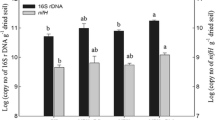
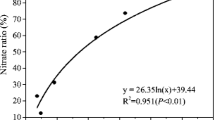
Abstract
Un-fertilized rice paddies have shown maintained soil nitrogen (N) status, stable N supply to the rice plant and sustained rice yields at moderate levels for hundreds of years. Microbial N2 fixation is known to contribute N to un-fertilized paddies, but it cannot fully explain the maintained N nutrition, where favourable conditions exist for N loss by denitrification. We used 15N tracer, 15N2 uptake, acetylene reduction assay and qPCR to simultaneously investigate N2 fixation, dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium (DNRA), denitrification and related microbial gene abundances in long-term low (or no) and high N input rice paddies of Myanmar. We also determined how varying soil organic carbon-to-nitrate (SOC/NO3−) ratios affect nitrate partitioning between DNRA and denitrification by manipulating these ratios through labile organic carbon addition. We observed more than 2.5 times higher N2 fixation (1.49–2.08 μg N g−1 soil day−1) and significantly higher N2 fixing gene (nifH) abundance in low compared with high N input paddies. Up to 60% of the soil nitrate (1.51–2.67 μg NO3−-N g−1 soil day−1) was ammonified through DNRA, and only 15% was lost as N2 through denitrification in low N input paddies, whereas denitrification exceeded DNRA in high N input paddies. The microbial gene related to DNRA activity (nrfA) was also higher in low input than in high input rice paddies. We found that nitrate retention can be improved in high N input rice paddies by maintaining a higher soil organic carbon-to-nitrate ratio. Our findings highlight the unique microbial N-cycling strategies in resource-limited paddies which support maintained N nutrition of the paddy system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arth I, Frenzel P, Conrad R (1998) Denitrification coupled to nitrification in the rhizosphere of rice. Soil Biol Biochem 30:509–515
Aulakh MS, Khera TS, Doran JW, Bronson KF (2001) Denitrification, N2O and CO2 fluxes in rice-wheat cropping system as affected by crop residues, fertilizer N and legume green manure. Biol Fertil Soils 34:375–389
Barron AR, Wurzburger N, Bellenger JP, Wright SJ, Kraepiel AM, Hedin LO (2009) Molybdenum limitation of asymbiotic nitrogen fixation in tropical forest soils. Nat Geosci 2:42–45
Bei Q, Liu G, Tang H, Cadisch G, Rasche F, Xie Z (2013) Heterotrophic and phototrophic 15N2 fixation and distribution of fixed 15N in a flooded rice–soil system. Soil Biol Biochem 59:25–31
Bei Q, Xie Z, Cadisch G, Rasche F (2019) K-strategic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria capitalize on biological nitrogen fixation in a flooded, un-fertilised rice soil. Biol Fertil Soils 55:713–722
Bi L, Zhang B, Liu G, Li Z, Liu Y, Ye C, Yu X, Lai T, Zhang J, Yin J, Liang Y (2009) Long-term effects of organic amendments on the rice yields for double rice cropping systems in subtropical China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129:534–541
Bru D, Sarr A, Philippot L (2007) Relative abundances of proteobacterial membrane-bound and periplasmic nitrate reductases in selected environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5971–5974. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00643-07
Cassman KG, Peng S, Olk D, Ladha J, Reichardt W, Dobermann A, Singh U (1998) Opportunities for increased nitrogen-use efficiency from improved resource management in irrigated rice systems. Field Crop Res 56:7–39
Castellano-Hinojosa A, González-López J, Bedmar EJ (2018) Distinct effect of nitrogen fertilisation and soil depth on nitrous oxide emissions and nitrifiers and denitrifiers abundance. Biol Fertil Soils 54:829–840
Cusack DF, Silver WL, Torn MS, Burton SD, Firestone MK (2011) Changes in microbial community characteristics and soil organic matter with nitrogen additions in two tropical forests. Ecology 92:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-0459.1
