Abstract
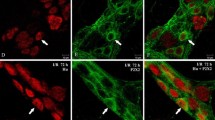
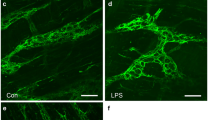
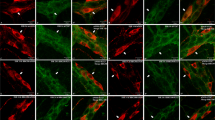
Damage following ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) is common in the intestine and can be caused during abdominal surgery, in several disease states and following intestinal transplantation. Most studies have concentrated on damage to the mucosa, although published evidence also points to effects on neurons. Moreover, alterations of neuronally controlled functions of the intestine persist after I/R. The present study was designed to investigate the time course of damage to neurons and the selectivity of the effect of I/R damage for specific types of enteric neurons. A branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the distal ileum of anesthetised guinea pigs was occluded for 1 h and the animals were allowed to recover for 2 h to 4 weeks before tissue was taken for the immunohistochemical localization of markers of specific neuron types in tissues from sham and I/R animals. The dendrites of neurons with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) immunoreactivity, which are inhibitory motor neurons and interneurons, were distorted and swollen by 24 h after I/R and remained enlarged up to 28 days. The total neuron profile areas (cell body plus dendrites) increased by 25%, but the sizes of cell bodies did not change significantly. Neurons of type II morphology (intrinsic primary afferent neurons), revealed by NeuN immunoreactivity, were transiently reduced in cell size, at 24 h and 7 days. These neurons also showed signs of minor cell surface blebbing. Calretinin neurons, many of which are excitatory motor neurons, were unaffected. Thus, this study revealed a selective damage to NOS neurons that was observed at 24 h and persisted up to 4 weeks, without a significant change in the relative numbers of NOS neurons.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An S, Hishikawa Y, Koji T (2005) Induction of cell death in rat small intestine by ischemia reperfusion: differential roles of Fas/Fas ligand and Bcl-2/Bax systems depending upon cell types. Histochem Cell Biol 123:249–261. doi:10.1007/s00418-005-0765-6
Baimbridge KG, Celio MR, Rogers JH (1992) Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 15:303–308. doi:10.1016/0166-2236(92)90081-I
Calcina F, Barocelli E, Bertoni S, Furukawa O, Kaunitz J, Impicciatore M, Sternini C (2005) Effect of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor blockade on neuronal plasticity and gastrointestinal transit delay induced by ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neuroscience 134:39–49. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.03.052
Chiocchetti R, Poole DP, Kimura H, Aimi Y, Robbins HL, Castelucci P, Furness JB (2003) Evidence that two forms of choline acetyltransferase are differentially expressed in subclasses of enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 311:11–22. doi:10.1007/s00441-002-0652-6
D’Orlando C, Fellay B, Schwaller B, Salicio V, Bloc A, Gotzos V, Celio MR (2001) Calretinin and calbindin D-28 k delay the onset of cell death after excitotoxic stimulation in transfected P19 cells. Brain Res 909:145–158. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02671-3
Dekkers J, Bayley P, Dick JRT, Schwaller B, Berchtold MW, Greensmith L (2004) Over-expression of parvalbumin in transgenic mice rescues motoneurons from injury-induced cell death. Neuroscience 123:459–466. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.07.013
Dong Z, Saikumar P, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA (2006) Calcium in cell injury and death. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 1:405–434. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100218
Fairman CL, Clagett Dame M, Lennon VA, Epstein ML (1995) Appearance of neurons in the developing chick gut. Dev Dyn 204:192–201
Ferens D, Baell J, Lessene G, Smith JE, Furness JB (2007) Effects of modulators of Ca2+-activated, intermediate-conductance potassium channels on motility of the rat small intestine, in vivo. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:383–389. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2007.00898.x
Fryer JP (2005) Intestinal transplantation: an update. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 21:162–168. doi:10.1097/01.mog.0000153313.43574.1b
