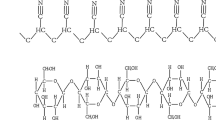
Abstract
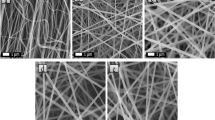
Bicomponent nanofibers of cellulose acetate (CA) and polyethylene imine were successfully fabricated by electrospinning technique to capture CO2 gas. The concentration of polyethylene imine was fixed to 25, 50, and 75% compared to the CA concentration. The nanofibers were characterized using FT-IR, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA). The effect of PEI on the morphology of CA nanofibers was studied using scanning electron microscope (SEM). The diameter of electrospun CA/PEI nanofibers becomes larger with the increase of PEI content due to repulsion of electrical force from side polar groups. In addition, PEI diffused on the nanofiber surface was observed at high concentrations of PEI. The CO2 adsorption capacity of electrospun CA/PEI nanofiber membranes was investigated at different temperatures using a BET. The increase of PEI content in nanofibers increased the CO2 adsorption capacity, and the adsorption capacity was larger at lower temperature. The decrease in CO2 adsorption capacity with increasing temperature indicates that CO2 adsorption is more responsible for physisorption. Moreover, the CA/PEI electrospun membrane retains 99% of its initial CO2 adsorption capacity after 5 cycles of the adsorption and desorption process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goeppert A, Czaun M, May RB, Prakash GKS, Olah GA, Narayanan SR (2011) Carbon dioxide capture from the air using a polyamine based regenerable solid adsorbent. J Am Chem Soc 133(50):20164–20167
Ochedi FO, Yu J, Yu H, Liu Y, Hussain A (2021) Carbon dioxide capture using liquid absorption methods: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(1):77–109
Hong SM, Jang E, Dysart AD, Pol VG, Lee G (2016) CO2 Capture in the sustainable wheat-derived activated microporous carbon compartments. Sci Rep 6(1):34590
Lin YF, Syu CR, Huang KW, Lin KYA (2019) Synthesis of silica aerogel membranes using low-cost silicate precursors for carbon dioxide capture. Chem Phys Lett 726:13–17
Sateesh C, Nandakishora Y, Sahoo RK, Murugan S (2021) Study of cryogenic CO2 capture with solar-assisted VAR system. Clean Eng Technol 5:100351
Wang P, Means N, Shekhawat D, Berry D, Massoudi M (2015) Chemical-looping combustion and gasification of coals and oxygen carrier development: a brief review. Energies 8(10):10605–10635
Chen G, Wang T, Zhang G, Liu G, Jin W (2022) Membrane materials targeting carbon capture and utilization. Adv Membr 2:100025
Sheng J, Zhang M, Xu Y, Yu J, Ding B (2016) Tailoring water-resistant and breathable performance of polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membranes modified by polydimethylsiloxane. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(40):27218–27226
Selatile MK, Ray SS, Ojijo V, Sadiku R (2018) Recent developments in polymeric electrospun nanofibrous membranes for seawater desalination. RSC Adv 8(66):37915–37938
Toriello M, Afasari M, Shon HY, Tijing LD (2020) Progress on the fabrication and application of electrospun nanofiber composites. Membranes 10(9):204
Xu Y, Yuan D, Bao J, Xie Y, He M, Shi Z, Chen S, He C, Zhao W, Zhao C (2018) Nanofibrous membranes with surface migration of functional groups for ultrafast wastewater remediation. J Mater Chem A 6(27):13359–13372
Osman AI, Hefny M, Abdel MMIA, Elgarahy AM, Rooney DW (2021) Recent advances in carbon capture storage and utilisation technologies: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(2):797–849
Li K, Jin S, Wei W, Li X, Li J (2021) Bioinspired hyperbranched protein adhesive based on boronic acid-functionalized cellulose nanofibril and water-soluble polyester. Compos B Eng 219:108943
Nawaz M, Habib S, Khan A, Shakoor RA, Kahraman R (2020) Cellulose microfibers (CMFs) as a smart carrier for autonomous self-healing in epoxy coatings. New J Chem 44(15):5702–5710
Silva FAGS, Dourado F, Gama M, Pocas F (2020) Nanocellulose bio-based composites for food packaging. Nanomaterials 10(10):2041
Cui X, Lee JJL, Chen WT (2019) Eco-friendly and biodegradable cellulose hydrogels produced from low cost okara: towards non-toxic flexible electronics. Sci Rep 9(1):18166
Zhu M, Cao Q, Liu B, Guo H, Wang X, Han Y, Sun G, Li Y, Zhou J (2020) A novel cellulose acetate/poly (ionic liquid) composite air filter. Cellulose 27(7):3889–3902
An S, Jeon B, Bae JH, Kim IS, Paeng K, Kim M, Lee H (2019) Thiol-based chemistry as versatile routes for the effective functionalization of cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr Polym 226:115259
Lamm ME, Li K, Qian J, Wang L, Lavoine N, Newman R, Gardner DJ, Li T, Hu L, Ragauskas AJ, Tekinalp H, Kunc V, Ozcan S (2021) Recent Advances in Functional Materials through Cellulose Nanofiber Templating. Adv Mater 33(12): 2005538
Kalwar K, Ming S (2019) Electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers and Au@AgNPs for antimicrobial activity - a mini review. Nanotechnol Rev 8(1):246–257
Emam HE, Shaheen TI (2019) Investigation into the role of surface modification of cellulose nanocrystals with succinic anhydride in dye removal. J Polym Environ 27(11):2419–2427
