Abstract
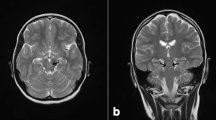
Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders (PBDs) consist of a heterogeneous group of autosomal recessive diseases, in which peroxisome assembly and proliferation are impaired leading to severe multisystem disease and early death. PBDs include Zellweger spectrum disorders (ZSDs) with a relatively mild clinical phenotype caused by PEX1, (MIM# 602136), PEX2 (MIM# 170993), PEX6 (MIM# 601498), PEX10 (MIM# 602859), PEX12 (MIM# 601758), and PEX16 (MIM# 603360) mutations. Three adult patients are reported belonging to a non-consanguineous French family affected with slowly progressive cerebellar ataxia, axonal neuropathy, and pyramidal signs. Mental retardation and diabetes mellitus were optional. The age at onset was in childhood or in adolescence (3–15 years). Brain MRI showed marked cerebellar atrophy. Biochemical blood analyses suggested a mild peroxisomal defect. With whole exome sequencing, two mutations in PEX10 were found in the three patients: c.827G>T (novel) causing the missense change p.Cys276Phe and c.932G>A causing the missense change p.Arg311Gln. The phenotypic spectrum related to PEX10 mutations includes slowly progressive, syndromic recessive ataxia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anheim M, Tranchant C, Koenig M (2012) The autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxias. N Engl J Med 366(7):636–646
Steinberg SJ, Dodt G, Raymond GV, Braverman NE, Moser AB, Moser HW (2006) Peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1763(12):1733–1748
Waterham HR, Ebberink MS (2012) Genetics and molecular basis of human peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(9):1430–1441
Sevin C, Ferdinandusse S, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ, Aubourg P (2011) Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia caused by mutations in the PEX2 gene. Orphanet J Rare Dis. BioMed Central Ltd 6(1):8
Régal L, Ebberink MS, Goemans N, Wanders RJA, de Meirleir L, Jaeken J et al (2010) Mutations in PEX10 are a cause of autosomal recessive ataxia. Ann Neurol 68(2):259–263
Zeharia A, Ebberink MS, Wanders RJA, Waterham HR, Gutman A, Nissenkorn A et al (2007) A novel PEX12 mutation identified as the cause of a peroxisomal biogenesis disorder with mild clinical phenotype, mild biochemical abnormalities in fibroblasts and a mosaic catalase immunofluorescence pattern, even at 40 °C. J Hum Genet 52(7):599–606
Guissart C, Drouot N, Oncel I, Leheup B, Gershoni-Barush R, Muller J et al (2015) Genes for spinocerebellar ataxia with blindness and deafness (SCABD/SCAR3, MIM# 271250 and SCABD2). Eur J Hum Genet EJHG. Nature Publishing Group 1–6
Anheim M, Fleury M, Monga B, Laugel V, Chaigne D, Rodier G et al (2010) Epidemiological, clinical, paraclinical and molecular study of a cohort of 102 patients affected with autosomal recessive progressive cerebellar ataxia from Alsace, Eastern France: implications for clinical management. Neurogenetics 11(1):1–12
Wanders RJ, Wiemer EA, Brul S, Schutgens RB, van den Bosch H, Tager JM (1989) Prenatal diagnosis of Zellweger syndrome by direct visualization of peroxisomes in chorionic villus fibroblasts by immunofluorescence microscopy. J Inherit Metab Dis 12(Suppl 2):301–304
Dacremont G, Vincent G (1995) Assay of plasmalogens and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in erythrocytes and fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis 18(Suppl 1):84–89
Wanders RJ, Ofman R, Romeijn GJ, Schutgens RB, Mooijer PA, Dekker C et al (1995) Measurement of dihydroxyacetone-phosphate acyltransferase (DHAPAT) in chorionic villous samples, blood cells and cultured cells. J Inherit Metab Dis 18(Suppl 1):90–100
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C et al (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43(5):491–498
Geoffroy V, Pizot C, Redin C, Piton A, Vasli N, Stoetzel C et al (2015) VaRank: a simple and powerful tool for ranking genetic variants. Peer J. 3:e796
Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA et al (2010) A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467(7319):1061–1073
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P et al (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7(4):248–249
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC (2009) Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 4(7):1073–1081
Finn RD, Bateman A, Clements J, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR et al (2014) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D222–D230
Okumoto K, Itoh R, Shimozawa N, Suzuki Y, Tamura S, Kondo N et al (1998) Mutations in PEX10 is the cause of Zellweger peroxisome deficiency syndrome of complementation group B. Hum Mol Genet 7(9):1399–1405
Chang CC, Warren DS, Sacksteder KA, Gould SJ (1999) PEX12 interacts with PEX5 and PEX10 and acts downstream of receptor docking in peroxisomal matrix protein import. J Cell Biol 147(4):761–774
Ebberink MS, Mooijer PAW, Gootjes J, Koster J, Wanders RJA, Waterham HR (2011) Genetic classification and mutational spectrum of more than 600 patients with a Zellweger syndrome spectrum disorder. Hum Mutat 32(1):59–69
Shimozawa N, Nagase T, Takemoto Y, Suzuki Y, Kondo N (2003) Genetic heterogeneity in Japanese patients with peroxisome biogenesis disorders and evidence for a founder haplotype for the most common mutation in PEX10 gene. Adv Exp Med Biol 544:71
Warren DS, Wolfe BD, Gould SJ (2000) Phenotype-genotype relationships in PEX10-deficient peroxisome biogenesis disorder patients. Hum Mutat 15(6):509–521
Steinberg SJ, Snowden A, Braverman NE, Chen L, Watkins PA, Clayton PT et al (2009) A PEX10 defect in a patient with no detectable defect in peroxisome assembly or metabolism in cultured fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis 32(1):109–119
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the help of Bernard Jost, Serge Vicaire, Stéphanie Legras, Michael Dumas, and Véronique Geoffroy for the next-generation sequencing and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The final manuscript has been read and approved by all authors who accepted full responsibility for the design and undertaking of the original article, had access to the data and controlled the decision to publish.
Ethical standards
The study was approved by the local ethics committee.
Funding
This study was supported by funds from the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche-Maladies Rares and Maladies Neurologiques et Psychiatriques (ANR-09-MNPS-001-01 to M.K.), the ANR/E-rare JTC 2011 “Euro-SCAR” (2011-RARE-004-01 to M.K.).
Web resources
UCSC Genome Browser: http://genome.ucsc.edu/index.html [April, 2015].
Ensembl Genome Browser: http://www.ensembl.org/index.html [April, 2015].
Exome Variant Server (EVS), NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project (ESP), Seattle, WA: http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS [June, 2013].
Human Splicing Finder version 2.4.1: http://www.umd.be/HSF/ [June, 2013].
VaRank: http://www.lbgi.fr/VaRank/ [April, 2015].
PEX database: http://www.dbpex.org/ [April, 2015].
Additional information
Mathilde Renaud and Claire Guissart have equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renaud, M., Guissart, C., Mallaret, M. et al. Expanding the spectrum of PEX10-related peroxisomal biogenesis disorders: slowly progressive recessive ataxia. J Neurol 263, 1552–1558 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8167-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-016-8167-3