Furness JB (2000) Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:87–96. doi:10.1016/S0165-1838(00)00127-2
Furness JB, Robbins HL, Selmer I-S, Hunne B, Chen MX, Hicks GA, Moore S, Neylon CB (2003) Expression of intermediate conductance potassium channel immunoreactivity in neurons and epithelial cells of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 314:179–189. doi:10.1007/s00441-003-0808-z
Furness JB, Trussell DC, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC, Smith TK (1990) Calbindin neurons of the guinea pig small intestine: quantitative analysis of their numbers and projections. Cell Tissue Res 260:261–272. doi:10.1007/BF00318629
Granger N, Korthuis RJ (1995) Physiologic mechanisms of postischemic tissue injury. Annu Rev Physiol 57:311–332
Grossie VB, Weisbrodt NW, Moore FA, Moody F (2001) Ischemia/reperfusion-induced disruption of rat small intestine transit is reversed by total enteral nutrition. Nutrition 17:939–943. doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00668-2
Hakgüder G, Akgür FM, Ateş O, Olguner M, Aktuğ T, Özer E (2002) Short-term intestinal ischemia–reperfusion alters intestinal motility that can be preserved by xanthine oxidase inhibition. Dig Dis Sci 47:1279–1283. doi:10.1023/A:1015314312730
Hierholzer C, Kalff JC, Audolfsson G, Billiar TR, Tweardy DJ, Bauer AJ (1999) Molecular and functional contractile sequelae of rat intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Transplantation 68:1244–1254. doi:10.1097/00007890-199911150-00006
Hind A, Migliori M, Thacker M, Staikopoulos V, Nurgali K, Chiocchetti R, Furness JB (2005) Primary afferent neurons intrinsic to the intestine, like primary afferent neurons of spinal and cranial sensory ganglia, bind the lectin, IB4. Cell Tissue Res 321:151–157. doi:10.1007/s00441-005-1129-1
Hossmann K-A (2006) Pathophysiology and therapy of experimental stroke. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:1057–1083. doi:10.1007/s10571-006-9008-1
Isaacs KR, Wolpoe ME, Jacobowitz DM (1997) Calretinin-immunoreactive dopaminergic neurons from embryonic rat mesencephalon are resistant to levodopa-induced neurotoxicity. Exp Neurol 146:25–32. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6530
Itoh H, Yagi M, Fushida S, Tani T, Hashimoto T, Shimizu K, Miwa K (2000) Activation of immediate early gene, c-fos, and c-jun in the rat small intestine after ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantation 69:598–604. doi:10.1097/00007890-200002270-00022
Kristián T, Siesjö BK (1998) Calcium in ischemic cell death. Stroke 29:705–718
Lindeström L-M, Ekblad E (2004) Structural and neuronal changes in rat ileum after ischemia with reperfusion. Dig Dis Sci 49:1212–1222. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000037815.63547.08
Lukas W, Jones KA (1994) Cortical neurons containing calretinin are selectively resistant to calcium overload and excitotoxicity in vitro. Neuroscience 61:307–316. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(94)90233-X
Maher AD, Kuchel PW (2003) The Gárdos channel: a review of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in human erythrocytes. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 35:1182–1197. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(02)00310-2
Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC, Seifalian AM (2004) Ischemia–reperfusion injury of the intestine and protective strategies against injury. Dig Dis Sci 49:1359–1377. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000042232.98927.91
Mei F, Guo S, He Y-T, Zhu J, Zhou D-S, Niu J-Q, Wang H-Z, Tian Y-P (2009) Apoptosis of interstitial cells of Cajal, smooth muscle cells, and enteric neurons induced by intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury in adult guinea pigs. Virchows Arch 454:401–409. doi:10.1007/s00428-009-0739-5
Moro MA, Cárdenas A, Hurtado O, Leza JC, Lizasoain I (2004) Role of nitric oxide after brain ischaemia. Cell Calcium 36:265–275. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2004.02.011
Nguyen TV, Matsuyama H, Baell J, Hunne B, Fowler CJ, Smith JE, Nurgali K, Furness JB (2007) Effects of compounds that influence I K (KCNN4) channels on after hyperpolarizing potentials, and determination of I K channel sequence, in guinea pig enteric neurons. J Neurophysiol 97:2024–2031. doi:10.1152/jn.00935.2006