Dail DB, Davidson EA, Chorover J (2001) Rapid abiotic transformation of nitrate in an acid forest soil. Biogeochemistry 54:131–146
Denning G, Baroang K, Sandar TM (2013) Rice productivity improvement in Myanmar. Background paper:21
Deutsch C, Sarmiento JL, Sigman DM, Gruber N, Dunne JP (2007) Spatial coupling of nitrogen inputs and losses in the ocean. Nature 445:163–167
Dobermann A, Witt C, Abdulrachman S, Gines HC, Nagarajan R, Son TT, Tan PS, Wang GH, Chien NV, Thoa VT, Phung CV (2003) Soil fertility and indigenous nutrient supply in irrigated rice domains of Asia. Agron J 95:913–923
Dou X, He P, Cheng X, Zhou W (2016) Long-term fertilization alters chemically-separated soil organic carbon pools: based on stable C isotope analyses. Sci Rep 6:19061
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1, Agron Monogr 9, 2nd Ed. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 383–412
Henry S, Bru D, Stres B, Hallet S, Philippot L (2006) Quantitative detection of the nosZ gene, encoding nitrous oxide reductase, and comparison of the abundances of 16S rRNA, narG, nirK, and nosZ genes in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5181–5189. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00231-06
Hori T, Müller A, Igarashi Y, Conrad R, Friedrich MW (2010) Identification of iron-reducing microorganisms in anoxic rice paddy soil by 13C-acetate probing. ISME J 4:267–278
Huygens D, Boeckx P, Templer P, Paulino L, Van Cleemput O, Oyarzún C, Müller C, Godoy R (2008) Mechanisms for retention of bioavailable nitrogen in volcanic rainforest soils. Nat Geosci 1:543–548
Jonsson A, Nordlund S (2007) In vitro studies of the uridylylation of the three PII protein paralogs from Rhodospirillum rubrum: the transferase activity of R. rubrum GlnD is regulated by α-ketoglutarate and divalent cations but not by glutamine. J Bacteriol 189:3471–3478
Keuter A, Veldkamp E, Corre MD (2014) Asymbiotic biological nitrogen fixation in a temperate grassland as affected by management practices. Soil Biol Biochem 70:38–46
Kimura M, Murase J, Lu YH (2004) Carbon cycling in rice field ecosystems in the context of input, decomposition and translocation of organic materials and the fates of their end products (CO2 and CH4). Soil Biol Biochem 36:1399–1416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.03.006
Kraft B, Strous M, Tegetmeyer HE (2011) Microbial nitrate respiration - genes, enzymes and environmental distribution. J Biotechnol 155:104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.12.025
Kraft B, Tegetmeyer HE, Sharma R, Klotz MG, Ferdelman TG, Hettich RL, Geelhoed JS, Strous M (2014) The environmental controls that govern the end product of bacterial nitrate respiration. Science 345:676–679
Kyaw KM, Toyota K, Okazaki M, Motobayashi T, Tanaka H (2005) Nitrogen balance in a paddy field planted with whole crop rice (Oryza sativa cv. Kusahonami) during two rice-growing seasons. Biol Fertil Soils 42:72–82
Lindau CW, Patrick WH, Delaune RD, Reddy KR (1990) Rate of accumulation and emission of N2, N2O and CH4 from a flooded rice soil. Plant Soil 129:269–276
Mills MM, Ridame C, Davey M, La Roche J, Geider RJ (2004) Iron and phosphorus co-limit nitrogen fixation in the eastern tropical North Atlantic. Nature 429:292–294
Minick K, Pandey C, Fox T, Subedi S (2016) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium and N2O flux: effect of soil redox potential and N fertilization in loblolly pine forests. Biol Fertil Soils 52:601–614
Moore CM, Mills MM, Achterberg EP, Geider RJ, LaRoche J, Lucas MI, McDonagh EL, Pan X, Poulton AJ, Rijkenberg MJ, Suggett DJ (2009) Large-scale distribution of Atlantic nitrogen fixation controlled by iron availability. Nat Geosci 2:867–871
Neff JC, Townsend AR, Gleixner G, Lehman SJ, Turnbull J, Bowman WD (2002) Variable effects of nitrogen additions on the stability and turnover of soil carbon. Nature 419:915–917
Ouyang Y, Evans SE, Friesen ML, Tiemann LK (2018) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on the abundance of nitrogen cycling genes in agricultural soils: a meta-analysis of field studies. Soil Biol Biochem 127:71–78
