Abstract
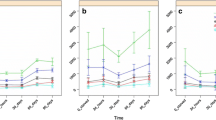
The effects of simulated acid rain and acidification, combined with liming, on amylolytic, laminarinolytic and xylanolytic activity in whole body homogenates of enchytraeids Cognettia sphagnetorum were studied under field conditions. Simulated acid rain (pH 2.5) and simulated acid rain with subsequent liming (CaCO3) were applied to experimental plots in a mixed forest soil. The pH of the soil was lowered by acid treatment (4.3), while the pH increased after liming (6.3) in comparison with the control (4.5). Acidification of soil caused a decrease in enchytraeid body mass and amylolytic activity. In acidified plots after liming, amylolytic activity and laminarinolytic activity increased, while live body mass decreased. The enzymatic activity of enchytraeids depended on season and also indirectly on individual mean mass.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 February 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sˇustr, V., Chalupsky´, J. & Krisˇtu˚fek, V. Effects of artificial acidification and liming on the activity of digestive enzymes in Cognettia sphagnetorum (Vejdovsky´, 1878) (Annelida, Enchytraeidae). Biol Fertil Soils 24, 227–230 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050235
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050235