Abstract
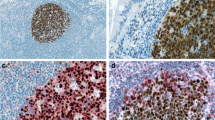
IFI 16 is a member of the HIN-200 protein family named for their haemopoietic expression, interferon-inducibility and nuclear localisation. These proteins have been characterised as transcriptional regulators that modulate the cell cycle. IFI 16 is expressed in some haemopoietic lineages including CD34+ progenitor cells, mature lymphocytes and monocytes, but is absent from granulocytes, erythrocytes and megakaryocytes. We present a wider study of IFI 16 expression in normal human tissues using a monoclonal antibody specifically recognising the C-terminus of IFI 16. As expected, IFI 16 was detected in the nuclei of lymphocytes in the spleen, thymus, lymph node and palatine tonsil, but was also found in epithelial cells in these tissues. Interestingly, IFI 16 protein was also expressed in non-lymphoid tissues including trachea, gastrointestinal tract, skin and testis, but was absent from others including heart and brain. In each tissue, IFI 16 was predominantly expressed in surface epithelial cells and staining was strongest in basal epithelial layers. Therefore, IFI 16 expression is not restricted to cells of the immune system, but is also expressed in epithelial cells. In contrast to the perceived role of HIN-200 proteins as suppressors of cell growth, maximal expression of IFI 16 was in cells with high proliferative potential.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke CJP, Trapani JA, Johnstone RW (2001) Mechanisms of interferon-mediated anti-viral resistance. Curr Drug Target Immune Endocr Metab Disord 1:117–130
Clarke CJP, Aposolidis V, Hii LLP, Gough DJ, Trapani JA, Johnstone RW (2002) A critical role of the transcription factor AP-1 for the constitutive and interferon-induced expression of IFI 16. J Cell Biochem (in press)
Datta B, Min W, Burma S, Lengyel P (1998) Increase in p202 expression during skeletal muscle differentiation: inhibition of MyoD protein expression and activity by p202. Mol Cell Biol 18:1074–1083
Dawson MJ, Trapani JA (1995) IFI 16 gene encodes a nuclear protein whose expression is induced by interferons in human myeloid leukaemia cell lines. J Cell Biochem 57:39–51
Dawson MJ, Trapani JA, Briggs RC, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Baker E (1995) The closely linked genes encoding the myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen (MNDA) and IFI16 exhibit contrasting haemopoietic expression. Immunogenetics 41:40–43
Dawson MJ, Elwood NJ, Johnstone RW, Trapani JA (1998) The IFN-inducible nucleoprotein IFI 16 is expressed in cells of the monocyte lineage, but is rapidly and markedly down-regulated in other myeloid precursor populations. J Leukoc Biol 64:546–554
DeYoung KL, Ray ME, Su YA, Anzick SL, Johnstone RW, Trapani JA, Meltzer PS, Trent JM (1997) Cloning a novel member of the human interferon-inducible gene family associated with control of tumorigenicity in a model of human melanoma. Oncogene 15:453–457
Engel DA, Snoddy J, Toniato E, Lengyel P (1988) Interferons as gene activators: close linkage of two interferon-activatable murine genes. Virology 166:24–29
Johnstone RW, Trapani JA (1999) Transcription and growth regulatory functions of the HIN-200 family of proteins. Mol Cell Biol 19:5833–5838
Johnstone RW, Kerry JA, Trapani JA (1998a) The human interferon-inducible protein, IFI 16, is a repressor of transcription. J Biol Chem 273:17172–17177
Johnstone RW, Kershaw MH, Trapani JA (1998b) Isotypic variants of the interferon-inducible transcriptional repressor IFI 16 arise through differential mRNA splicing. Biochemistry 37:11924–11931
Johnstone RW, Wei W, Greenway A, Trapani JA (2000) Functional interaction between p53 and the interferon-inducible nucleoprotein IFI 16. Oncogene 19:6033–6042
Kaelin WG Jr, Pallas DC, DeCaprio JA, Kaye FJ, Livingston DM (1991) Identification of cellular proteins that can interact specifically with the T/E1A-binding region of the retinoblastoma gene product. Cell 64:521–532
