Abstract
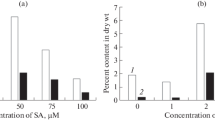
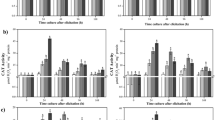
Stevia rebaudiana is a medicinal plant widely used as a sweetener, and the sweetening power comes from the diterpenoid glycosides known as steviol glycosides (SGs). The studies of gene expression patterns in response to elicitors treatment are of extreme importance for biotechnological purposes. Methyl jasmonate (MeJa), spermidine (SPD), salicylic acid (SA), and paclobutrazol (PBZ) (100 µM) were applied to stevia plants growing in a hydroponic system to examine the effect of these elicitors along the time (24, 48, 72, and 96 h). SGs’ contents and transcription levels of fifteen genes involved in the three stages comprising their biosynthesis pathway were evaluated. The results provide direct evidence that HDR, GGDPS, CDPS, KS, KO, and KAH are elicitor-responsive genes and they can be effectively regulated at least at the transcriptional level. MeJa and SPD treatments resulted in positive effects on the transcription of SGs biosynthetic genes, with SPD exhibiting the highest number of regulated genes at 48 h of exposure. PBZ treatment down-regulated genes encoding kaurenoid enzymes. SA treatment did not affect transcription of UGT85C2, UGT74G1, and UGT76G1 and decreased stevioside levels. Overall, this study offers new insights into the transcriptional response mechanisms in S. rebaudiana plants under the effect of the elicitors MeJa, SPD, SA, and PBZ.






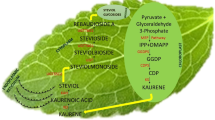
Source: reproduced with permission from Modi and others (2013). (Color figure online)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez-Robles MJ, López-Orenes A. Ferrer MA, Calderón AA (2016) Methanol elicits the accumulation of bioactive steviol glycosides and phenolics in Stevia rebaudiana shoot cultures. Ind Crop Prod 87:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.054
Barroso M, Barros L, Rodrigues MA, Sousa MJ, Santos-Buelga C. Ferreira ICFR. (2016) Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni cultivated in Portugal: a prospective study of its antioxidant potential in different conservation conditions. Ind Crop Prod 99:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.06.013
Bayraktar M, Naziri E, Hakki I, Fatih A (2016) Elicitor induced stevioside production, in vitro shoot growth, and biomass accumulation in micropropagated Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 127:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-0161049-7
Behroozi P, Baghizadeh A, Saei A, Kharazmi S (2017) Quantitative analysis of uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase UGT85C2. UGT74G1 and UGT76G1 genes expression in Stevia rebaudiana under different irrigations. Russ J Plant Physiol 64:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443717010034
Brandle JE, Rosa N (1992) Heritability for yield, leaf:stem ratio and stevioside content estimated from landrace cultivar of Stevia rebaudiana. Can J Plant Sci 72:1263–1266. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps92-159
Brandle JE, Telmer PG (2007) Steviol glycoside biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 68:1855–1863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.010
Ceunen S, Geuns JMC (2013) Steviol glycosides: chemical diversity, metabolism, and function. J Nat Prod 76:1201–1228. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400203b
Cocetta G, Rossoni M, Gardana C, Mignani I, Ferrante A, Spinardi A (2015) Methyl jasmonate affects phenolic metabolism and gene expression in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum). Physiol Plant 153:269–283. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12243
Cordoba E, Salmi M, Leo P (2009) Unraveling the regulatory mechanisms that modulate the MEP pathway in higher plants. J Exp Bot 60:2933–2943. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp190
De Geyter N, Gholami A, Goormachtig S, Goossens A (2012) Transcriptional machineries in jasmonate-elicited plant secondary metabolism. Trends Plant Sci 17:349–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.03.001
Deng N, Liu C, Chang E, Ji J, Yao X, Yue J, Bartish IV, Chen L, Jiang Z, Shi S (2017) High temperature and UV-C treatments affect stilbenoid accumulation and related gene expression levels in Gnetum parvifolium. Electron J Biotechnol 25:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.11.001
Fleet CM, Yamaguchi S, Hanada A, Kawaide H, David CJ, Kamiya Y, Sun T (2003) Overexpression of AtCPS and AtKS in Arabidopsis confers increased ent-kaurene production but no increase in bioactive gibberellins. Plant Physiol 132:830–839. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.021725
