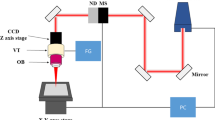
Abstract
Enhanced cutting tool blades are required to manufacture next-generation small multilayer ceramic capacitors. Cemented tungsten carbide is used as the material for these blades. Recently, laser ablation has been used to fabricate sharp fine blades. In this study, a femtosecond laser was used to precisely and finely machine cemented tungsten carbide. Furthermore, we analyzed the interaction between the femtosecond laser and cemented tungsten carbides depending on the laser fluence. Scanning electron microscopy, confocal laser scanning microscopy, and a two-temperature model were used for the analysis. Based on this analysis, we understood the formation of burrs, nanoparticles, and droplets induced by a femtosecond laser. A laser beam with a diameter of ~ 16 µm was used for irradiation. Moreover, beams with fluence values of 0.24, 1.13, 2.12, and 3.40 J/cm2 were irradiated on the surface of cemented tungsten carbides. The total fluence was the same as that of the absorbed surface. Although the total fluence was the same, burrs, nanoparticles, and droplets were generated at higher fluences. Owing to the higher fluence, the temperature increased, thus increasing the time required to achieve thermal equilibrium between the electron and the lattice. Consequently, we propose the formation process for burrs, nanoparticles, and droplets. In addition, we demonstrate a machining solution without burrs, nanoparticles, or droplets. These results will prove useful across a number of different industries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Chen, H. Wang, P. Zhao, C. Zhu, Z. Cai, Z. Cen, L. Li, X. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 4178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16292
R. Muhammad, Y. Iqbal, I.M. Reaney, C. Randall, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2089 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14212
L. Chen, H. Wang, P. Zhao, Z. Shen, C. Zhu, Z. Cen, L. Li, X. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 102, 2781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.16157
T. Im, J. Pyo, J.-S. Lee, C.S. Lee, Powder Technol. 382, 118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.12.043
K. Hong, T.H. Lee, J.M. Suh, S.H. Yoon, H.W. Jang, J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 9782 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tc02921d
X. Wang, H. Zheng, J. Laser Appl. 30, 032203 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.5040602
K. Jia, T.E. Fischer, B. Gallois, Nanostruct. Mater. 10, 875 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0965-9773(98)00123-8
M. Eriksson, M. Radwan, Z. Shen, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 36, 31 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2012.03.007
E. M. Trent, P. K. Wright, E. M. Trent, P. K. Wright, Met. Cut. 175 (2000)
A. Abdullah, M.R. Shabgard, A. Ivanov, M.T. Shervanyi-Tabar, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 41, 268 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-008-1476-7
K. Bonny, P. De Baets, W. Ost, S. Huang, J. Vleugels, W. Liu, B. Lauwers, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 27, 350 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2008.09.002
C. Momma, B.N. Chichkov, S. Nolte, F. Von Alvensleben, A. Tünnermann, H. Welling, B. Wellegehausen, Opt. Commun. 129, 134 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(96)00250-7
B. Rethfeld, K. Sokolowski-Tinten, D. Von Der Linde, S.I. Anisimov, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 79, 767 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-2805-9
Q. Bian, X. Yu, B. Zhao, Z. Chang, S. Lei, Opt. Laser Technol. 45, 395 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2012.06.018
V. Malkhasyan, M. Assoul, G. Monteil, 2016 Conf. Lasers Electro-Optics, CLEO 2016 V, 4 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1364/cleo_at.2016.atu4k.2
H.-Y. Kim, J.-W. Jeon, W. Choi, Y.-G. Shin, S.-Y. Ji, S.-H. Cho, Materials (Basel) 11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040530
N.M. Bulgakova, Ultrafast Laser Processing, in Fundamentals of Ultrafast Laser Processing. ed. by K. Sugioka, Y. Cheng (Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, 2013), pp.122–124
J.P. Calderón Urbina, C. Daniel, C. Emmelmann, Phys. Proc. 41, 752 (2013)
J.M. Liu, Opt. Lett. 7, 196 (1982)
Y.G. Shin, W. Choi, J. Choi, S.H. Cho, J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 9, 1 (2021)
M.D. Perry, B.C. Stuart, P.S. Banks, M.D. Feit, V. Yanovsky, A.M. Rubenchik, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6803 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.370197
G. Tani, L. Orazi, A. Fortunato, G. Cuccolini, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 130, 0311111 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2917326
G. Eberle, K. Wegener, Phys. Proc. 56, 951 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2014.08.115
C. Cheng, X. Xu, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 72, 1 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.165415
C.M. Fernandes, A.M.R. Senos, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 29, 405 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.02.004
J.P. Colombier, P. Combis, R. Stoian, E. Audouard, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 75, 1 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.104105
W. Kautek, P. Rudolph, G. Daminelli, J. Krüger, Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 81, 65 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-005-3211-7
M. Mostafa, M.F. Hameed, S.S. Obayya, J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 31, 472 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.07.012
N.M. Bulgakova, A.V. Bulgakov, V. P. Zhukov, W. Marine, A.Y. Vorobyev, C. Guo, High-Power Laser Ablation VII 7005, 70050C (2008). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.782643
J. Perrière, C. Boulmer-Leborgne, R. Benzerga, S. Tricot, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 7069 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/40/22/031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, YG., Ji, SY., Choi, J. et al. Morphologies of cemented tungsten carbide ablated by pulsed femtosecond laser to manufacture next-generation blades of a cutting tool. Appl. Phys. A 128, 828 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05945-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05945-8