Abstract
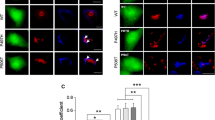
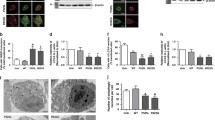
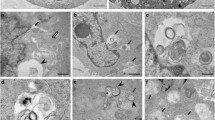
Several diverse proteins are linked genetically/pathologically to neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) including SOD1, TDP-43 and FUS. Using a variety of cellular and biochemical techniques, we demonstrate that ALS-associated mutant TDP-43, FUS and SOD1 inhibit protein transport between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus in neuronal cells. ER–Golgi transport was also inhibited in embryonic cortical and motor neurons obtained from a widely used animal model (SOD1G93A mice), validating this mechanism as an early event in disease. Each protein inhibited transport by distinct mechanisms, but each process was dependent on Rab1. Mutant TDP-43 and mutant FUS both inhibited the incorporation of secretory protein cargo into COPII vesicles as they bud from the ER, and inhibited transport from ER to the ER–Golgi intermediate (ERGIC) compartment. TDP-43 was detected on the cytoplasmic face of the ER membrane, whereas FUS was present within the ER, suggesting that transport is inhibited from the cytoplasm by mutant TDP-43, and from the ER by mutant FUS. In contrast, mutant SOD1 destabilised microtubules and inhibited transport from the ERGIC compartment to Golgi, but not from ER to ERGIC. Rab1 performs multiple roles in ER–Golgi transport, and over-expression of Rab1 restored ER–Golgi transport, and prevented ER stress, mSOD1 inclusion formation and induction of apoptosis, in cells expressing mutant TDP-43, FUS or SOD1. Rab1 also co-localised extensively with mutant TDP-43, FUS and SOD1 in neuronal cells, and Rab1 formed inclusions in motor neurons of spinal cords from sporadic ALS patients, which were positive for ubiquitinated TDP-43, implying that Rab1 is misfolded and dysfunctional in sporadic disease. These results demonstrate that ALS-mutant forms of TDP-43, FUS, and SOD1 all perturb protein transport in the early secretory pathway, between ER and Golgi compartments. These data also imply that restoring Rab1-mediated ER–Golgi transport is a novel therapeutic target in ALS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hauri HP (2006) The ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC): in search of its identity and function. J Cell Sci 119:2173–2183. doi:10.1242/jcs.03019
Aridor M, Fish KN (2009) Selective targeting of ER exit sites supports axon development. Traffic 10:1669–1684. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00974.x
Atkin JD, Farg MA, Soo KY, Walker AK, Halloran M, Turner BJ, Nagley P, Horne MK (2014) Mutant SOD1 inhibits ER-Golgi transport in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 129:190–204. doi:10.1111/jnc.12493
Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R (1994) COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 77:895–907
Bilsland LG, Sahai E, Kelly G, Golding M, Greensmith L, Schiavo G (2010) Deficits in axonal transport precede ALS symptoms in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20523–20528. doi:10.1073/pnas.1006869107
Borg J, Grimby L, Hannerz J (1979) Motor neuron firing range, axonal conduction velocity, and muscle fiber histochemistry in neuromuscular diseases. Muscle Nerve 2:423–430. doi:10.1002/mus.880020603
Botzolakis EJ, Zhao J, Gurba KN, Macdonald RL, Hedera P (2011) The effect of HSP-causing mutations in SPG3A and NIPA1 on the assembly, trafficking, and interaction between atlastin-1 and NIPA1. Mol Cell Neurosci 46:122–135. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2010.08.012
Chang LY, Slot JW, Geuze HJ, Crapo JD (1988) Molecular immunocytochemistry of the CuZn superoxide dismutase in rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol 107:2169–2179
Chen S, Zhang X, Song L, Le W (2012) Autophagy dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Pathol 22:110–116. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00546.x
Comley L, Allodi I, Nichterwitz S, Nizzardo M, Simone C, Corti S, Hedlund E (2015) Motor neurons with differential vulnerability to degeneration show distinct protein signatures in health and ALS. Neuroscience 291:216–229. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.02.013
Cooper AA, Gitler AD, Cashikar A, Haynes CM, Hill KJ, Bhullar B, Liu K, Xu K, Strathearn KE, Liu F et al (2006) Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science 313:324–328. doi:10.1126/science.1129462