Pan H, Ying S, Liu H, Zeng L, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Xu J, Li Y, Di H (2018) Microbial pathways for nitrous oxide emissions from sheep urine and dung in a typical steppe grassland. Biol Fertil Soils 54:717–730
Pandey A, Suter H, He J-Z, Hu H-W, Chen D (2018) Nitrogen addition decreases dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in rice paddies. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:e00870–e00818
Pandey A, Suter H, He J-Z, Hu H-W, Chen D (2019) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium dominates nitrate reduction in long-term low nitrogen fertilized rice paddies. Soil Biol Biochem 131:149–156
Perakis SS, Hedin LO (2001) Fluxes and fates of nitrogen in soil of an unpolluted old-growth temperate forest, southern Chile. Ecology 82:2245–2260
Putz M, Schleusner P, Rütting T, Hallin S (2018) Relative abundance of denitrifying and DNRA bacteria and their activity determine nitrogen retention or loss in agricultural soil. Soil Biol Biochem 123:97–104
Rayment GE, Lyons DJ (2011) Soil chemical methods: Australasia vol 3. CSIRO publishing, Clayton
Rice CW, Tiedje JM (1989) Regulation of nitrate assimilation by ammonium in soils and in isolated soil-microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 21:597–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(89)90135-1
Rocca JD, Hall EK, Lennon JT, Evans SE, Waldrop MP, Cotner JB, Nemergut DR, Graham EB, Wallenstein MD (2015) Relationships between protein-encoding gene abundance and corresponding process are commonly assumed yet rarely observed. ISME J 9:1693–1699
Rösch C, Bothe H (2005) Improved assessment of denitrifying, N2-fixing, and total-community bacteria by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis using multiple restriction enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2026–2035
Schmidt CS, Richardson DJ, Baggs EM (2011) Constraining the conditions conducive to dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in temperate arable soils. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1607–1611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.02.015
Silver WL, Herman DJ, Firestone MK (2001) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in upland tropical forest soils. Ecology 82:2410–2416
Song GD, Liu SM, Marchant H, Kuypers MMM, Lavik G (2013) Anammox, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in the East China Sea sediment. Biogeosciences 10:6851–6864. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-10-6851-2013
Song B, Lisa JA, Tobias CR (2014) Linking DNRA community structure and activity in a shallow lagoonal estuarine system. Front Microbiol 5:460. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00460
Stewart BA (1995) Soil management: experimental basis for sustainability and environmental quality, vol 4. CRC press, Boca Raton
Stone MM, Kan JJ, Plante AF (2015) Parent material and vegetation influence bacterial community structure and nitrogen functional genes along deep tropical soil profiles at the Luquillo Critical Zone Observatory. Soil Biol Biochem 80:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.10.019
Strohm TO, Griffin B, Zumft WG, Schink B (2007) Growth yields in bacterial denitrification and nitrate ammonification. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1420–1424. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.02508-06
Tang Y, Zhang M, Chen A, Zhang W, Wei W, Sheng R (2017) Impact of fertilization regimes on diazotroph community compositions and N2 fixation activity in paddy soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 247:1–8
Thwe HM, Kristiansen P, Herridge DF (2019) Benchmarks for improved productivity and profitability of monsoon rice in lower Myanmar. Field Crop Res 233:59–69
Trimmer M, Nicholls JC (2009) Production of nitrogen gas via anammox and denitrification in intact sediment cores along a continental shelf to slope transect in the North Atlantic. Limnol Oceanogr 54:577–589. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2009.54.2.0577