Nitsch C, Scotti A, Sommacal A, Kalt G (1989) GABAergic hippocampal neurons resistant to ischemia-induced neuronal death contain the Ca2+-binding protein parvalbumin. Neurosci Lett 105:263–268. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(89)90631-9
Piao DX, Jiang HC, Kosaka M, Shibata T, Ohtsuka A, Murakami T (1999) Cytoplasmic delayed neuronal death in the myenteric plexus of the rat small intestine after ischemia. Arch Histol Cytol 62:383–392. doi:10.1679/aohc.62.383
Pompolo S, Furness JB (1990) Ultrastructure and synaptology of neurons immunoreactive for gamma-aminobutyric acid in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurocytol 19:539–549. doi:10.1007/BF01257242
Qu Z-D, Thacker M, Castelucci P, Bagyánszki M, Epstein ML, Furness JB (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of neuron types in the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 334:147–161. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0684-7
Rodriguez R, Ventura-Martinez R, Santiago-Mejia J, Avila-Costa MR, Fortoul TI (2006) Altered responsiveness of the guinea pig isolated ileum to smooth muscle stimulants and to electrical stimulation after in situ ischemia. Br J Pharmacol 147:371–378. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706618
Segundo C, Medina F, Rodríguez C, Martínez-Palencia R, Leyva-Cobián F, Brieva JA (2008) Surface molecule loss and bleb formation by human germinal center B cells undergoing apoptosis: role of apoptotic blebs in monocyte chemotaxis. Blood 94:1012–1020
Shimojima N, Nakaki T, Morikawa Y, Hoshino K, Ozaki H, Hori M, Kitajima M (2006) Interstitial cells of Cajal in dysmotility in intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res 135:255–261. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.04.022
Silva MACP, de Meirelles LR, Bustorff-Silva JM (2007) Changes in intestinal motility and in the myenteric plexus in a rat model of intestinal ischemia–reperfusion. J Pediatr Surg 42:1062–1065. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.07.009
Türler A, Kalff JC, Heeckt P, Abu-Elmagd KM, Schraut WH, Bond GJ, Moore BA, Brünagel G, Bauer AJ (2002) Molecular and functional observations on the donor intestinal muscularis during human small bowel transplantation. Gastroenterology 122:1886–1897. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.33628
Udassin R, Eimeri D, Schiffman J, Haskel Y (1995) Postischemic intestinal motility in rat is inversely correlated to length of ischemia, an in vivo animal model. Dig Dis Sci 40:1035–1038. doi:10.1007/BF02064193
Ventura-Martinez R, Santiago-Mejia J, Gomez C, Rodriguez R, Fortoul TI (2007) Acute morphological changes in guinea pig ileum myenteric neurons after ischemia in situ with superfusion in vitro. Pathol Res Pract 204:121–127
Wang J, Morishima S, Okada Y (2003) IK channels are involved in the regulatory volume decrease in human epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 284:C77–C84
Wedel T, Krammer HJ, Kühnel W, Sigge W (1998) Alterations of the enteric nervous system in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis revealed by whole-mount immunohistochemistry. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med 18:57–70. doi:10.1080/107710498174227
Williamson S, Pompolo S, Furness JB (1996) GABA and nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivities are colocalized in a subset of inhibitory motor neurons of the guinea pig small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 284:29–37. doi:10.1007/s004410050564
Yamamoto S, Tanabe M, Wakabayashi G, Shimazu M, Matsumoto K, Kitajima M (2001) The role of tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in ischemia–reperfusion injury of the rat small intestine. J Surg Res 99:134–141. doi:10.1006/jsre.2001.6106
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a University of Melbourne visiting scholar award and a Fellowship of the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, number 2008/05718-9 (to PC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rivera, L.R., Thacker, M., Castelucci, P. et al. The reactions of specific neuron types to intestinal ischemia in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 118, 261–270 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0549-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0549-5