113(17):3896–3902
Yamamoto W, Tomita N, Watanabe R, Hattori Y, Nakajima Y, Hyo R et al (2010) Central nervous system involvement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 85(1):6–10
Arkenau HT, Chong G, Cunningham D, Watkins D, Agarwal R, Sirohi B et al (2007) The role of intrathecal chemotherapy prophylaxis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 18(3):541–545
Tomita N, Takasaki H, Ishiyama Y, Kishimoto K, Ishibashi D, Koyama S et al (2015) Intrathecal methotrexate prophylaxis and central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma following rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone. Leukemia Lymphoma 56(3):725–729
Korfel A (2011) Prevention of central nervous system relapses in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: which patients and how? Curr Opin Oncol 23(5):436–440
Kwong Y-L, Yeung DYM, Chan JCW (2008) Intrathecal chemotherapy for hematologic malignancies: drugs and toxicities. Ann Hematol 88(3):193–201
Abramson JS, Hellmann M, Barnes JA, Hammerman P, Toomey C, Takvorian T et al (2010) Intravenous methotrexate as central nervous system (CNS) prophylaxis is associated with a low risk of CNS recurrence in high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer 116(18):4283–4290
Ferreri AJM, Bruno-Ventre M, Donadoni G, Ponzoni M, Citterio G, Foppoli M et al (2015) Risk-tailored CNS prophylaxis in a mono-institutional series of 200 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. Br J Haematol. 168(5):654–662
Kumar A, Vanderplas A, Lacasce AS, Rodriguez MA, Crosby AL, Lepisto E et al (2012) Lack of benefit of central nervous system prophylaxis for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era: findings from a large national database. Cancer 118(11):2944–2951
Schmiegelow K (2009) Advances in individual prediction of methotrexate toxicity: a review. Br J Haematol. 146(5):489–503
Ghose A, Elias HK, Guha G, Yellu M, Kundu R, Latif T (2015) Influence of rituximab on central nervous system relapse in diffuse large b-cell lymphoma and role of prophylaxis—a systematic review of prospective studies. Clin Lymph Myeloma Leukemia 15(8):451–457
Haioun C, Besson C, Lepage E, Thieblemont C, Simon D, Rose C et al (2000) Incidence and risk factors of central nervous system relapse in histologically aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma uniformly treated and receiving intrathecal central nervous system prophylaxis: a GELA study on 974 patients. Ann Oncol. 11(6):685–690
Fletcher CD, Kahl BS (2014) Central nervous system involvement in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: an analysis of risks and prevention strategies in the post-rituximab era. Leuk Lymphoma. 55(10):2228–2240
Zhang J, Chen B, Xu X (2014) Impact of rituximab on incidence of and risk factors for central nervous system relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Leuk Lymph 55(3):509–514
Cheah C, Seymour J (2015) Central nervous system prophylaxis in non-hodgkin lymphoma: who, what, and when? Curr Oncol Rep. 17(6):1–11
Hollender A, Kvaloy S, Nome O, Skovlund E, Lote K, Holte H (2002) Central nervous system involvement following diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a risk model. Ann Oncol. 13(7):1099–1107
Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Nickelsen M, Ziepert M, Pfreundschuh M, Glass B et al (2013) A new prognostic model to assess the risk of CNS disease in patients with aggressive B-Cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol 31(S1):111
Savage K, Zeynalova S, Kansara R, Nickelsen M, Villa D, Sehn L, et al. Validation of a prognostic model to assess the risk of CNS disease in patients with aggressive B-Cell lymphoma. 56th ASH Annual Meeting and Exposition; 2014; San Francisco, CA
Schmitz N, Zeynalova S, Nickelsen M, Kansara R, Villa D, Sehn LH et al (2016) CNS international prognostic index: a risk model for cns relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J Clin Oncol 34(26):3150–3156
Gleeson M, Cunningham D, Hawkes EA, Qian W, Smith P, Chadwick N et al (2014) Risk of CNS relapse with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the rituximab era: results from the UK NCRI R-CHOP 14 v 21 Trial. Blood 124(21):1723
Perazella MA, Moeckel GW (2010) Nephrotoxicity from chemotherapeutic agents: Clinical manifestations, pathobiology, and prevention/therapy. Semin Nephrol 30(6):570–581
Acknowledgements
Appreciation and gratitude to the following individuals and institutions who contributed to the completion of this project: Health Information Services and Information Technology staff at Austin and Box Hill hospitals, Austin Clinical School, Olivia Newton John Cancer Wellness and Research Centre, Austin Health and Eastern Health.
Funding
This study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Research funding: Amgen, Beigene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Merck Serono, Celgene, Merck Sharpe Dome, Novartis, Pharmacyclics, Hutchison MediPharma, Incyte, Bayer. Travel Expenses: Takeda. Advisory board: Janssen.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was obtained for this non-interventional retrospective study from the institutional research committees.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not applicable for this non-interventional retrospective study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garwood, M.J., Hawkes, E.A., Churilov, L. et al. Patient selection and tolerability of high-dose methotrexate as central nervous system prophylaxis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 85, 133–140 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-04007-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-04007-w