del Toro D, Canals JM, Gines S, Kojima M, Egea G, Alberch J (2006) Mutant huntingtin impairs the post-Golgi trafficking of brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not its Val66Met polymorphism. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 26:12748–12757. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3873-06.2006
Deng HX, Zhai H, Bigio EH, Yan J, Fecto F, Ajroud K, Mishra M, Ajroud-Driss S, Heller S, Sufit R et al (2010) FUS-immunoreactive inclusions are a common feature in sporadic and non-SOD1 familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 67:739–748. doi:10.1002/ana.22051
Dompierre JP, Godin JD, Charrin BC, Cordelieres FP, King SJ, Humbert S, Saudou F (2007) Histone deacetylase 6 inhibition compensates for the transport deficit in Huntington’s disease by increasing tubulin acetylation. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 27:3571–3583. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0037-07.2007
Emr S, Glick BS, Linstedt AD, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Luini A, Malhotra V, Marsh BJ, Nakano A, Pfeffer SR, Rabouille C et al (2009) Journeys through the Golgi—taking stock in a new era. J Cell Biol 187:449–453. doi:10.1083/jcb.200909011
Farg MA, Soo KY, Walker AK, Pham H, Orian J, Horne MK, Warraich ST, Williams KL, Blair IP, Atkin JD (2012) Mutant FUS induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and interacts with protein disulfide-isomerase. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.02.009
Farg MA, Sundaramoorthy V, Sultana JM, Yang S, Atkinson RA, Levina V, Halloran MA, Gleeson P, Blair IP, Soo KY et al (2014) C9ORF72, implicated in amytrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia, regulates endosomal trafficking. Hum Mol Genet. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu068
Filipeanu CM, Zhou F, Claycomb WC, Wu G (2004) Regulation of the cell surface expression and function of angiotensin II type 1 receptor by Rab1-mediated endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 279:41077–41084. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405988200
Forsberg K, Andersen PM, Marklund SL, Brannstrom T (2011) Glial nuclear aggregates of superoxide dismutase-1 are regularly present in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 121:623–634. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0805-3
Forsberg K, Jonsson PA, Andersen PM, Bergemalm D, Graffmo KS, Hultdin M, Jacobsson J, Rosquist R, Marklund SL, Brannstrom T (2010) Novel antibodies reveal inclusions containing non-native SOD1 in sporadic ALS patients. PLoS One 5:e11552. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011552
Garcia IA, Martinez HE, Alvarez C (2011) Rab1b regulates COPI and COPII dynamics in mammalian cells. Cell Logist 1:159–163. doi:10.4161/cl.1.4.18221
Ghaemmaghami S, Huh WK, Bower K, Howson RW, Belle A, Dephoure N, O’Shea EK, Weissman JS (2003) Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 425:737–741. doi:10.1038/nature02046
Haas AK, Yoshimura S, Stephens DJ, Preisinger C, Fuchs E, Barr FA (2007) Analysis of GTPase-activating proteins: Rab1 and Rab43 are key Rabs required to maintain a functional Golgi complex in human cells. J Cell Sci 120:2997–3010. doi:10.1242/jcs.014225
Hetz C, Mollereau B (2014) Disturbance of endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 15:233–249. doi:10.1038/nrn3689
Hirschberg K, Miller CM, Ellenberg J, Presley JF, Siggia ED, Phair RD, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1998) Kinetic analysis of secretory protein traffic and characterization of golgi to plasma membrane transport intermediates in living cells. J Cell Biol 143:1485–1503
Ilieva H, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2009) Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J Cell Biol 187:761–772
Ishida M, Ohbayashi N, Maruta Y, Ebata Y, Fukuda M (2012) Functional involvement of Rab1A in microtubule-dependent anterograde melanosome transport in melanocytes. J Cell Sci 125:5177–5187. doi:10.1242/jcs.109314
Ito D, Suzuki N (2007) Molecular pathogenesis of seipin/BSCL2-related motor neuron diseases. Ann Neurol 61:237–250. doi:10.1002/ana.21070
Jin L, Pahuja KB, Wickliffe KE, Gorur A, Baumgartel C, Schekman R, Rape M (2012) Ubiquitin-dependent regulation of COPII coat size and function. Nature 482:495–500. doi:10.1038/nature10822