Emam HE, Darwesh OM, Abdelhameed RM (2020) Protective cotton textiles via amalgamation of cross-linked zeolitic imidazole frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 59(23):10931–10944
Emam HE, Shaheen TI (2022) Design of a dual pH and temperature responsive hydrogel based on esterified cellulose nanocrystals for potential drug release. Carbohyd Polym 278:118925
Xu X, Myers MB, Versteeg FG, Pejcic B, Heath C, Wood CD (2020) Direct air capture (DAC) of CO2 using polyethylenimine (PEI) “snow”: a scalable strategy. Chem Commun 56(52):7151–7154
Choi W, Min K, Kim C, Ko YS, Jeon JW, Seo H, Park YK, Choi M (2016) Epoxide-functionalization of polyethyleneimine for synthesis of stable carbon dioxide adsorbent in temperature swing adsorption. Nat Commun 7(1):12640
He Y, Xia Y, Zhao J, Song Y, Yi L, Zhao L (2019) One-step fabrication of PEI-modified GO particles for CO2 capture. Appl Phys A 125(3):160
Irani V, Khosh AG, Tavasoli A (2020) Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Functionalized metal oxide nanoparticles recovered from the catalytic converters of spent automotive exhaust systems and application for CO2 adsorption. Front Energy Res 8:196
Shen X, Du H, Mullins RH, Kommalapati RR (2017) Polyethylenimine applications in carbon dioxide capture and separation: from theoretical study to experimental work. Energy Technol 5(6):822–833
Wan X, Lu X, Liu J, Pan Y, Xiao H (2019) Impregnation of PEI in novel porous MgCO3 for carbon dioxide capture from flue gas. Ind Eng Chem Res 58(12):4979–4987
Xie Z, Yan G, Tang K, Ding CF (2022) Post-synthesis modification of covalent organic frameworks for ultrahigh enrichment of low-abundance glycopeptides from human saliva and serum. Talanta 236:122831
Yang J, Zhang P, Tang L, Sun P, Liu W, Sun P, Zuo A, Liang D (2010) Temperature-tuned DNA condensation and gene transfection by PEI-g-(PMEO2MA-b-PHEMA) copolymer-based nonviral vectors. Biomaterials 31(1):144–155
Zaarour B, Zhu L, Jin X (2020) A review on the secondary surface morphology of electrospun nanofibers: formation mechanisms, characterizations, and applications. ChemistrySelect 5(4):1335–1348
Pal S, Srivastava RK, Nandan B (2021) Effect of spinning solvent on crystallization behavior of confined polymers in electrospun nanofibers. Polym Cryst 6:e10209
Philip P, Tomlal JE, Chacko JK, Philip KC, Thomas PC (2019) Preparation and characterisation of surface roughened PMMA electrospun nanofibers from PEO - PMMA polymer blend nanofibers. Polym Test 74:257–265
Hou JZ, Xue HL, Li LL, Dou YL, Wu ZN, Zhang PP (2016) Fabrication and morphology study of electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylenimine nanofiber. Polym Bull 73(10):2889–2906
Kriegel C, Kit KM, Weiss MDJ (2009) Nanofibers as carrier systems for antimicrobial microemulsions part i: fabrication and characterization. Langmuir 25(2):1154–1161
Fang X, Ma H, Xiao S, Shen M, Guo R, Cao X, Shi X (2011) Facile immobilization of gold nanoparticles into electrospun polyethyleneimine/polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers for catalytic applications. J Mater Chem 21(12):4493–4501
Liu H, Kuila T, Ku KNH, Lee JH (2013) In situ synthesis of the reduced graphene oxide–polyethyleneimine composite and its gas barrier properties. J Mater Chem A 1(11):3739–3746
Tan M, Feng Y, Wang H, Zhang L, Khan M, Guo J, Chen Q, Liu J (2013) Immobilized bioactive agents onto polyurethane surface with heparin and phosphorylcholine group. Macromol Res 21(5):541–549
Salleh WNW, Ismail AF (2012) Fabrication and characterization of PEI/PVP-based carbon hollow fiber membranes for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation. AIChE J 58(10):3167–3175
Sumisha A, Arthanareeswaran G, Ismail AF, Kumar DP, Shankar MV (2015) Functionalized titanate nanotube–polyetherimide nanocomposite membrane for improved salt rejection under low pressure nanofiltration. RSC Adv 5(49):39464–39473
Liu C, Liu H, Lu C, Tang K, Zhang Y (2017) Polyethyleneimine-modified graphene oxide/PNIPAm thermoresponsive hydrogels with rapid swelling/deswelling and improved mechanical properties. J Mater Sci 52(19):11715–11724
Zhu H, Zhang M, Cai S, Cai Y, Wang P, Bao S, Zou M, Du M (2014) In situ growth of Rh nanoparticles with controlled sizes and dispersions on the cross-linked PVA–PEI nanofibers and their electrocatalytic properties towards H2O2. RSC Adv 4(2):794–804
Zainab G, Babar AA, Ali N, Aboalhassan AA, Yu J, Ding B (2020) Electrospun carbon nanofibers with multi-aperture/opening porous hierarchical structure for efficient CO2 adsorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 561:659–667
Huang CL, Wang PY, Li YY (2020) Fabrication of electrospun CO2 adsorption membrane for zinc-air battery application. Chem Eng J 395:125031
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government (MOTIE) (No. 20224000000440, Sector Coupling Energy Industry Advancement Manpower Training Program)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, J., Lee, J. & Oh, SG. Preparation of electrospun cellulose acetate/polyethylene imine bicomponent nanofibers for CO2 capture. Polym. Bull. 81, 1389–1401 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04773-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-023-04773-x