Abstract
Introduction
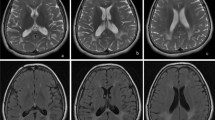
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis is progressive, fatal encephalitis caused by a persistent defective measles virus in the central nervous system. The diagnosis is based upon characteristic clinical manifestations, the presence of characteristic periodic EEG discharges, and demonstration of elevated antibody titer against measles in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. There has been no correlation between the clinical status and the MRI findings.
Methods
We performed single voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) on white matter areas that appeared normal or abnormal on conventional MRI in three patients with different clinical stages.
Results
N-acetyl aspartate:creatine ratios were decreased and choline:creatine ratios were increased in white matter lesions in the late stages of the disease. A lactate peak was observed in a patient in the last stage of the disease. Increased myoinositol:creatine ratio was seen in white matter areas on conventional MRI and in the white matter lesions at early stage of the disease, before neuronal loss.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicardi J (1998) Infectious diseases. In: Aicardi J (ed) Diseases of the nervous system in childhood. MacKeith, London, pp 410–411
Akdal G, Baklan B, Cakmakci H, Kovanlikaya A (2001) MRI follow-up of basal ganglia involvement in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Pediatr Neurol 24:393–395
Anlar B, Saatci I, Kose G, Yalaz K (1996) MRI findings in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Neurology 47:1278–1283
Anlar B (1997) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: diagnosis and drug treatment options. CNS Drugs 7:111–120
Bale JF(1999) Viral infections of the nervous system. In: Swaiman KF, Ashwal S (eds) Pediatric neurology. Mosby, St Louis, pp 1003–1004
Barkovich AJ (2000) Normal development of the neonatal and infant brain, skull and spine. In: Barkovich AJ (ed) Pediatric neuroimaging. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 55–61
Bohlega S, al-Kawi MZ (1994) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Imaging and clinical correlation. J Neuroimaging 4:71–76
Brismar J, Gascon GG, von Steyern KV, Bohlega S (1996) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: evaluation with CT and MR. Am J Neuroradiol 17:761–772
Danielsen ER, Ross B (1999) The clinical significance of metabolites. In: Danielsen ER, Ross B (eds) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy diagnosis of neurological diseases. Dekker, New York, pp 23–43
Dyken PR, Cunningham S (1987) From the National SSPE Registry. Neurology 37:1883
Kato Z, Saito K, Yamada M, Asano T, Kondo N (2002) Proton MRS in a case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Child Neurol 17:788–790
Kulczycki J, Kryst-Widzgowska T, Sobczyk W, Milewska D, Bochynska A (1994) Changes in NMR and CT images in SSPE. Neurol Neurochir Pol 28 [Suppl 1]:79–90
Novotny E, Ashwal S, Shevell M (1998) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: an emerging technology in pediatric neurology research. Pediatr Res 44:1–10
Salvan AM, Confort-Gouny S, Cozzone PJ, Vion-Dury J, Chabrol B, Mancini J (1999) In vivo cerebral proton MRS in a case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:547–555
Tsuchiya K, Yamauchi T, Fusui S (1988) MR imaging vs CT in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Am J Neuroradiol 9:943–946
Tuncay R, Akman-Demir G, Gokyigit A, Eraksoy M, Barlas M, Tolun R, Gursoy G (1996) MRI in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Neuroradiology 38:636–640
Vion-Dury J, Meyerhoff DJ, Cozzone PJ (1994) What might be the impact on neurology of the analysis of brain metabolism by in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy? J Neurol 241:354–371
Wirguin I, Steiner I, Brenner T, Abramsky O (1991) Intraventricular interferon treatment for subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Ann Neurol 30:227
Zilber N, Kahana E (1998) Environmental risk factors for subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Acta Neurol Scand 98:49–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cakmakci, H., Kurul, S., Iscan, A. et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in three subacute sclerosing panencephalitis patients: correlation with clinical status. Childs Nerv Syst 20, 216–220 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0896-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-003-0896-9