Fletcher R, Gilley A, Sankhlam N, Davis TD (2000) Triazoles as plant growth regulators and stress protectants. Hortic Rev 2:55–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470650776.ch3
Geuns JMC (2003) Stevioside. Phytochemistry 64:913–921. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00426-6
Gong Y, Liao Z, Guo B, Sun X, Tang K (2006) Molecular cloning and expression profile analysis of Ginkgo biloba DXS gene encoding 1-Deoxy- d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase, the first committed enzyme of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate pathway. Planta Med 72:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-916234
Guleria P, Masand S, Kumar S (2014) Overexpression of SrUGT85C2 from Stevia reduced growth and yield of transgenic Arabidopsis by influencing plastidial MEP pathway. Gene 539:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.01.071
Gundlach H, Müller MJ, Kutchan TM, Zenk MH (1992) Jasmonic acid is a signal transducer in elicitor-induced plant cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2389–2393. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.89.6.2389
Gupta P, Sharma S, Saxena S (2014) Effect of salts (NaCl and Na2CO3) on Callus and suspension culture of Stevia rebaudiana for steviol glycoside production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:2894–2906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0736-2
Hajihashemi S, Ehsanpour AA (2013) Influence of exogenously applied paclobutrazol on some physiological traits and growth of Stevia rebaudiana under in vitro drought stress. Biologia 68:414–420. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0165-7
Hajihashemi S, Geuns JMC (2017) Steviol glycosides correlation to genes transcription revealed in gibberellin and paclobutrazol-treated Stevia rebaudiana. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 26(4):387–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-017-0399-5
Hajihashemi S, Geuns JMC, Ehsanpour AA (2013) Gene transcription of steviol glycoside biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under polyethylene glycol, paclobutrazol and gibberellic acid treatments in vitro. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2009–2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1226-9
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347:1–32
Huang Y, Lin C, He F, Li Z, Guan Y, Hu Q, Hu J (2017) Exogenous spermidine improves seed germination of sweet corn via involvement in phytohormone interactions, H2O2 and relevant gene expression. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0951-9
Humphrey TV, Richman AS, Menassa R, Brandle JE (2006) Spatial organisation of four enzymes from Stevia rebaudiana that are involved in steviol glycoside synthesis. Plant Mol Biol 61:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-5966-9
JECFA (2010) Steviol glycosides. In: compendium of food additive specifications. FAO JECFA Monogr 10:17–21
Kakkar RK, Sawhney VK (2002) Minireview polyamine research in plants—a changing perspective. Physiol Plant 116:281–292. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.13993054.2002.1160302.x
Karimi M, Ahmadi A, Hashemi J, Abbasi A, Angelini LG (2014) Effect of two plant growth retardants on steviol glycosides content and antioxidant capacity in Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni). Acta Physiol Plant 36:1211–1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738014-1498-8
Khalil SA, Kamal N, Sajid M, Ahmad N, Zamir R, Ahmad N, Ali S (2016) Synergism of polyamines and plant growth regulators enhanced morphogenesis, stevioside content, and production of commercially important natural antioxidants in Stevia rebaudiana Bert. Vitr. Cell Dev Biol Plant 52:74–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-016-9749-6
Kilam D, Sai M, Abdin MZ, Agnihotri A, Varma A (2017) Physiological and molecular plant pathology endophytic root fungus Piriformospora indica affects transcription of steviol biosynthesis genes and enhances production of steviol glycosides in Stevia rebaudiana. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 97:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.12.003
Kumar H, Kaul K, Bajpai-Gupta S, Kaul VK, Kumar S (2012a) A comprehensive analysis of fifteen genes of steviol glycosides biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni). Gene 492:276–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2011.10.015