Joshi G, Chi Y, Huang Z, Wang Y (2014) Abeta-induced Golgi fragmentation in Alzheimer’s disease enhances Abeta production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E1230–E1239. doi:10.1073/pnas.1320192111
Kabuta T, Kinugawa A, Tsuchiya Y, Kabuta C, Setsuie R, Tateno M, Araki T, Wada K (2009) Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant SOD1 aberrantly interacts with tubulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:121–126. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.138
Li L, Zhang X, Le W (2008) Altered macroautophagy in the spinal cord of SOD1 mutant mice. Autophagy 4:290–293
Lord C, Ferro-Novick S, Miller EA (2013) The highly conserved COPII coat complex sorts cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum and targets it to the golgi. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(2), pii: a013367. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a013367
Lorenz H, Hailey DW, Wunder C, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2006) The fluorescence protease protection (FPP) assay to determine protein localization and membrane topology. Nat Protoc 1:276–279. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.42
Mackenzie IR, Bigio EH, Ince PG, Geser F, Neumann M, Cairns NJ, Kwong LK, Forman MS, Ravits J, Stewart H et al (2007) Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Ann Neurol 61:427–434. doi:10.1002/ana.21147
Manders EMM, Verbeek FJ, Atenm JA (1993) Measurement of co-localization of objects in dual-colour confocal images. J Microsc 169:375–382
Marie M, Sannerud R, Avsnes Dale H, Saraste J (2008) Take the ‘A’ train: on fast tracks to the cell surface. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 65:2859–2874. doi:10.1007/s00018-008-8355-0
Matsuoka K, Orci L, Amherdt M, Bednarek SY, Hamamoto S, Schekman R, Yeung T (1998) COPII-coated vesicle formation reconstituted with purified coat proteins and chemically defined liposomes. Cell 93:263–275
Mourelatos Z, Gonatas NK, Stieber A, Gurney ME, Dal Canto MC (1996) The Golgi apparatus of spinal cord motor neurons in transgenic mice expressing mutant Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase becomes fragmented in early, preclinical stages of the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5472–5477
Nakagomi S, Barsoum MJ, Bossy-Wetzel E, Sutterlin C, Malhotra V, Lipton SA (2008) A Golgi fragmentation pathway in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 29:221–231. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2007.08.015
Nishitoh H, Kadowaki H, Nagai A, Maruyama T, Yokota T, Fukutomi H, Noguchi T, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2008) ALS-linked mutant SOD1 induces ER stress- and ASK1-dependent motor neuron death by targeting Derlin-1. Genes Dev 22:1451–1464
Nuoffer C, Davidson HW, Matteson J, Meinkoth J, Balch WE (1994) A GDP-bound of rab1 inhibits protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport between Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 125:225–237
Orci L, Palmer DJ, Ravazzola M, Perrelet A, Amherdt M, Rothman JE (1993) Budding from Golgi membranes requires the coatomer complex of non-clathrin coat proteins. Nature 362:648–652. doi:10.1038/362648a0
Pelletier S, Gingras S, Howell S, Vogel P, Ihle JN (2012) An early onset progressive motor neuron disorder in Scyl1-deficient mice is associated with mislocalization of TDP-43. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 32:16560–16573. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1787-12.2012
Perdiz D, Mackeh R, Pous C, Baillet A (2011) The ins and outs of tubulin acetylation: more than just a post-translational modification? Cell Signal 23:763–771. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.10.014
Philips T, Rothstein JD (2014) Glial cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 262(Pt B):111–120. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.05.015
Plutner H, Cox AD, Pind S, Khosravi-Far R, Bourne JR, Schwaninger R, Der CJ, Balch WE (1991) Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 115:31–43
Preston AM, Gurisik E, Bartley C, Laybutt DR, Biden TJ (2009) Reduced endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi protein trafficking contributes to ER stress in lipotoxic mouse beta cells by promoting protein overload. Diabetologia 52:2369–2373. doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1506-5
Prosser DC, Tran D, Gougeon PY, Verly C, Ngsee JK (2008) FFAT rescues VAPA-mediated inhibition of ER-to-Golgi transport and VAPB-mediated ER aggregation. J Cell Sci 121:3052–3061. doi:10.1242/jcs.028696