Koul D, Lapushin R, Xu HJ, Mills GB, Gutterman JU, Choubey D (1998) p202 prevents apoptosis in murine AKR-2B fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 247:379–382
Landolfo S, Gariglio M, Gribaudo G, Lembo D (1998) The IFI 200 genes: an emerging family of IFN-inducible genes. Biochimie 80:721–728
Lash AE, Tolstoshev CM, Wagner L, Schuler GD, Strausberg RL, Riggins GJ, Altschul SF (2000) SAGEmap: a public gene expression resource. Genome Res 10:1051–1060
Lembo D, Angeretti A, Benefazio S, Hertel L, Gariglio M, Novelli F, Landolfo S (1995) Constitutive expression of the interferon-inducible protein p202 in NIH 3T3 cells affects cell cycle progression. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 9:42–46
Lembo M, Sacchi C, Zappador C, Bellomo G, Gaboli M, Pandolfi PP, Gariglio M, Landolfo S (1998) Inhibition of cell proliferation by the interferon-inducible 204 gene, a member of the IFI 200 cluster. Oncogene 16:1543–1551
Liu CJ, Wang H, Lengyel P (1999) The interferon-inducible nucleolar p204 protein binds the ribosomal RNA-specific UBF1 transcription factor and inhibits ribosomal RNA transcription. EMBO J 18:2845–2854
Luu P, Flores O (1997) Binding of SP1 to the immediate-early protein-responsive element of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase promoter. J Virol 71:6683–6691
Min W, Ghosh S, Lengyel P (1996) The interferon-inducible p202 protein as a modulator of transcription: inhibition of NF-kappa B, c-Fos, and c-Jun activities. Mol Cell Biol 16:359–368
Miranda RN, Briggs RC, Shults K, Kinney MC, Jensen RA, Cousar JB (1999) Immunocytochemical analysis of MNDA in tissue sections and sorted normal bone marrow cells documents expression only in maturing normal and neoplastic myelomonocytic cells and a subset of normal and neoplastic B lymphocytes. Hum Pathol 30:1040–1049
Pawlowski K, Pio F, Chu Z, Reed JC, Godzik A (2001) PAAD: a new protein domain associated with apoptosis, cancer and autoimmune diseases. Trends Biochem Sci 26:85–87
Rozzo SJ, Allard JD, Choubey D, Vyse TJ, Izui S, Peltz G, Kotzin BL (2001) Evidence for an interferon-inducible gene, IFI202, in the susceptibility to systemic lupus. Immunity 15:435–443
Staub E, Dahl E, Rosenthal A (2001) The DAPIN family: a novel domain links apoptotic and interferon response proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 26:83–85
Trapani JA, Browne KA, Dawson MJ, Ramsay RG, Eddy RL, Show TB, White PC, Dupont B (1992) A novel gene constitutively expressed in human lymphoid cells is inducible with interferon-gamma in myeloid cells. Immunogenetics 36:369–376
Wang H, Chatterjee G, Meyer JJ, Liu CJ, Manjunath NA, Bray-Ward P, Lengyel P (1999) Characteristics of three homologous 202 genes (IFI202a, IFI202b, and IFI202c) from the murine interferon-activatable gene 200 cluster. Genomics 60:281–294
Wen Y, Yan DH, Spohn B, Deng J, Lin SY, Hung MC (2000) Tumor suppression and sensitization to tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis by an interferon-inducible protein, p202, in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60:42–46
Wen Y, Yan DH, Wang B, Spohn B, Ding Y, Shao R, Zou Y, Xie K, Hung MC (2001) p202, an interferon-inducible protein, mediates multiple antitumor activities in human pancreatic cancer xenograft models. Cancer Res 61:7142–7147
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Wellcome Trust (UK). J.A.T. is a Principal Research Fellow of the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. R.W.J. is a Senior Research Fellow of the Wellcome Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wu Wei and Christopher J.P. Clarke contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Clarke, C.J.P., Somers, G.R. et al. Expression of IFI 16 in epithelial cells and lymphoid tissues. Histochem Cell Biol 119, 45–54 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-002-0485-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-002-0485-0