Abstract
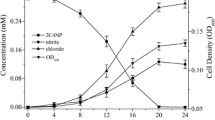
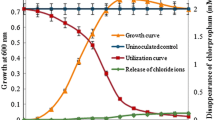
Degradation of 2-Chloro-4-nitrophenol (2C4NP) was studied by Arthrobacter sp. SJCon, isolated from the soil of a pesticide contaminated site. This strain utilized 2C4NP as sole source of carbon and energy and degraded 2C4NP with stoichiometric release of nitrite and chloride ions. A metabolite was detected during the study of 2C4NP degradation and identified as chlorohydroquinone (CHQ) by thin layer chromatography (TLC), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Inhibition study using 2,2′-dipyridyl showed that CHQ is a terminal aromatic compound in degradation pathway of 2C4NP. CHQ dioxygenase activity was observed in the crude extract of 2C4NP induced cells of the strain SJCon that suggested the cleavage of the CHQ to maleylacetate (MA). Our study clearly showed that Arthrobacter sp. SJCon degraded 2C4NP via formation of CHQ that further cleaved to MA by CHQ dioxygenase. This mechanism of degradation of 2C4NP differs from previously reported degradation pathways of 2C4NP.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora PK, Chauhan A, Pant B, Korpole S, Mayilraj S, Jain RK (2011) Description of Chryseomicrobium imtechense gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Planococcaceae. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol 61:1859–1864
Beunink J, Rehm HJ (1990) Coupled reductive and oxidative degradation of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol by a co-immobilized mixed culture system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:108–115
Bruhn C, Bayly RC, Knackmuss HJ (1988) The in vivo construction of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol assimilatory bacteria. Arch Microbiol 150:171–177
Ghosh A, Khurana M, Chauhan A, Takeo M, Chakraborti AK, Jain RK (2010) Degradation of 4-nitrophenol, 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol, and 2,4-dinitrophenol by Rhodococcus imtechensis strain RKJ300. Environ Sci Tech 44:1069–1077
Katsivela E, Wray V, Pieper DH, Wittich RM (1999) Initial reactions in the biodegradation of 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene by a newly isolated bacterium, strain LW1. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1405–1412
Li BZ, Xu XY, Zhu L (2010) Catalytic ozonation-biological coupled processes for treatment of industrial wastewater containing refractory chlorinated nitroaromatic compounds. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 11:177–189
Li Q, Minami M, Hanaoka T, Yamamura Y (1999) Acute immunotoxicity of p-chloronitrobenzene in mice: II. Effect of p-chloronitrobenzene on the immunophenotype of murine splenocytes determined by flow cytometry. Toxicology 137:35–45
Miyauchi K, Adachi Y, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1999) Cloning and sequencing of a novel meta-cleavage dioxygenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 181:6712–6719
Miyauchi K, Suh SK, Nagata Y, Takagi M (1998) Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone reductive dehalogenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane by Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J Bacteriol 180:1354–1359
Nair RS, Johannsen FR, Levinskas GJ, Terrill JB (1986) Subchronic inhalation toxicity of p-nitroaniline and p-nitrochlorobenzene in rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 6:618–627
Nair RS, Johannsen FR, Levinskas GJ, Terrill JB (1986) Assessment of toxicity of o-nitrochlorobenzene in rats following a 4-week inhalation exposure. Fundam Appl Toxicol 7:609–614
Ohtsubo Y, Miyauchi K, Kanda K, Hatta T, Kiyohara H, Senda T, Nagata Y, Mitsui Y, Takagi M (1999) PcpA, which is involved in the degradation of pentachlorophenol in Sphingomonas chlorophenolica ATCC39723, is a novel type of ring-cleavage dioxygenase. FEBS Lett 459:395–398
Pandey J, Heipieper H, Chauhan A, Arora P, Prakash D, Jain RK (2011) Reductive dehalogenation mediated initiation of aerobic degradation of 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol (2C4NP) by Burkholderia sp. strain SJ98. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3254-y
Reddy GV, Gelpke MD, Gold MH (1998) Degradation of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: involvement of reductive dechlorination. J Bacteriol 180:5159–5164
Travlos GS, Mahler J, Ragan HA, Chou BJ, Bucher JR (1996) Thirteen-week inhalation toxicity of 2- and 4-chloronitrobenzene in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Fundam Appl Toxicol 30:75–92
Volskay VT, Grady CPL (1990) Respiration inhibition kinetic-analysis. Water Res 24:863–874
Wu HZ, Wei CH, Wang YQ, He QC, Liang SZ (2009) Degradation of o-chloronitrobenzene as the sole carbon and nitrogen sources by Pseudomonas putida OCNB-1. J Environ Sci-China 21:89–95
Wu JF, Jiang CY, Wang BJ, Ma YF, Liu ZP, Liu SJ (2006) Novel partial reductive pathway for 4-chloronitrobenzene and nitrobenzene degradation in Comamonas sp. strain CNB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1759–1765
Zaborina O, Latus M, Eberspacher J, Golovleva LA, Lingens F (1995) Purification and characterization of 6-chlorohydroxyquinol 1,2-dioxygenase from Streptomyces rochei 303: comparison with an analogous enzyme from Azotobacter sp. strain GP1. J Bacteriol 177:229–234
Zhen D, Liu H, Wang SJ, Zhang JJ, Zhao F, Zhou NY (2006) Plasmid-mediated degradation of 4-chloronitrobenzene by newly isolated Pseudomonas putida strain ZWL73. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:797–803
Acknowledgments
PKA is thankful to the University Grants Commission for Dr. D. S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Govt. of India for Junior and Senior Research Fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Rakesh Kumar Jain—Deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, P.K., Jain, R.K. Pathway for Degradation of 2-Chloro-4-Nitrophenol in Arthrobacter sp. SJCon. Curr Microbiol 63, 568 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-0022-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-0022-2