Pun S, Santos AF, Saxena S, Xu L, Caroni P (2006) Selective vulnerability and pruning of phasic motoneuron axons in motoneuron disease alleviated by CNTF. Nat Neurosci 9:408–419. doi:10.1038/nn1653
Rabin SJ, Kim JM, Baughn M, Libby RT, Kim YJ, Fan Y, La Spada A, Stone B, Ravits J (2010) Sporadic ALS has compartment-specific aberrant exon splicing and altered cell-matrix adhesion biology. Hum Mol Genet 19:313–328. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp498
Ramirez OA, Couve A (2011) The endoplasmic reticulum and protein trafficking in dendrites and axons. Trends Cell Biol 21:219–227. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.12.003
Reed NA, Cai D, Blasius TL, Jih GT, Meyhofer E, Gaertig J, Verhey KJ (2006) Microtubule acetylation promotes kinesin-1 binding and transport. Curr Biol CB 16:2166–2172. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.014
Robberecht W, Philips T (2013) The changing scene of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:248–264. doi:10.1038/nrn3430
Rosen DR, Siddique T, Patterson D, Figlewicz DA, Sapp P, Hentati A, Donaldson D, Goto J, O’Regan JO, Deng HX (1993) Mutation in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362:59–62
Saraste J, Lahtinen U, Goud B (1995) Localization of the small GTP-binding protein rab1p to early compartments of the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 4):1541–1552
Saris CG, Horvath S, van Vught PW, van Es MA, Blauw HM, Fuller TF, Langfelder P, DeYoung J, Wokke JH, Veldink JH et al (2009) Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of the peripheral blood from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis patients. BMC Genom 10:405. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-10-405
Saxena S, Cabuy E, Caroni P (2009) A role for motoneuron subtype-selective ER stress in disease manifestations of FALS mice. Nat Neurosci 12:627–636
Schaefer MK, Schmalbruch H, Buhler E, Lopez C, Martin N, Guenet JL, Haase G (2007) Progressive motor neuronopathy: a critical role of the tubulin chaperone TBCE in axonal tubulin routing from the Golgi apparatus. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 27:8779–8789. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1599-07.2007
Schmitt-John T, Drepper C, Mussmann A, Hahn P, Kuhlmann M, Thiel C, Hafner M, Lengeling A, Heimann P, Jones JM et al (2005) Mutation of Vps54 causes motor neuron disease and defective spermiogenesis in the wobbler mouse. Nat Genet 37:1213–1215. doi:10.1038/ng1661
Schmitt HD, Wagner P, Pfaff E, Gallwitz D (1986) The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell 47:401–412
Shaw PJ, Eggett CJ (2000) Molecular factors underlying selective vulnerability of motor neurons to neurodegeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 247(Suppl 1):I17–I27
Slavin I, Garcia IA, Monetta P, Martinez H, Romero N, Alvarez C (2011) Role of Rab1b in COPII dynamics and function. Eur J Cell Biol 90:301–311. doi:10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.10.001
Smith BN, Ticozzi N, Fallini C, Gkazi AS, Topp S, Kenna KP, Scotter EL, Kost J, Keagle P, Miller JW et al (2014) Exome-wide rare variant analysis identifies TUBA4A mutations associated with familial ALS. Neuron 84:324–331. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.027
Soo KY, Atkin JD, Farg M, Walker AK, Horne MK, Nagley P (2012) Bim links ER stress and apoptosis in cells expressing mutant SOD1 associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 7:e35413. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035413
Soo KY, Atkin JD, Horne MK, Nagley P (2009) Recruitment of mitochondria into apoptotic signaling correlates with the presence of inclusions formed by amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated SOD1 mutations. J Neurochem 108:578–590
Spang A, Matsuoka K, Hamamoto S, Schekman R, Orci L (1998) Coatomer, Arf1p, and nucleotide are required to bud coat protein complex I-coated vesicles from large synthetic liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11199–11204
Sreedharan J, Blair IP, Tripathi VB, Hu X, Vance C, Rogelj B, Ackerley S, Durnall JC, Williams KL, Buratti E et al (2008) TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 319:1668–1672. doi:10.1126/science.1154584
Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:513–525. doi:10.1038/nrm2728
