Abstract
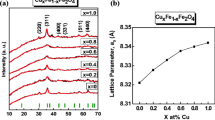
A new catalyst is produced using Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O and Mn(NO3)2·4H2O. The magnetic properties of the nanoparticles of “iron–cobalt–manganese catalysts (ICMC)” have been studied, with magnesium oxide as a support employing co-precipitation method. The effects of calcination and drying conditions such as temperature, time, and different percentage of MgO-supported Fe–Co–Mn oxides on the magnetic properties were investigated using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Our results indicated that calcination at 600 °C can change magnetic phase of the sample, and calcination at 700 °C changed the sample from ferromagnetic to superparamagnetic by adding 15% MgO into the ICMC. By increasing the calcination temperature, the values of remnant magnetization (M r) and saturation magnetization (M S) were increased. By increasing the calcination time duration, values of the M r and coercivity (H C) were increased. Furthermore, when the percentages of MgO increased, the values of M r, M S, and H C were decreased. It was observed that most variables in the experiments affected the magnetic properties of the new catalysts.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.M.I. Abdallah, T. Moyo, Superparamagnetic behavior of Mn x Ni1−x Fe2O4 spinel nano ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 361, 170–174 (2014)
Y. Shi, J. Ding, X. Liu, J. Wang, NiFe2O4 ultrafine particles prepared by co-precipitation/mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 205(2–3), 249–254 (1999)
D.T.T. Nguyet, N.P. Duong, L.T. Hung, T.D. Hien, T. Satoh, Crystallization and magnetic behavior of nanosized nickel ferrite prepared by citrate precursor method. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6621 (2011)
H.M.I. Abdallah, T. Moyo, J.Z Msomi, Structural and Mössbauer studies of Mn0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 ferrites prepared by high energy ball milling and glycolthermal methods. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 217, 012141 (2010)
P.A. Chernavskii, J.-A. Dalmon, N.S. Perov, A.Y. Khodakov, Magnetic characterization of Fischer-Tropsch catalysts, oil and gas science and technology—Rev. IFP 64(1), 25–48 (2009). doi:10.2516/ogst/2008050. (Copyright © 2009, Institut francais du petrole)
A. Ghasemi, A.M. Davarpanah, M. Ghadiri, Structure and magnetic properties of oxide nanoparticles of Fe–Co–Ni synthesized by co-precipitation method. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8(4), 207–214 (2012)
Arsalanfar M, The effect of preparation procedures and operational conditions over the catalytic performance of Fe–Co–Mn catalysts on the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis process and study of kinetic and mechanism reaction, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sistan and Baluchestan, 2012
M. Arsalanfar, A.A. Mirzaei, H.R. Bozorgzadeh, Effect of calcination conditions on the structure and catalytic performance of MgO supported Fe–Co–Mn catalyst for CO hydrogenation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 6, 1–13 (2012)
M. Arsalanfar, A.A. Mirzaei, H.R. Bozorgzadeh, H. Atashi, Effect of process conditions on the surface reaction rates and catalytic performance of MgO supported Fe–Co–Mn catalyst for CO hydrogenation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 18, 2092–2102 (2012)
M. Arsalanfar, A.A. Mirzaei, H. Atashi, H.R. Bozorgzadeh, S. Vahid, A. Zare, An investigation of the kinetics and mechanism of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis on Fe–Co–Mn supported catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 96, 150–159 (2012)
M. Arsalanfar, A.A. Mirzaei, H.R. Bozorgzadeh, Effect of preparation method on catalytic performance, structure and surface reaction rates of MgO supported Fe–Co–Mn catalyst for CO hydrogenation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 19, 478–487 (2013)
X. An, B. Wu, W. Hou, H. Wan, Z. Tao, T. Li, Z. Zhang, H. Xiang, Y. Li, B. Xu, F. Yi, J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 263, 266 (2007)
www.mdk-magnetics.com. Accessed 27 July 2017
A. Dahmardeh, A.M. Davarpanah, Investigation on influences of synthesis methods on the magnetic properties of trimetallic nanoparticles of iron–cobalt manganese supported by magnesium oxide. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11(4), 249–256 (2015)
S. Singhal, J. Singh, S.K. Barthwal, K. Chandra, Preparation and characterization of nanosize nickel-substituted cobalt ferrites (Co1−x Ni x Fe2O4). J. Solid State Chem. 178, 3183–3189 (2005)
W.B. Dlamini, J.Z. Msomi, T. Moyo, XRD, Mössbauer and magnetic properties of Mg x Co1−x Fe2O4 Nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 373, 78–82 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Corresponding author would like to thank Prof. A. A. Mirzaei and Dr M. Arsalanfar for their samples. Authors thank the University of Sistan and Baluchestan, I. R. of IRAN for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davarpanah, A.M., Arsalanfar, M. Study of different effects on magnetic properties of MgO-supported Fe–Co–Mn oxides. Appl. Phys. A 123, 551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1164-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-1164-2