Trimmer M, Engstrom P, Thamdrup B (2013) Stark contrast in denitrification and anammox across the deep Norwegian trench in the Skagerrak. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:7381–7389. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01970-13
Van den Berg EM, Van Dongen U, Abbas B, Van Loosdrecht MC (2015) Enrichment of DNRA bacteria in a continuous culture. ISME J 9:2153–2161
Van den Berg EM, Boleij M, Kuenen JG, Kleerebezem R, van Loosdrecht M (2016) DNRA and denitrification coexist over a broad range of acetate/N-NO3− ratios, in a chemostat enrichment culture. Front Microbiol 7:1842
Walker JKM, Egger KN, Henry GHR (2008) Long-term experimental warming alters nitrogen-cycling communities but site factors remain the primary drivers of community structure in high arctic tundra soils. ISMEJ J 2:982–995. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2008.52
Wang J, Zhang L, Lu Q, Raza W, Huang Q, Shen Q (2014) Ammonia oxidizer abundance in paddy soil profile with different fertilizer regimes. Appl Soil Ecol 84:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.06.009
Wang C, Zheng M, Song W, Wen S, Wang B, Zhu C, Shen R (2017) Impact of 25 years of inorganic fertilization on diazotrophic abundance and community structure in an acidic soil in southern China. Soil Biol Biochem 113:240–249
Welsh A, Chee-Sanford JC, Connor LM, Löffler FE, Sanford RA (2014) Refined NrfA phylogeny improves PCR-based nrfA gene detection. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:2110–2119
Wu Y, Lu L, Wang B, Lin X, Zhu J, Cai Z, Yan X, Jia Z (2011) Long-term field fertilization significantly alters community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria rather than archaea in a paddy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:1431–1439
Xia L, Li X, Ma Q, Lam SK, Wolf B, Kiese R, Butterbach-Bahl K, Chen D, Li Z, Yan X (2020) Simultaneous quantification of N2, NH3 and N2O emissions from a flooded paddy field under different N fertilization regimes. Glob Chang Biol 26:2292–2303
Yang Y, Zhang M, Li Y, Fan X, Geng Y (2013) Controlled-release urea commingled with rice seeds reduced emission of ammonia and nitrous oxide in rice paddy soil. J Environ Qual 42:1661–1673. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2013.06.0255
Yang WH, Ryals RA, Cusack DF, Silver WL (2017) Cross-biome assessment of gross soil nitrogen cycling in California ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 107:144–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.01.004
Yoon S, Cruz-García C, Sanford R, Ritalahti KM, Löffler FE (2015) Denitrification versus respiratory ammonification: environmental controls of two competing dissimilatory NO3−/NO2− reduction pathways in Shewanella loihica strain PV-4. ISME J 9:1093–1104
Zhang J, Cai Z, Yang W, Zhu T, Yu Y, Yan X, Jia Z (2012) Long-term field fertilization affects soil nitrogen transformations in a rice-wheat-rotation cropping system. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 175(6):939–946
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Melbourne Trace Analysis for Chemical, Earth and Environmental Sciences (TrACEES), The University of Melbourne for analytical support. We gratefully thank Grahame Hunter, Soe Thura (both from International Fertilizer Development Center, Myanmar), Aung Myo Thant and Dr. Aung Kyaw Myint (both from Yezin Agricultural University, Myanmar) for their technical and logistic support.
Funding
This research was funded by ACIAR (Grant No. SMCN/2014/044) and ARC (Grant No. DP160101028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5406 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, A., Suter, H., He, JZ. et al. Dissimilatory nitrate ammonification and N2 fixation helps maintain nitrogen nutrition in resource-limited rice paddies. Biol Fertil Soils 57, 107–115 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01508-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01508-2