Stylli SS, Stacey TT, Verhagen AM, Xu SS, Pass I, Courtneidge SA, Lock P (2009) Nck adaptor proteins link Tks5 to invadopodia actin regulation and ECM degradation. J Cell Sci 122:2727–2740. doi:10.1242/jcs.046680
Sundaramoorthy V, Walker AK, Tan V, Fifita JA, McCann EP, Williams KL, Blair IP, Guillemin GJ, Farg MA, Atkin JD (2015) Defects in optineurin- and myosin VI-mediated cellular trafficking in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddv126
Sundaramoorthy V, Walker AK, Yerbury J, Soo KY, Farg MA, Hoang V, Zeineddine R, Spencer D, Atkin JD (2013) Extracellular wildtype and mutant SOD1 induces ER-Golgi pathology characteristic of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in neuronal cells. Cellular Mol Life Sci CMLS. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1385-2
Thayanidhi N, Helm JR, Nycz DC, Bentley M, Liang Y, Hay JC (2010) Alpha-synuclein delays endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi transport in mammalian cells by antagonizing ER/Golgi SNAREs. Mol Biol Cell 21:1850–1863. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-09-0801
Todd AG, Lin H, Ebert AD, Liu Y, Androphy EJ (2013) COPI transport complexes bind to specific RNAs in neuronal cells. Hum Mol Genet 22:729–736. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds480
Tsvetanova NG, Riordan DP, Brown PO (2012) The yeast Rab GTPase Ypt1 modulates unfolded protein response dynamics by regulating the stability of HAC1 RNA. PLoS Genet 8:e1002862. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002862
Uchiyama K, Miyata H, Sakaguchi S (2013) Disturbed vesicular trafficking of membrane proteins in prion disease. Prion 7:447–451
van Dis V, Kuijpers M, Haasdijk ED, Teuling E, Oakes SA, Hoogenraad CC, Jaarsma D (2014) Golgi fragmentation precedes neuromuscular denervation and is associated with endosome abnormalities in SOD1-ALS mouse motor neurons. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:38. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-2-38
Vance C, Rogeli B, Hortobagyi T, De Vos KJ, Nishimura AL, Sreedharan J, Hu X, Smith B, Ruddy D, Wright P et al (2009) Mutations in FUS, an RNA processing protein, cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 6. Science 323:1208–1211
Walker AK, Soo KY, Sundaramoorthy V, Parakh S, Ma Y, Farg MA, Wallace RH, Crouch PJ, Turner BJ, Horne MK et al (2013) ALS-associated TDP-43 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, which drives cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation and stress granule formation. PLoS One 8:e81170. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0081170
Winslow AR, Chen CW, Corrochano S, Acevedo-Arozena A, Gordon DE, Peden AA, Lichtenberg M, Menzies FM, Ravikumar B, Imarisio S et al (2010) Alpha-synuclein impairs macroautophagy: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol 190:1023–1037. doi:10.1083/jcb.201003122
Xu D, Hay JC (2004) Reconstitution of COPII vesicle fusion to generate a pre-Golgi intermediate compartment. J Cell Biol 167:997–1003. doi:10.1083/jcb.200408135
Yang YS, Harel NY, Strittmatter SM (2009) Reticulon-4A (Nogo-A) redistributes protein disulfide isomerase to protect mice from SOD1-dependent amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 29:13850–13859. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2312-09.2009
Zhang F, Strom AL, Fukada K, Lee S, Hayward LJ, Zhu H (2007) Interaction between familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)-linked SOD1 mutants and the dynein complex. J Biol Chem 282:16691–16699
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Malcolm Horne and Professor Phillip Nagley for helpful discussions. Human patient and control lumbar region tissues were received from the Victorian Brain Bank Network, supported by University of Melbourne, Mental Health Research Institute of Victoria, and Victorian Forensic Institute of Medicine and funded by Neurosciences Australia and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC). This work was supported by NHMRC Project grants [# 1006141, 1030513 to JA], Bethlehem Griffiths Research Foundation, and Angie Cunningham Laugh to Cure MND grant [to JDA and KYS].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soo, K.Y., Halloran, M., Sundaramoorthy, V. et al. Rab1-dependent ER–Golgi transport dysfunction is a common pathogenic mechanism in SOD1, TDP-43 and FUS-associated ALS. Acta Neuropathol 130, 679–697 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1468-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1468-2