Kumar H, Singh K, Kumar S (2012b) 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2, 4-cyclodiphosphate synthase from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni is a functional gene. Mol Biol Rep 39:10971–10978. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1998-9
Li Z, Peng Y, Zhang X, Pan M, Ma X, Huang L, Yan Y (2014) Exogenous spermidine improves water stress tolerance of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) involved in antioxidant defence, gene expression and proline metabolism. Plant Omics 7:517–526
Liu JH, Kitashiba H, Wang J, Ban Y, Moriguchi T (2007) Polyamines and their ability to provide environmental stress tolerance to plants. Plant Biotechnol 24:117–126. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.24.117
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lois LM, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Gallego F, Campos N, Boronat A (2000) Carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development: regulatory role of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase. Plant J 22:503–513. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365313x.2000.00764.x
Mandal S, Upadhyay S, Singh VP, Kapoor R (2015) Enhanced production of steviol glycosides in mycorrhizal plants: a concerted effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis on transcription of biosynthetic genes. Plant Physiol Biochem 89:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.02.010
McGarvey DJ, Croteau R (1995) Terpenoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1015–1026. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.7.7.1015
Modi AR, Raj S, Kanani P, Patel A, Narayanan S (2013) Analysis of differentially expressed genes involved in stevioside biosynthesis in cultures of Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni treated with steviol as an immediate precursor. J Plant Growth Regul 33:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-013-9396-7
Modi A, Litoriya N, Prajapati V, Rafalia R, Narayanan S (2014) Transcriptional profiling of genes involved in steviol glycoside biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana bertoni during plant hardening. Dev Dyn 243:1067–1073. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.24157
Mohamed AAA, Ceunen S, Geuns JMC, Van den Ende W, De Ley M (2011) UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of steviol glycosides. J Plant Physiol 168:1136–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2011.01.030
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissues. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Pérez-Tortosa V, López-Orenes A, Pérez-Martínez A, Ferrer MA, Calderón AA (2012) Antioxidant activity and rosmarinic acid changes in salicylic acid-treated Thymus membranaceus shoots. Food Chem 130:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.051
Richman AS, Gijzen M, Starratt AN, Yang Z, Brandle JE (1999) Diterpene synthesis in Stevia rebaudiana: recruitment and up-regulation of key enzymes from the gibberellin biosynthetic pathway. Plant J 19:411–421. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365313X.1999.00531
Richman A, Swanson A, Humphrey T, Chapman R, Mcgarvey B, Pocs R, Brandle J (2005) Functional genomics uncovers three glucosyltransferases involved in the synthesis of the major sweet glucosides of Stevia rebaudiana. Plant J 41:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02275.x
Rodrigues-Brandão I, Kleinowski AM, Millech AE, Lima MC, Amarante L, Peters JA, Braga EJB (2014) Salicylic acid on antioxidant activity and betacyan in production from leaves of Alternanthera tenella. Cienc Rural 44:1893–1898. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-8478cr20130873
Saifi M, Nasrullah N, Ahmad MM, Ali A, Khan JA, Abdin MZ (2015) In silico analysis and expression profiling of miRNAs targeting genes of steviol glycosides biosynthetic pathway and their relationship with steviol glycosides content in different tissues of Stevia rebaudiana. Plant Physiol Biochem 94:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.05.009
Saxena P, Ahlawat S, Ali A, Khan S, Abdin MZ (2017) Gene expression analysis of the withanolide biosynthetic pathway in hairy root cultures of Withania somnifera elicited with methyl jasmonate and the fungus Piriformospora indica. Symbiosis 71:143–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0416-9
Serfaty M, Ibdah M, Fischer R, Chaimovitsh D, Saranga Y, Dudai N (2013) Dynamics of yield components and stevioside production in Stevia rebaudiana grown under different planting times, plant stands and harvest regime. Ind Crop Prod 50:731–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.08.063
Singh SD, Rao GP (2005) Stevia: the herbal sugar of 21st century. Sugar Technol 7:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942413
Singh J, Sangwan NS, Narnoliya LK, Singh N, Bansal S (2017a) Over-expression of DXS gene enhances terpenoidal secondary metabolite accumulation in rose-scented geranium and Withania somnifera: active involvement of plastid isoprenogenic pathway in their biosynthesis. Physiol Plant 151:381–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12507
Singh G, Singh G, Singh P, Parmar R, Paul N, Vashist R, Swarnkar MK, Kumar A, Singh S, Singh AK, Kumar S, Sharm RM (2017b) Molecular dissection of transcriptional reprogramming of steviol glycosides synthesis in leaf tissue during developmental phase transitions in Stevia rebaudiana Bert. Sci Rep 7:11835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12025-y
Totté N, Charon L, Rohmer M, Compernolle F, Baboeuf I, Geuns JMC (2000) Biosynthesis of the diterpenoid steviol, an ent-kaurene derivative from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway. Tetrahedron Lett 41:6407–6410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(00)01094-7
Wang AL, Lin C (2016) The effect of paclobutrazol on physiological and biochemical changes in the primary roots of pea. J Exp Bot 43:1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/43.10.1367
Wang QJ, Zheng LP, Sima YH, Yuan HY, Wang JW (2013) Methyl jasmonate stimulates 20-hydroxyecdysone production in cell suspension cultures of Achyranthes bidentate. Plant Omics 6:116–120
Yadav SK, Guleria P (2012) Steviol glycosides from Stevia: biosynthesis pathway review and their application in foods and medicine. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:988–998. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2010.519447
Yan X, Zhang L, Wang J, Liao P, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Kai G (2009) Molecular characterization and expression of 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) gene from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Acta Physiol Plant 31:1015–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-009-0320-5
Yang Y, Huang S, Han Y, Yuan H, Gu S, Zhao Y (2014) Base substitution mutations in uridinediphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferase 76G1 gene of Stevia rebaudiana causes the low levels of rebaudioside A Mutations in UGT76G1, A key gene of steviol glycosides synthesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.04.005
Yoneda Y, Nakashima H, Miyasaka J, Ohdoi K, Shimizu H (2017) Impact of blue, red, and far-red light treatments on gene expression and steviol glycoside accumulation in Stevia rebaudiana. Phytochemistry 137:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.02.002
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for their financial support and research fellowship EJBB, the CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), and the FAPERGS (Research Foundation of Rio Grande do Sul) for supporting the research. Part of this work was carried out at the Instituto de Biotecnología Vegetal, UPCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
344_2018_9795_MOESM3_ESM.tiff
Heatmap showing expression profile fifteen genes of SGs biosynthesis pathway in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni under the effect of elicitors agents, paclobutrazol (PBZ), spermidine (SPD), methyl jasmonate, (MeJa) and salicylic acid (SA) during four exposure times (24, 48, 72 and 96h). DXS, Deoxyxyulose-5-phosphate synthase; DXR, deoxyxyulose-5-phosphate reductase; CMS, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol synthase; CMK, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase; MCS, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase; HDS, 1- hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate synthase; HDR, 1-hydroxy-2-methyl-2(E)-butenyl-4-diphosphate reductase; GGDPS, geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase; CDPS, copalyl diphosphate synthase; KS, kaurene synthase; KO, kaurene oxidase; KAO, kaurenoic acid oxidase; KAH, kaurenoic acid hydroxylase; UGT85C2, UDP glucosyltransferase-85C2; UGT74G1, UDP glucosyltransferase-74G1; UGT76G1, UDP glucosyltransferase-76G1. (TIFF 4127 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucho, S.R., do Amaral, M.N., Milech, C. et al. Elicitor-Induced Transcriptional Changes of Genes of the Steviol Glycoside Biosynthesis Pathway in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. J Plant Growth Regul 37, 971–985 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9795-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9795-x